Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
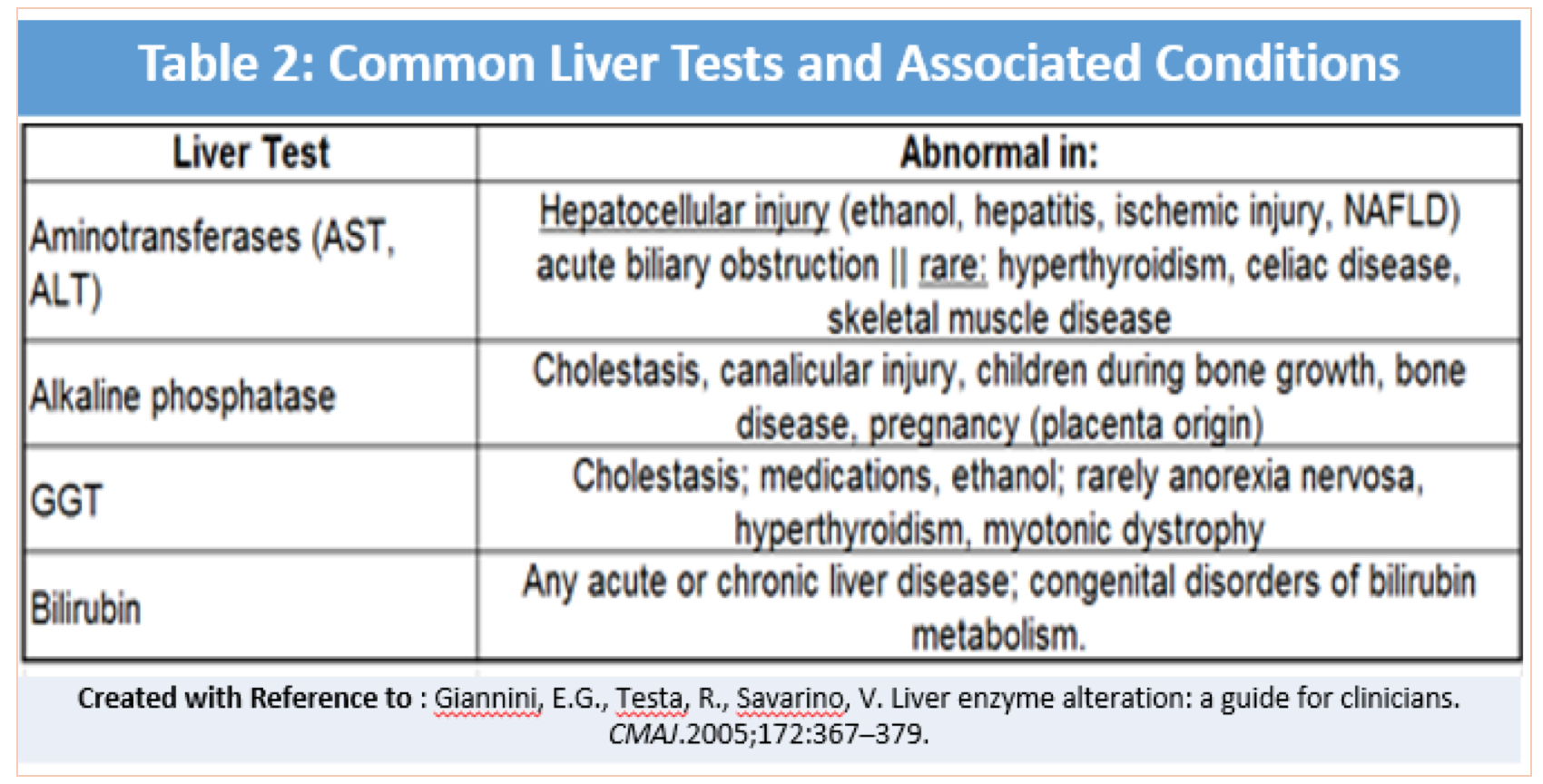
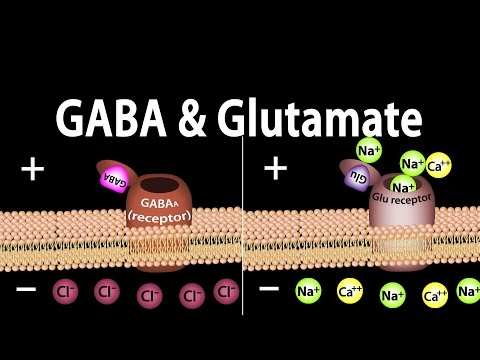
Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography showed no biliary abnormalities. After gabapentin was discontinued, liver enzymes began to downtrend with discharge values of AST 16, ALT 35, ALP 413, Tbili 9.3 and INR 1.1 (Figure). Discussion: Gabapentin induced liver injury is rare with few reported cases, many of which did not exclude other Can administration of gabapentin for trigeminal neuralgia dramatically increase liver function tests? What else can cause an Alk-P to elevate while the other liver enzymes stay the same? Liver tumors. I’ve seen both benign and cancerous masses on the liver causes this change in the bloodwork. One patient had a tumor the size of a volleyball on her liver. She had it removed at the specialist, her Alk-P went back to normal, and she went on with Gabapentin caused elevated liver function enzymes AST, ALT, and ALP beside bilirubin. Gabapentin effects on lipid profile, Blood electrolytes, and functions of kidney and liver of laboratory There are several liver enzymes, but the ones that show liver damage from medications are aspartate transaminase (AST) and alanine transaminase (ALT). Medications may cause liver enzymes to be elevated without serious liver damage until they reach 3 to 5 times the normal levels. In general, some studies have shown that gabapentin is an antiepileptic drug with a low profile of interaction with other drugs. 68, 69 Specifically, a general review stated that gabapentin lacks interactions with hepatic enzymes, plasma proteins and other drugs; these factors make gabapentin suitable for elderly patients suffering from hepatic In biological systems, Vitamin E is a major antioxidant that acts as a powerful chain-breaking agent through peroxyl radicals scavenging [58] with increasing the activities of antioxidant enzymes like catalase, SOD, and glutathione-S-transferase in rats [59,60,62,63]. Gabapentin and Cirrhosis of the Liver - Fatty Liver Disease Gabapentin (Neurontin) usually isn’t bad for your liver or kidneys. In most cases, it has little effect on these organs. In rare instances, gabapentin can cause DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms) syndrome. Therapy with gabapentin is not associated with serum aminotransferase elevations, but several cases of clinically apparent liver injury from gabapentin have been reported. This elevation probably results from a decreased synthesis of mitochondrial acetyl CoA, leading to a decrease in N-acetylglutamate, an activator of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase. 2 A more than two to three fold increase in liver enzymes during AED therapy should caution the physician of a potential of coexistent liver disease. If subsequent Other AEDs with rising and currently highest prescription rates were associated with few or no cases of liver injury including gabapentin (45.3 million), clonazepam (18.8 million), pregabalin (10.6 million), topiramate (9.3 million), and levetiracetam (7.7 million) and many of cases were judged as only “probable”. Gabapentin is an uncommon cause of DILI reported to cause a hepatocellular, cholestatic, or mixed picture of liver injury. Given the limitations of prior cases, we feel our report most closely ties gabapentin use to the resultant transaminase elevation. Can gabapentin cause liver enzymes to be elevated? Gabapentin is a unique anticonvulsant used as an adjunctive therapy in managing epilepsy and neuropathic pain syndromes. It is a structural analogue of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and has been approved for use in the United States in 1993. Here, we’ll discuss 10 medications that could potentially harm your liver or lead to elevated liver enzymes. We’ll also cover what symptoms to look out for and what you can do to prevent liver toxicity (hepatotoxicity). 1. Tylenol (acetaminophen) is a common over-the-counter (OTC) pain reliever and fever reducer. The activity of liver enzymes, with 20 mg/kg of GPN were not significantly different from the control group but, the serum levels of aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase, lactate dehydrogenase, direct bilirubin and total bilirubin were enhanced significantly with 100 mg/kg of GPN. Gabapentin, a common over-the-counter pain reliever and fever reducer, has been linked to rare individual case reports of liver injury. The causal relationship between gabapentin and liver damage is unclear, with the latency to onset being 1 to 8 weeks. Gabapentin is not metabolized by the liver. Instead, it is excreted unchanged in your kidneys after circulating in your blood. Gabapentin affects nerves and chemicals in your body that are involved in some types of pain and in seizures. In conclusion, while gabapentin can potentially cause a mild increase in liver enzymes, it is generally well-tolerated and does not typically cause significant liver damage. Regular monitoring of liver enzyme levels and prompt reporting of any symptoms are important for ensuring the safe and effective use of this medication. In prelicensure clinical trials, gabapentin enacarbil was not linked to an increased rate of serum enzyme elevations during treatment or to episodes of clinically apparent acute liver injury.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |