Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
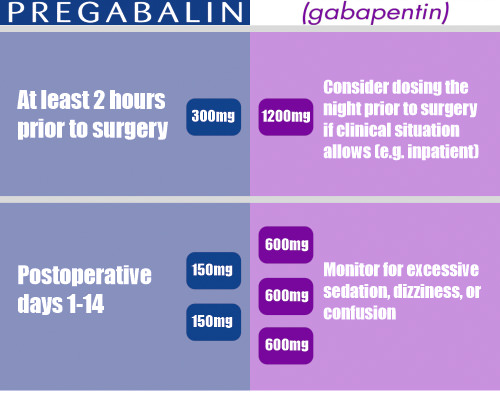
When comparing Gabapentin for dogs and humans, it is important to understand the differences in its mechanism of action, dosage, administration, and potential side effects. Gabapentin works by affecting certain neurotransmitters, producing an analgesic effect in both species. From a pharmacology standpoint: human gabapentin and "dog" gabapentin are the exact same, but given at different doses, intervals (times or frequencies) and used for different amounts of total time. I've personally been on gabapentin for a period of time due to nerve pain and was warned by various doctors about the possible long-term effects. Gabapentin is a medication that is commonly used to treat nerve pain in both humans and animals. It is often prescribed to dogs for various conditions such as seizures, anxiety, and chronic pain. However, many pet owners wonder if the gabapentin that is prescribed for dogs is the same as the one that is prescribed for humans. Many pet medications began as human prescriptions. Gabapentin, aka Pfizer’s Neurontin®, is one example. But that doesn’t mean we can share those drugs. An animal given Neurontin® could die from Xylitol that’s included in the liquid form of the human version. The core difference between animal gabapentin and human gabapentin lies not in the active ingredient itself, but primarily in formulation, dosage, and regulatory approval. The active pharmaceutical ingredient, gabapentin, is the same in both. The short answer is: No, the active ingredient, gabapentin itself, is the same in both veterinary and human formulations. The difference lies primarily in how the medication is prepared and the specific ingredients it contains. According to a veterinary pharmacist, “Pet gabapentin and human gabapentin are essentially the same drug. The main difference lies in the dosages and formulations. The dosages for pets are typically lower than those for humans, as their bodies metabolize medications differently. The core difference between gabapentin used for humans and pets isn’t the active ingredient itself; it’s primarily the way it’s regulated, prescribed, and formulated. Gabapentin is the same chemical compound whether it’s given to a human or a dog, cat, or other animal. Veterinarians commonly prescribe gabapentin to treat pain, seizures, and anxiety in dogs. Gabapentin is a human medication, and its use in veterinary medicine is “off-label,” meaning it is not FDA-approved for pets. Sedation is the main potential side effect of gabapentin, and the level of sleepiness varies from patient to patient. Chiming in as a human pharmacist. Some medications that we take, our animals can take the exact same thing. The gabapentin and insulin you might be on, your companions can take the same medication, no "recipe" changes necessary. Other times they need animal-specific "recipes". Canine gabapentin and human gabapentin are indeed the same medication, in terms of the active ingredient. Both forms contain the drug gabapentin, which works by affecting the chemicals and nerves in the body that are involved in seizures and pain. Gabapentin is a medication that is commonly used to treat epilepsy in humans. However, it is also being prescribed by veterinarians as a treatment for various conditions in dogs. But are human and dog gabapentin the same? First and foremost, it is important to note that Gabapentin is a medication that is commonly used in both humans and animals. While the formulation of Gabapentin may vary slightly between the two, the active ingredient is the same, making it safe for use in dogs . However, it is readily utilized in the veterinary field, and veterinarians can legally prescribe certain human drugs for use in animals in certain circumstances. This is called extra-label or off-label use because this use isn’t described on the drug label. Common brand names of gabapentin include Neurontin® and Gralise®. The human oral solution of gabapentin contains xylitol, which should be avoided in veterinary patients. Do not give your pet human gabapentin. Gabapentin should be used with caution in animals with decreased liver or renal function. How does gabapentin differ in dogs vs. humans? Gabapentin is a prescription medication. This means that a healthcare professional prescribes this medication for a specific condition. The dosage and form for humans depends on several factors, such as: the condition its treating; your age (dosing differs for adults and children) The core difference between gabapentin used for dogs and gabapentin used for humans lies not in the active ingredient itself, but primarily in the formulation and potential added ingredients. Both human and veterinary gabapentin utilize the same active pharmaceutical ingredient (API): gabapentin. It is also used to treat anxiety in dogs. Off-label use means dog-specific research on gabapentin has not been done. This medication is not FDA-approved for use in animals. However, human gabapentin appears to be safe and effective in dogs, cats, and other animals. Human dosage forms of gabapentin include 100 mg, 300 mg, and 400 mg capsules Often better recognized by its brand name, Neurontin, gabapentin is FDA approved for use in humans. However, like many medications, vets can, and often do, use it “off label” in dogs. This means it’s used in a way that’s not included in the FDA’s approved packaging label and insert. Gabapentin for pets is similar to human gabapentin. But, the dosage and administration differ. It’s important to follow your vet’s instructions carefully. This ensures safety and effectiveness for your pet. Never use human gabapentin on animals without veterinary help.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |