Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
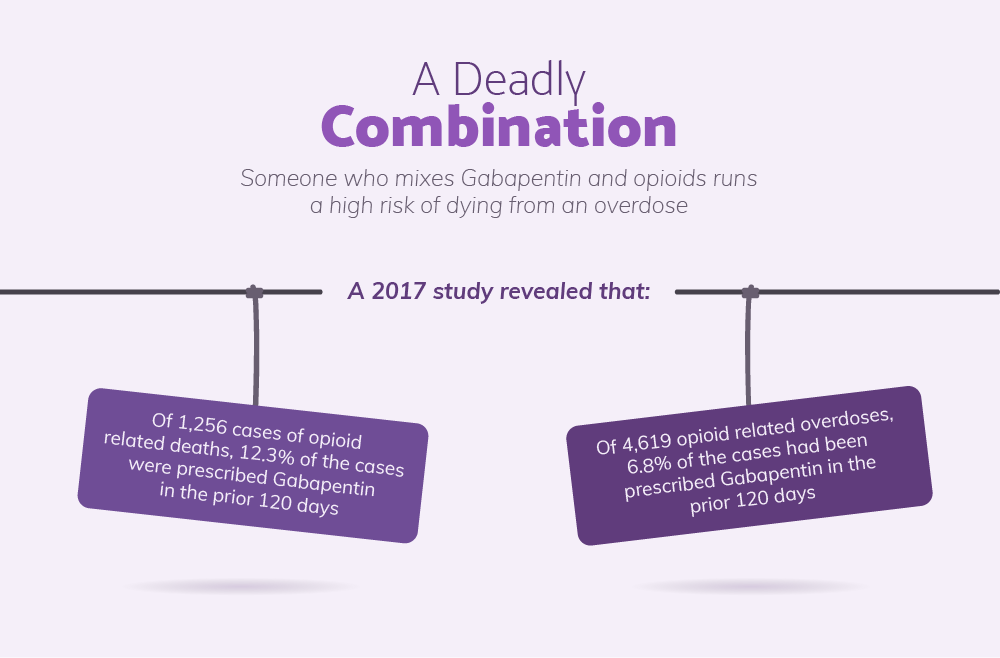 |  |
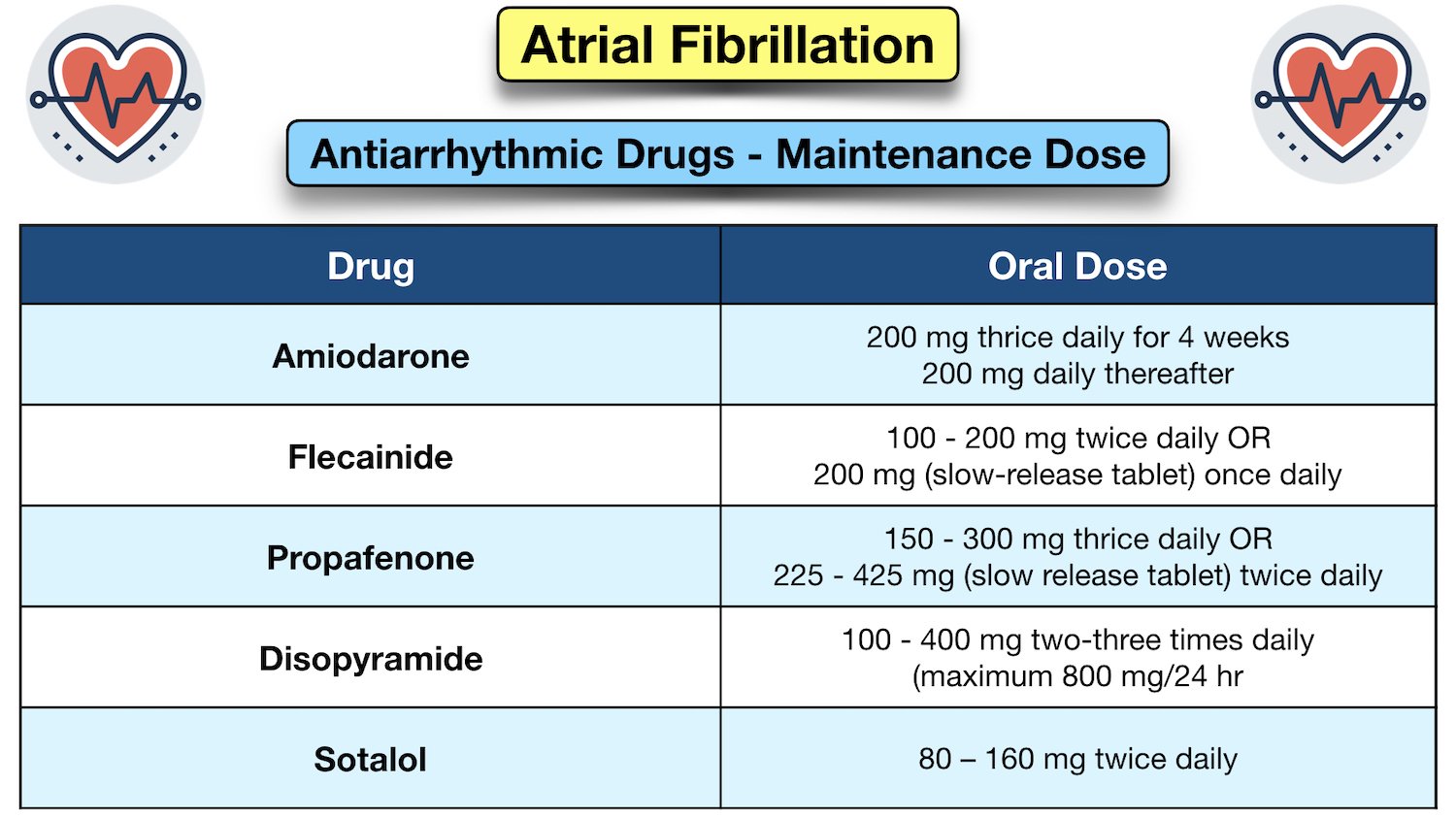
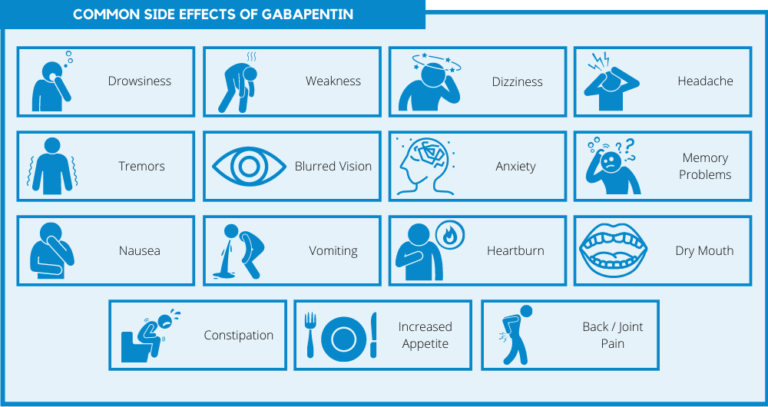
Some antibiotics, like amoxicillin and azithromycin, can cause abnormal electrical activity in your heart. This could lead to irregular or fast heart rates that cause AFib or other arrhythmias. Of these, gabapentin was found in 9.7%. Gabapentin was judged to contribute to overdose death in 52.3% of those deaths—or 5.0% of the total deaths from overdose. Individuals who died from a gabapentin-related overdose were most likely to be non-Hispanic white (83%), between the ages of 35 and 54 years (52%), with men and women equally affected. Postmortem toxicology tests detected gabapentin in almost 1 in 10 US overdose deaths between 2019 and 2020. In about half of the cases, a medical examiner or coroner ruled the drug was a cause of the death, according to a report from the CDC’s Division of Overdose Prevention. Patients who have undergone heart transplantation without evidence for autonomic re-innervation should not receive atropine because it can cause paradoxical heart block or even sinus arrest. Treatment for overdose of sinus or AV node blocking agents includes: gastric lavage, activated charcoal, glucagon, and insulin with concomitant intravenous Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly prescribed medications for the treatment of seizure disorders, neuropathic pain (eg, postherpetic neuralgia), fibromyalgia, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder, and restless leg syndrome. Gabapentinoids are commonly ingested in self-harm attempts and often misused for their sedative and euphoric Arrhythmias is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Metformin, and have High blood pressure. Case reports and observational studies have showed that gabapentin can be associated with increased risk of atrial fibrillation. However, all the evidence is concentrated in patients older than 65 years old with comorbidities that predispose them to the development of arrhythmias. When combined with a central nervous system depressant, a gabapentin overdose may cause respiratory depression and coma, potentially requiring artificial ventilation to ensure airflow. If you suspect a gabapentin overdose, call 911. Although less common than central nervous system toxicities, cardiovascular toxicities of gabapentin and pregabalin may lead to serious consequences, including worsening heart failure and arrhythmias. Pregabalin and gabapentin are widely used analgesic, anticonvulsant and anxiolytic agents as they are relatively reliable and easily tolerated. However, they may cause some side effects such as dizziness, somnolence, dose-dependent peripheral edema, and weight gain, which may cause patients to aband Gabapentin is a commonly used medication used as an anti-convulsant or analgesic. The well-known side-effects of gabapentin are dizziness, drowsiness and fatigue. In rare cases, it can lead to development of new onset congestive heart failure (CHF) or decompensation of pre-existing CHF. Some side effects of gabapentin may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine. Also, your health care professional may be able to tell you about ways to prevent or reduce some of these side effects. High doses of gabapentin can pose significant risks to health. As gabapentin becomes more widely prescribed, understanding its potential side effects is crucial. While this medication is often used to manage nerve pain and seizures, misuse and overdose can lead to severe consequences. Neurological Side Effects of Gabapentin Overdose With rapidly increasing usage of gabapentin for approved and off-label indications, it is important to identify unintended adverse effects of this drug as they are considered safe alternatives to opioids. New-onset atrial fibrillation could be induced by gabapentin in young individuals. Objective: To raise awareness of serious toxicity, including respiratory depression and PRES (posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome) caused by gabapentin in the setting of overdose and abuse. Background Gabapentin, a structural analog of γ-aminobutyric acid, although developed for epilepsy, is often used for pain, insomnia and anxiety. A gabapentin overdose is rare, but it is possible. The likelihood of an overdose increases when you abuse gabapentin with other drugs like opioids and alcohol. If you or someone you know is experiencing a gabapentin overdose, seek medical help immediately. Results: Compared with opiate analgesics, both gabapentin and pregabalin were associated with an increased risk of initiating OAC/APA + AA. Many widely used medications may cause or exacerbate a variety of arrhythmias. Numerous antiarrhythmic agents, antimicrobial drugs, psychotropic medications, and methadone, as well as a growing list of drugs from other therapeutic classes (neurological drugs, anticancer agents, and many others), can prolong the QT interval and provoke torsades de pointes. Perhaps less familiar to clinicians is Gabapentin and pregabalin are widely prescribed to elderly people, but data on their pharmacokinetics, safety, and efficacy in this population are scarce. Neurological adverse effects are common. Atrial fibrillation (AF) associated with their use Gabapentin is commonly prescribed to dogs for pain management, particularly for conditions like arthritis, neuropathic pain, or to control seizures. While it’s an effective treatment for many dogs, it’s essential to understand the potential side effects that may occur, especially with long-term use. In this guide, we’ll explore the most common side effects, how to manage them, and what
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |