Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 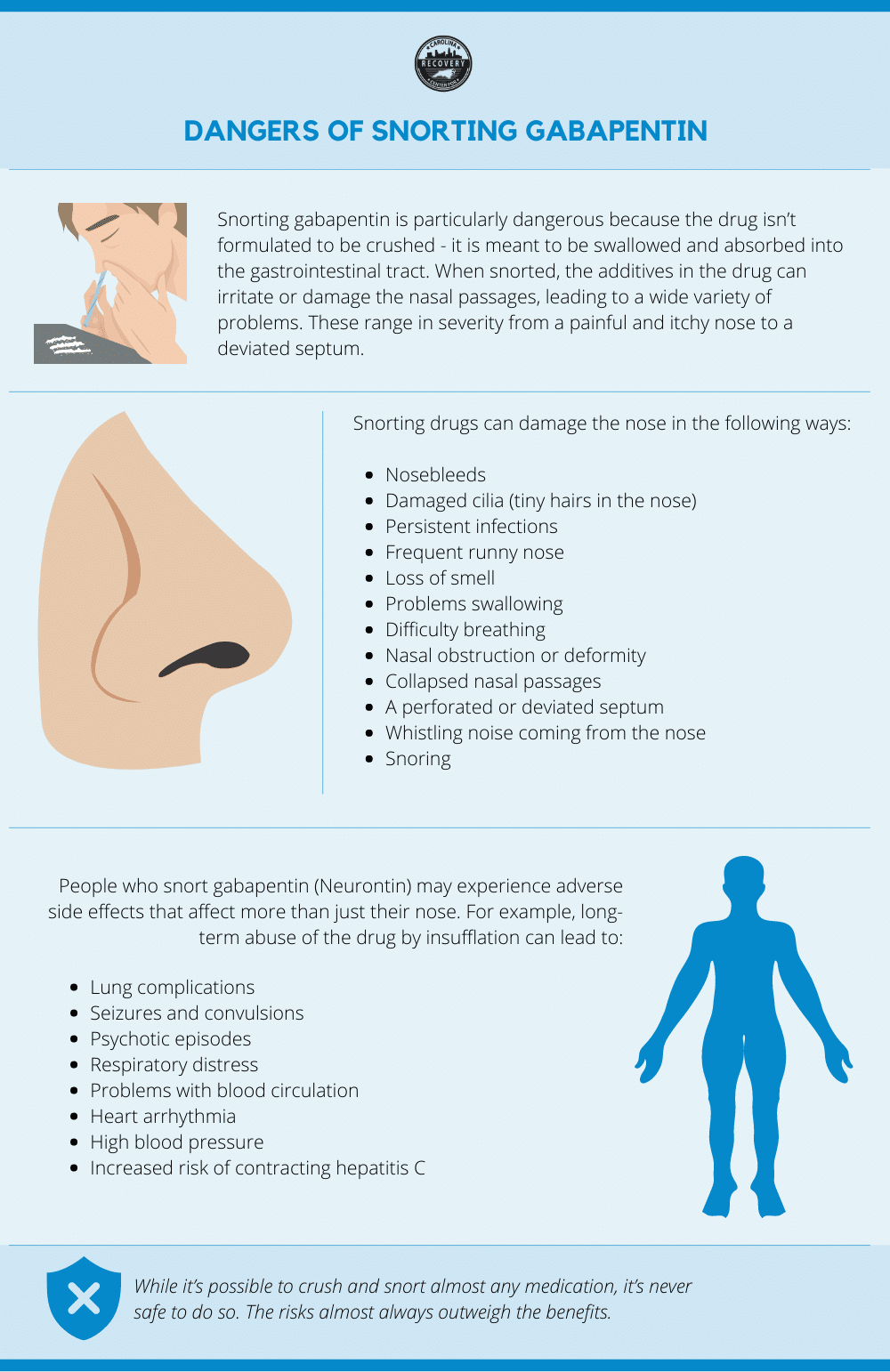 |
Gabapentin, used to treat epilepsy and neuropathic pain, can be beneficial but comes with side effects like dizziness, drowsiness, and potential for long-term cognitive impact or dependence, especially when misused or combined with other drugs. Monitoring usage is crucial for safety. In rare instances, gabapentin can cause DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms) syndrome. This is a severe allergic reaction that can cause damage to major organs, including the liver and kidneys. If you have existing kidney problems, you may need a lower dose of gabapentin. Gabapentin and Cirrhosis of the Liver - Fatty Liver Disease If you’re taking gabapentin, avoid driving until you know how it affects you. More rarely, gabapentin can cause fluid buildup (edema), weight gain, and vision problems. It can also cause diarrhea. Some side effects of gabapentin may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine. Also, your health care professional may be able to tell you about ways to prevent or reduce some of these side effects. If you’re taking gabapentin more than once a day, it’s best to space out your doses as evenly as you can. Taking them too close together could put you at a higher risk for side effects. Doing so can also make gabapentin less effective since only so much of it can be absorbed at once. Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) are both gabapentinoids—psychotropic medications that cross the blood-brain barrier and mimic the inhibitory neurotransmitter Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Gabapentin was first approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 as an adjunctive treatment for partial seizures. In 2002 Gabapentin for dogs is commonly prescribed for pain, anxiety, or seizures. It's generally safe, but there are some known side effects to be aware of. Driving or Operating Machinery: Due to the common side effects of dizziness and drowsiness, operating heavy machinery or driving should be avoided until you know how gabapentin affects you. These side effects can impair your ability to react quickly and safely. Sudden Discontinuation: Do not suddenly stop taking gabapentin. Gabapentin is fairly safe when you use it correctly. It does come with some possible side effects, though. People who misuse this drug are also at risk of additional side effects. Stopping gabapentin suddenly can cause serious problems, including increasing your risk of seizures (if you are taking gabapentin to control seizures) or not improving your symptoms (if taking gabapentin for other indications). While less common, the most serious side effects of gabapentin are described below, along with what to do if they happen. Severe Allergic Reactions. Gabapentin can cause allergic reactions, If you have impaired kidney function, taking a lower dose or spacing out the dosing time is essential to prevent unwanted side effects. Taking gabapentin with opioids (e.g., morphine, hydrocodone) can cause respiratory depression and sedation, and lead to fatal outcomes. Tell your healthcare provider if you are also taking opioids. To make sure this medicine is safe for you, tell your doctor if you have ever had: kidney disease (or if you are on dialysis). Some people have thoughts about suicide while taking seizure medicine. Children taking gabapentin may have behavior changes. Stay alert to changes in your mood or symptoms. Gabapentin has been associated with a discontinuation syndrome when abruptly stopped. Symptoms include anxiety, insomnia, nausea, pain, and sweating. It should be tapered off slowly under a doctor's advice. The dosage of gabapentin needs to be reduced for kidney disease. Rarely do hypersensitivity reactions occur. But gabapentin side effects are not trivial, as you will read. And a brand new gabapentin side effect has just emerged. Canadian researchers have just dropped a bombshell on gabapentin ( Annals of Internal Medicine , Jan. 15, 2024 ). Physical Health Risks: High doses of gabapentin can lead to severe respiratory depression, particularly when combined with opioids or depressants. This can result in a potentially life-threatening situation or fatal overdose. Development of Dependence: Chronic misuse of gabapentin can lead to physical dependence. Withdrawal symptoms such as Despite its benefits, gabapentin has potential long-term side effects that users should be aware of. The long-term use of gabapentin may result in a range of physical side effects, some of which may become more pronounced the longer a person takes the medication. 1. Sedation and Fatigue. Gabapentin may cause breathing problems in people who use opioid pain medicines and those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Older adults who take gabapentin also are at higher risk of breathing problems. So can cats take gabapentin? They sure can! In this article, you’ll learn what gabapentin is, how it works, and some safety guidelines regarding dosage for kitties. We’ll also cover some frequently asked questions. What Is Gabapentin? Gabapentin is a medication kind of in a class by itself, classified as an anticonvulsant neuropathic pain
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |