Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
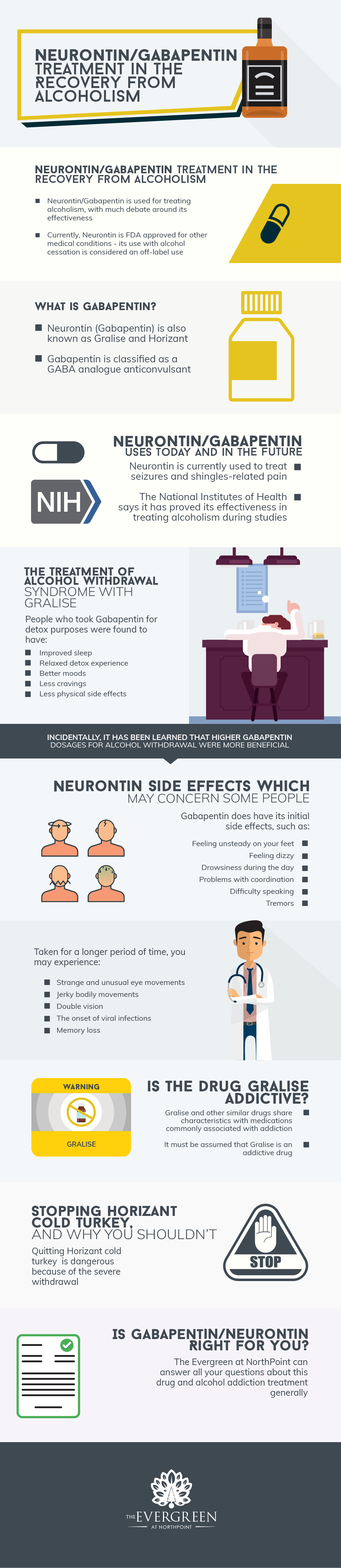
Objective: To review the literature evaluating gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal and dependence. Data Sources: A literature search of MEDLINE (1966 to end of March 2015) and PubMed was performed using the terms alcohol, gabapentin, withdrawal, and Gabapentin has been shown to be safe and effective for mild alcohol withdrawal but is not appropriate as mono-therapy for severe withdrawal owing to risk of seizures. During early abstinence, gabapentin may improve sleep, cravings, and mood—factors associated with relapse. Some research shows that gabapentin has promise as an alcohol withdrawal treatment, possibly in combination with other medications. Gabapentin can: Help stop the impulse to A study published this week concluded that gabapentin can relieve alcohol withdrawal symptoms but is most effective for people with a history of more severe symptoms after a few days Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29,30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32,33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Gabapentin has been found to help with alcohol withdrawal symptoms, including easing alcohol cravings, as well as reducing alcohol consumption and maintaining abstinence after withdrawal. 4,5,6 Using gabapentin for withdrawal constitutes one example of off-label use of the drug. 4. Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29,30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32,33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or This explains its use in treating nerve-related pain such as shingles, as well as epileptic seizures. In fact, seizures are among the more extreme reactions people can have to alcohol withdrawal, and can be prevented by taking gabapentin. For alcohol use disorder (AUD), gabapentin is considered “off-label.” An off-label medication is a drug It is important to use caution while using gabapentin, even if it is sometimes given to alleviate alcohol withdrawal symptoms. There is an increased risk of sleepiness, decreased coordination, and accidents when using gabapentin and alcohol together since they increase each other’s sedative effects. alcohol withdrawal.12,14,15 Gabapentin for Alcohol Withdrawal at VAPORHCS Although not currently included in the alcohol withdrawal protocol at Veterans Affairs Port-land Health Care System (VAPORHCS), gaba-pentin has been added to the standard of care in select patients per the discretion of the at-tending physician. Anecdotal reports of patients withdrawal symptoms like confusion, delirium, and seizures. • Alcohol withdrawal symptoms usually go away in 5–7 days. You and your health care provider will decide the best next steps together. Ԉ You can stop taking gabapentin by gradually reducing your dose over 3–5 days. Ԉ You can continue taking gabapentin to help To use Gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal, it’s essential to follow a healthcare professional’s guidance, as they can tailor the dosage and regimen to individual needs and symptom severity. Given the medication’s potent effects, it must be used under strict medical supervision, particularly to adapt to the changing needs during the Gabapentin can help with alcohol withdrawal by counteracting the physiological effects of the syndrome. Evidence indicates that symptoms of alcohol withdrawal syndrome stem from While gabapentin is not yet an FDA-approved treatment for alcoholism, a number of studies support the its use withdrawal and cravings: In a 12-day study detoxifying with either gabapentin or lorazepam (a benzodiazepine prescribed with the brand name Ativan), the former was less likely to drink – and had less craving, anxiety, and sedation. Gabapentin has been shown to be safe and effective for mild alcohol withdrawal but is not appropriate as mono-therapy for severe withdrawal owing to risk of seizures. During early abstinence, gabapentin may improve sleep, cravings, and mood—factors associated with relapse. Gabapentin is Dangerous When Misused: Addictive Potential. Prescribing gabapentin for opioid withdrawal has helped many people kick the habit and is generally safe when used as directed. However, gabapentin itself can be addicting when misused. Gabapentin is a non-narcotic medication, initially thought to present a low potential for abuse. A lcohol withdrawal occurs as a result of cessation of or reduction in alcohol use, particularly after a period of heavy and prolonged drinking. The diagnosis requires the presence of ≥ 2 of a set of 8 criteria: autonomic hyperactivity (eg, sweating or pulse rate > 100 beats per minute); increased hand tremor; insomnia; nausea or vomiting; transient visual, tactile, or auditory Gabapentin is a calcium channel GABAergic modulator that is widely used for pain. Studies showing reduced drinking and decreased craving and alcohol-related disturbances in sleep and affect in the months following alcohol cessation suggest therapeutic potential for alcohol use disorder. Given gabapentin’s effectiveness for acute alcohol withdrawal problems, a research team at the Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC) explored whether AUD patients who exhibit more severe withdrawal symptoms might experience greater improvements with gabapentin than those who experience fewer symptoms.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |