Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
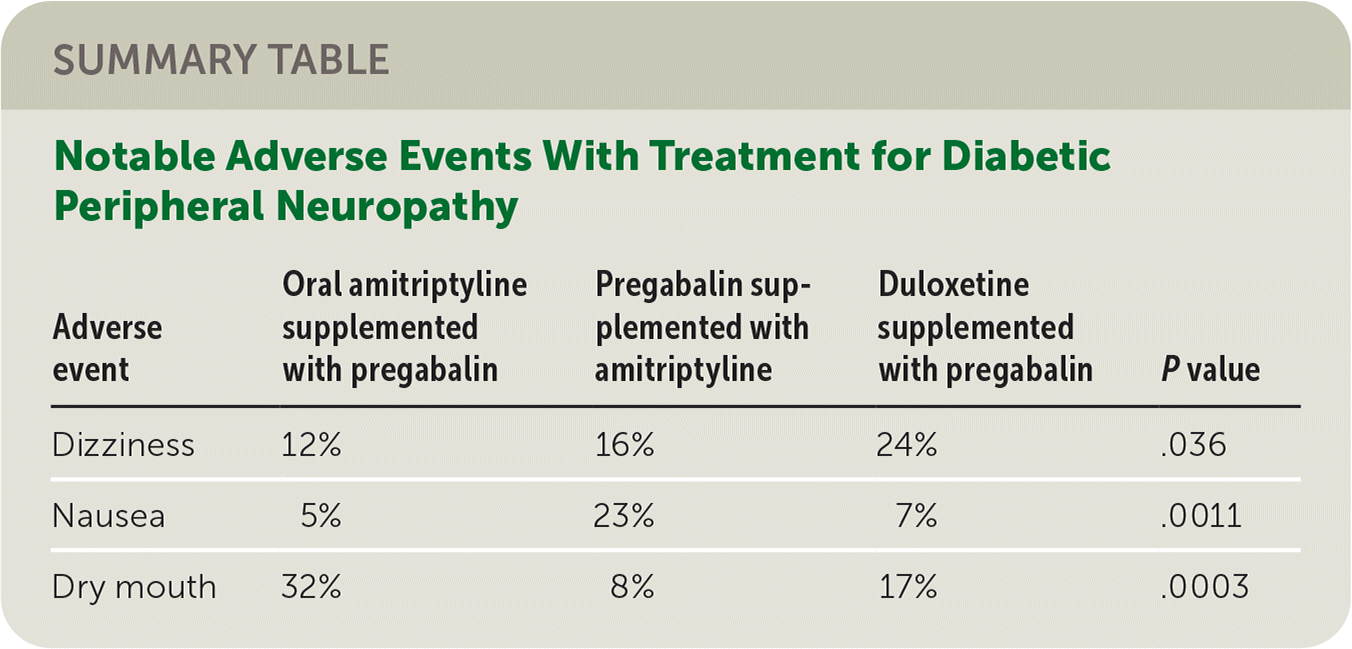
In the treatment of depression, you should feel some relief from amitriptyline in 2 to 4 weeks, but it may take up to 8 to 12 weeks to feel the full therapeutic effects. For nerve-related (neuropathic) pain, lower doses of amitriptyline are typically used and it also may take up to 6 weeks to feel the full effects. Gabapentin produced greater improvements than amitriptyline in pain and paresthesia associated with diabetic neuropathy. Additionally, gabapentin was better tolerated than amitriptyline. Further controlled trials are needed to confirm these preliminary results. Amitriptyline may be used to treat depression or off-label to relieve chronic pain, fibromyalgia, or insomnia. Experts are unsure exactly how amitriptyline works, although historically it was believed that amitriptyline’s effects for depression were due to its ability to rebalance chemicals in the brain, such as serotonin and/or norepinephrine. Neuropathic pain largely influences the well-being of patients. Anticonvulsant and antidepressant medications, such as Pregabalin, Gabapentin, and Amitriptyline, are routinely prescribed as initial treatments for neuropathic pain. There are several treatment options for nerve pain, including antidepressants, anticonvulsants, opioids, and topicals. such as gabapentin or pregabalin, alongside a TCA antidepressant could be We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Researchers publishing in JAMA Neurology describe the results of a unique trial in which 402 people with idiopathic sensory polyneuropathy were randomly assigned to one of four medications: duloxetine, mexiletine, nortriptyline, or pregabalin. Combination treatment of amitriptyline and pregabalin offers additional pain relief for people whose pain is not adequately controlled with one medication and is usually safe. [ 30 ] [ 31 ] Amitriptyline in certain formulations may also induce the level of sciatic -nerve blockade needed for local anesthesia therein. [ 32 ] Study results indicate that, although both gabapentin and amitriptyline provide statistically significant pain relief by the end of treatment, there was no statistically significant difference between the 2 drugs, as measured by daily pain diary scores and global ratings of pain relief. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Amitriptyline therapy, unlike gabapentin therapy, may be detrimental for patients with cardiac conduction disturbances. Our experience is that most of gabapentin therapy failures occur as a result of subtherapeutic dosing. Amitriptyline vs gabapentin both treat nerve pain, but amitriptyline is a tricyclic antidepressant that also helps with mood disorders, while gabapentin is an anticonvulsant specifically designed for nerve pain relief. Learn how gabapentin and amitriptyline work against neuropathic pain, their side effects, and their interactions. Compare the benefits and drawbacks of each drug and find out which one is better for you. However, Amitriptyline is used at a low dose to manage neuropathic pain. Amitriptyline is available as tablets of various strengths (10mg, 25mg and 50mg) and as a liquid oral solution (25mg/5ml that is, every 5ml of liquid contains 25mg of the active ingredient). Amitriptyline is an effective antidepressant but it may cause drowsiness initially and a withdrawal syndrome with abrupt discontinuation. It may be used off-label to treat other conditions such as more. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant with pain-relieving effects that may be used to treat certain seizure disorders or relieve nerve pain. Gabapentin produced greater improvements than amitriptyline in pain and paresthesia associated with diabetic neuropathy. Additionally, gabapentin was better tolerated than amitriptyline. Further controlled trials are needed to confirm these preliminary results. A Cochrane review of combination therapy for neuropathic pain demonstrated that gabapentin and opioids provide better pain relief than gabapentin or opioids alone, but this was associated with increased levels of adverse events. The calculated NNT was 9.5 (5.0–86), and the NNH was 10 (6.5–25). These recommendations are largely based on the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) guideline: Neuropathic pain - pharmacological management. The pharmacological management of neuropathic pain in adults in non-specialist settings [NICE, 2019a]. Offering amitriptyline, duloxetine, gabapentin, or pregabalin Both gabapentin and amitriptyline provided effective pain control in peripheral neuropathic pain. Additionally gabapentin was more effective especially in paroxysmal shooting pain than other pain qualities. Practical insight: Gabapentin is widely favored for nerve-related conditions, while amitriptyline is known for its potency in both pain relief and mood regulation. The latter, though, may not be suitable for individuals sensitive to anticholinergic effects.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |