Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_Early-Symptoms-of-Kidney-Failure_Illustrator_Ellen-Lindner_Final-d6abfd220e5b4ccfa407688366218c92.jpg) | 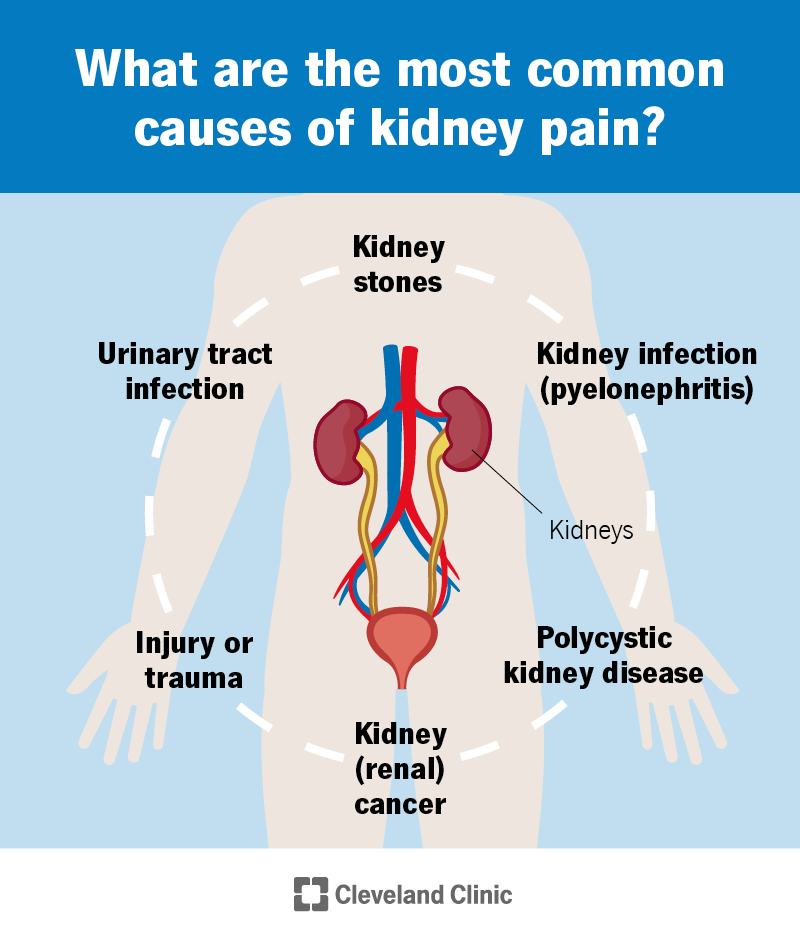 |
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/kidneypainfinal-01-5c3ba11dc9e77c0001033b11.png) |  |
Other causes of kidney pain. Urinary retention. When you can't fully empty your bladder, urine backs up into your kidneys. Your kidneys swell up from the extra urine and press on nearby organs Gabapentin can also cause another type of allergic reaction called DRESS syndrome. It usually starts with a fever, rash, and swelling of the lymph nodes. But it can progress and cause damage to major organs, like the liver, kidneys, or heart. Angioedema, anaphylaxis, and DRESS syndrome are medical emergencies that require immediate treatment. The straightforward answer is yes, you can potentially take gabapentin if you have stage 3 kidney disease, but with significant caveats. It’s crucial to understand that gabapentin is primarily eliminated by the kidneys, meaning that impaired kidney function can lead to a buildup of the drug in your system. Gabapentin is also used to manage a condition called postherpetic neuralgia, which is pain that occurs after shingles. Gabapentin works in the brain to prevent seizures and relieve pain for certain conditions in the nervous system. It is not used for routine pain caused by minor injuries or arthritis. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. Some side effects of gabapentin may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine. Also, your health care professional may be able to tell you about ways to prevent or reduce some of these side effects. This drug can also act as a pain reliever for various Gabapentin can cause different side effects in children that may require medical attention. people with preexisting kidney disease or Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication commonly used to treat epilepsy and neuropathic pain. Rare cases of liver and kidney damage have been reported with Gabapentin use. Individuals with pre-existing liver or kidney conditions may be at a higher risk. Regular monitoring of liver and kidney function is essential while taking Gabapentin. If a patient has kidney stones with no underlying renal issues, then any OTC pain medication can be used to manage the pain symptoms associated with passing a kidney stone. How they can affect the kidneys: Don’t assume that because they’re “natural” herbal supplements are always safe. Some can interact badly with prescription medication. Others can act as a diuretic or a water pill and can cause kidney irritation or damage. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. While gabapentin is a widely used medication, particularly for nerve pain and seizures, its interaction with kidney disease is a serious concern. Gabapentin is primarily eliminated from the body through the kidneys. In summary, we can conclude that although it happens infrequently, gabapentin may cause myotoxicity, rhabdomyolysis and renal failure even in patients whose renal function was previously normal. This is because they can further reduce your kidney function and cause fluid retention. They may be safe to take if you are on dialysis and do not produce any urine. However, they can cause bleeding from the stomach and gut and should not be taken for long periods of time or if you have a history of ulcers. Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. Gabapentin can help control seizures as well as nerve pain from shingles. It may sometimes cause side effects, especially if you misuse it. Learn more. The short answer is: yes, gabapentin can be problematic for individuals with kidney failure and chronic kidney disease (CKD). While gabapentin is often prescribed for pain management, particularly nerve pain, and sometimes for seizures, its primary elimination pathway is through the kidneys. When it comes to gabapentin and kidney disease, kidney disease sufferers should be aware of the risks that are involved in taking gabapentin with kidney disease. Gabapentin is actually toxic to the kidneys. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Gabapentin isn’t known to cause liver or kidney problems. However, it can cause an allergic reaction called DRESS syndrome, which can lead to liver or kidney damage. But this is extremely rare. If you have existing kidney problems, your healthcare provider may start you at a lower gabapentin dose.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_Early-Symptoms-of-Kidney-Failure_Illustrator_Ellen-Lindner_Final-d6abfd220e5b4ccfa407688366218c92.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/kidneypainfinal-01-5c3ba11dc9e77c0001033b11.png) |  |