Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
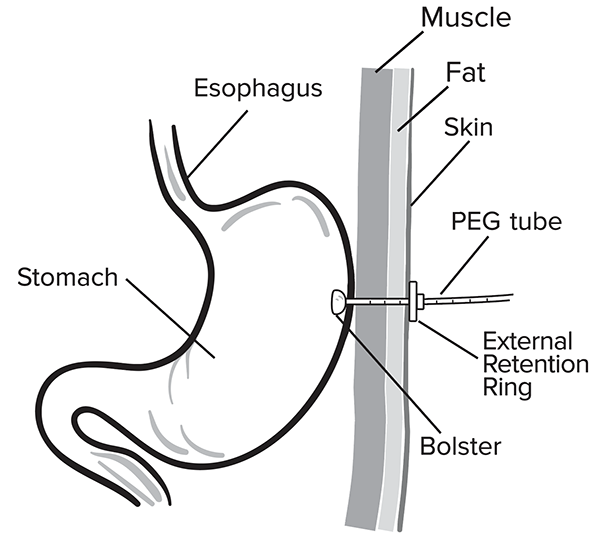 |  |
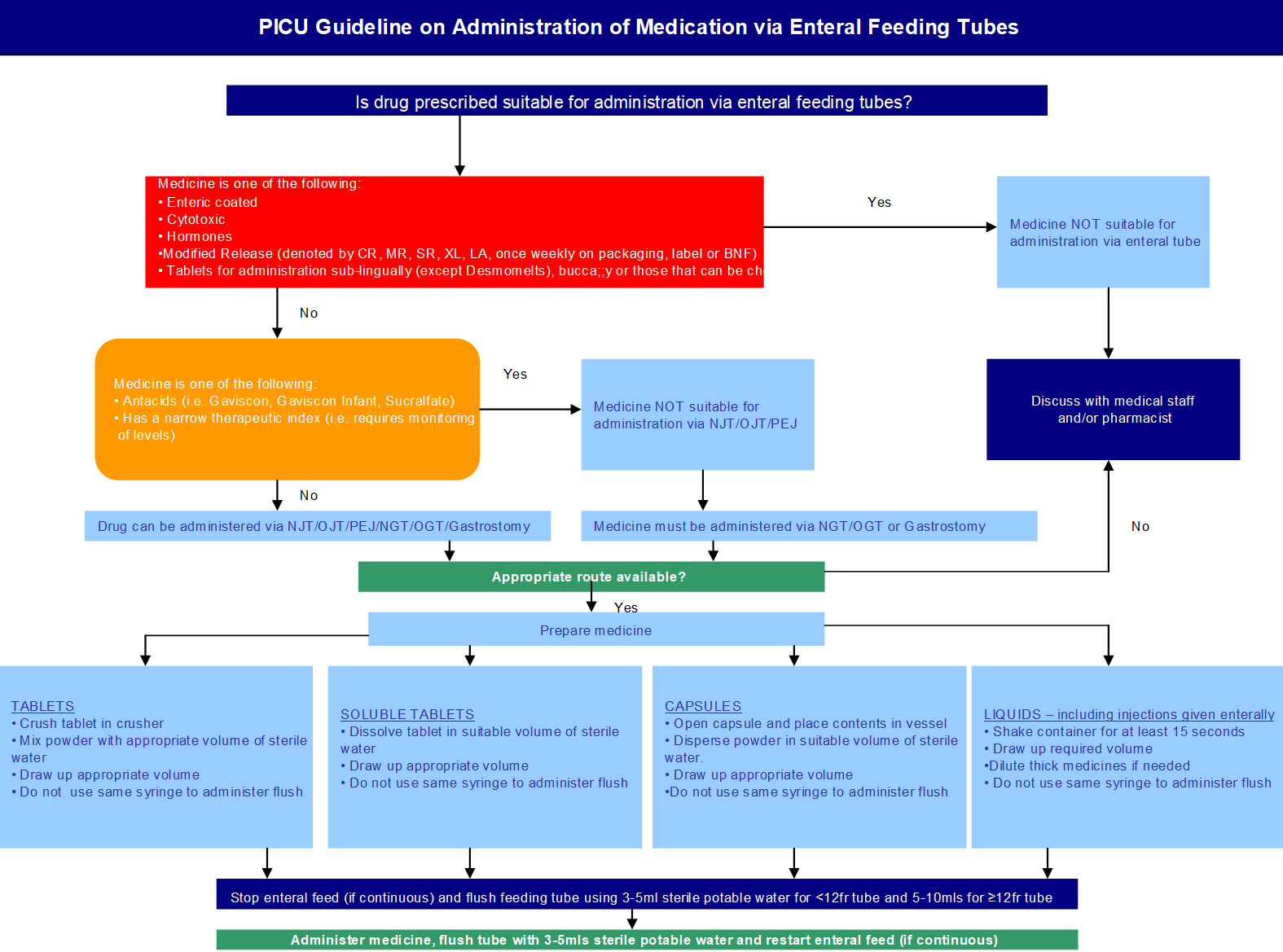
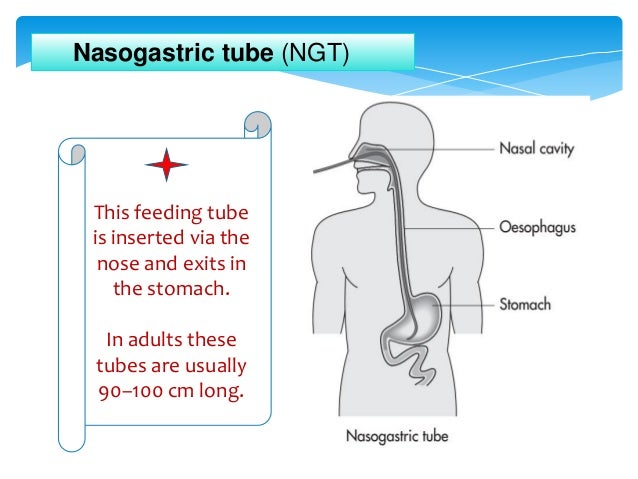
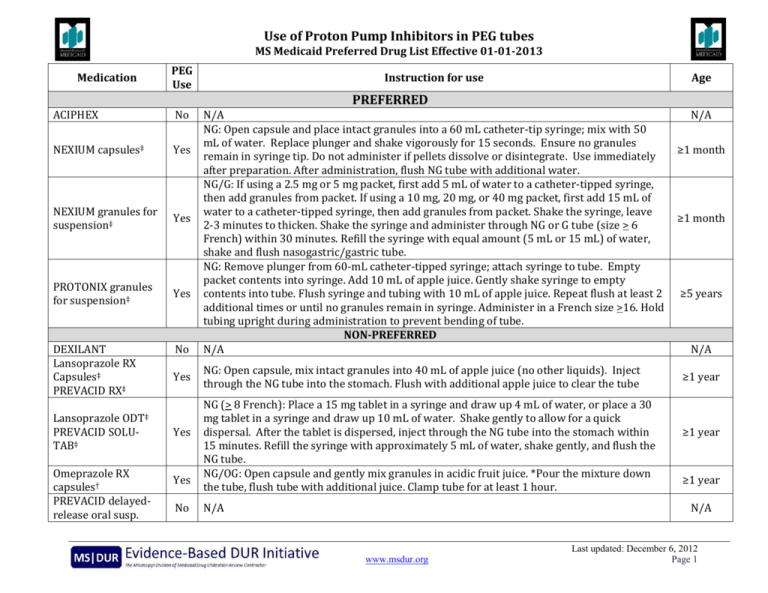
Many medications may be put into your PEG. Here are some important things you need to know: If any medications cannot be put in your PEG, your pharmacist may help you by reaching out to the healthcare provider that prescribed a medication to suggest another option. Administered Via Enteral Feeding Tube: In Vitro Testing and Labeling Recommendations . Gastrostomy 12-30 Gastrojejunal 12-22 Jejunostomy 12-18 105 * Fr = French 106 If necessary, Gabapentin Colonis 50 mg/ml Oral Solution can be administered via intragastric feeding tubes (nasogastric (NG) or percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) tubes). Tubes should be rinsed twice with 10 ml of water immediately after administration. What medications can be given through the G-tube? Only liquid medications can be given through the G-tube. If the medication comes in a capsule, open the capsule and mix the content in 5mL of warm water. If the medication comes as a pill, please ask your pharmacist if it can be crushed and mixed with water. Tips for giving medications. Each Some oral solutions are licensed for administration via NG/PEG feeding tubes, check product information for specific advice. Notes NICE guidelines advise that patients prescribed Gabapentin for epilepsy should receive the same formulation consistently. Attach the syringe to your feeding tube or button adapter, if you’re using one. Unclamp the tube and gently push in the medication. Reclamp the tube. Attach the syringe filled with 60 mL of water to your feeding tube. Unclamp the tube and flush it thoroughly. Reclamp the tube. Repeat the flushing if the water moves too slowly through the tube. Some medications may be given via an EFT while others are unsuitable for this form of administration. Inappropriate drug selection for EFT administration can cause potential toxicity, reduced efficacy, and tube obstruction. Gabapentin Oral Solution 50mg/mL All of the above medicines can now be safely administered through an enteral tube in the knowledge that no medicine is lost on the tube and that the tube is unlikely to block if the individualised flushing guidance is followed. In most cases, the pharmacist was unaware if the patient was receiving medication via a feeding tube. An internal audit medication administration identified that 90% of the medications being administered by nurses through the feeding tube were listed on the medication order as “oral”. Any adverse effects, including problems with feeding tubes, should be reported to the prescriber and pharmacist immediately. 4 GENERAL PRINCIPLES When administering medication via enteral tube consideration needs to be taken regarding drug formulation, interactions with feed, type of tube, site of placement, and site of drug absorption. When the oral route is not available, patients may need to be fed and administered medicines through an enteral tube. Tubes may terminate in the stomach or the jejunum, and they may enter via the nose or through the abdominal wall. medication administration can be improved or maintained through the appropriate use of enteral alternatives such as gastrostomy tubes (GT), nasogastric tubes (NG), gastrostomy buttons (G-Buttons; GB), jejunostomy tubes (JT), and nasojejunal tubes (NJ). Embeda morphine sulfate Capsule Extended‐release (a); do not give via N/G tube E‐Mycin erythromycin Tablet Enteric‐coated Enablex darifenacin Tablet Slow‐release Entocort EC budesonide Capsule Extended‐release; Enteric‐coated (a) Equetro carBAMazepine Capsule Extended‐release (a) Gastrostomy tubes may be inserted endoscopically (percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy or PEG), radiologically (radiologically inserted gastrostomy tube, or RIG) or surgically inserted. However, it is important to seek advice as not all oral liquids are suitable for PEG tube administration, for example, co-amoxiclav and lansoprazole suspensions may form clumps; and diazepam, and possibly carbamazepine, adhere to plastic tubes (Naysmith and Nicholson 1998).Due to the fact that any failure to consider the details of formulation Gabapentin Rosemont Oral Solution 50mg/mL Instructions for administration via nasogastric (NG) or percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) tubes. Gabapentin Rosemont Oral Solution is suitable for use with the following type of NG and PEG tubes: Ensure that the enteral feeding tube is free from obstruction before administration. 1. A number of specific drug interactions can occur when drugs are administered via feeding tubes (Box A10.D). The most important clinically are with drugs with a narrow therapeutic range, e.g. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2008;65(24):2347-2357. Administer medications via the oral route when possible. Determine the enteral feeding tube size (e.g., small bore or large bore), insertion site (e tube 4 3. Flushing enteral feeding tubes 9 4. Restoring and maintaining patency of enteral feeding tubes 15 5. Drug therapy review 23 6. Choice of medication formulation Alimemazine (Trimeprazine) tartrate25 7. The legal and professional consequences of administering drugs via enteral feeding tubes 38 8. Health and safety and clinical
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |