Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
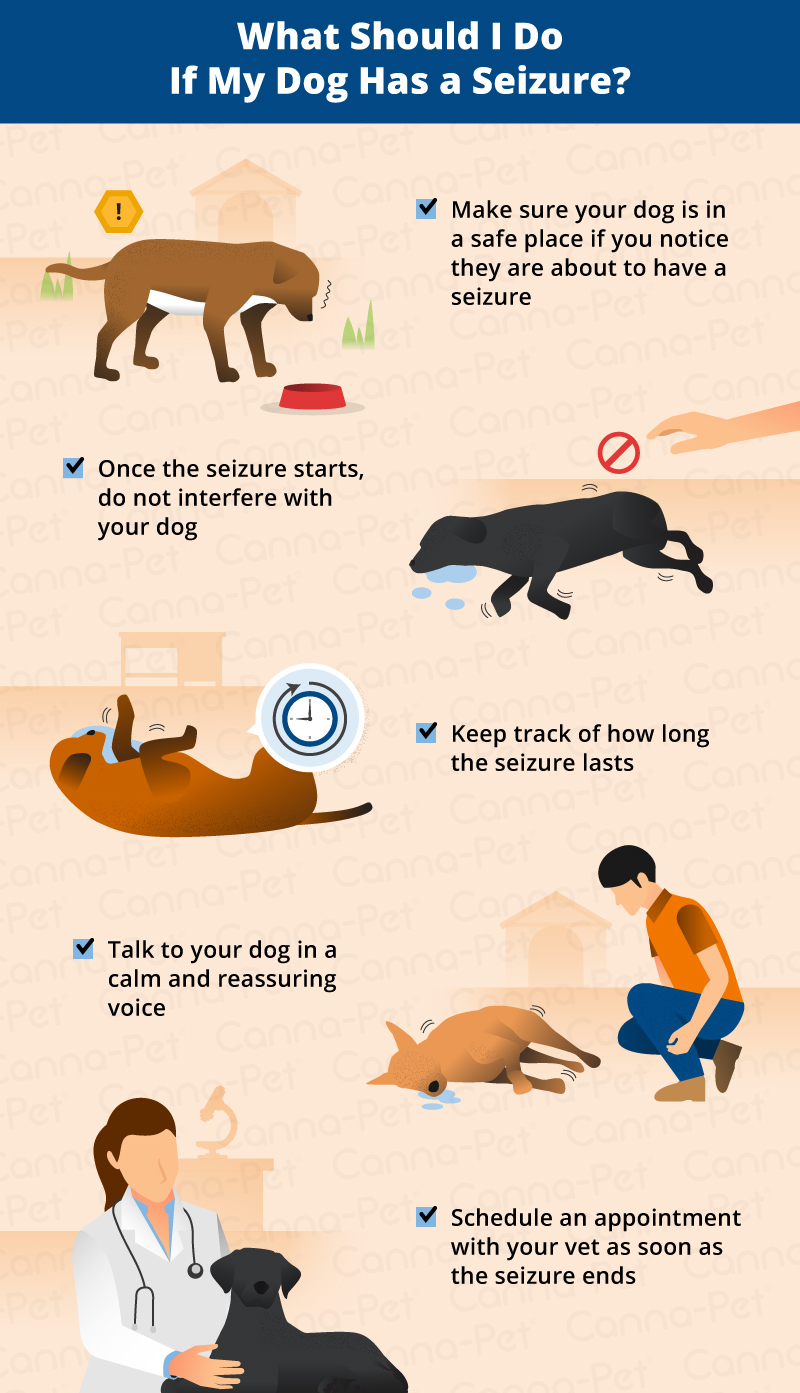
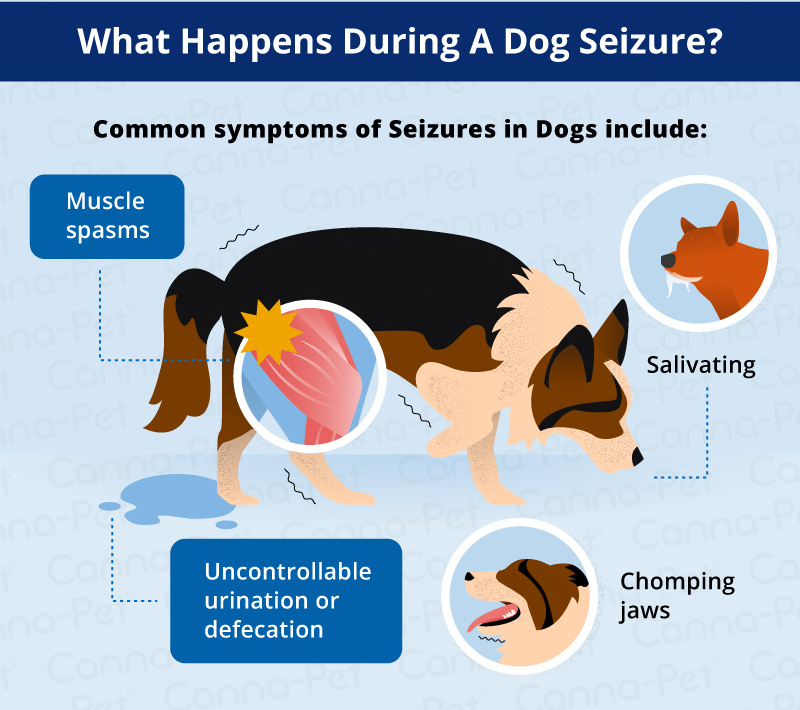
:strip_icc()/If-your-dog-has-a-seizure-1117423_final-a65066098f2742daa2427e19fc454e2a.jpg) |  |
 |  |
Gabapentin can treat and reduce the frequency of seizures and is commonly used as an anticonvulsant to treat or prevent seizures in dogs. Gabapentin may also be used to provide pain relief for dogs, particularly when other medications have proved ineffective or are not well tolerated. Gabapentin is a medication primarily used as an anticonvulsant in humans, but in veterinary medicine, it’s frequently used off-label to manage chronic pain, neuropathic pain, and seizures in dogs. It works by modulating nerve signals in the brain and spinal cord, which helps reduce pain and control abnormal electrical activity that causes Gabapentin is commonly prescribed to dogs for pain management, particularly for conditions like arthritis, neuropathic pain, or to control seizures. While it’s an effective treatment for many dogs, it’s essential to understand the potential side effects that may occur, especially with long-term use. In this guide, we’ll explore the most common side effects, how to manage them, and what Gabapentin can be prescribed to treat epilepsy in dogs, but it is not usually a go-to drug for dogs who have frequent generalized seizures. Gabapentin may be used to control focal/partial seizures or as an adjunct medication for generalized seizures if the previous medication regimen isn’t working. Yes, it is essential to taper off gabapentin gradually rather than stopping abruptly, to avoid withdrawal symptoms such as seizures and rebound pain. 10. Can I stop giving my dog gabapentin cold turkey? No, never stop gabapentin cold turkey, as this can lead to withdrawal seizures and other issues. Always follow your veterinarian’s While gabapentin is commonly well-tolerated by puppies, it is essential to be aware about the capacity side outcomes. Here’s a breakdown of the common and much less not unusual facet results to watch out for. Sedation: As with many medications, gabapentin can cause drowsiness or sleepiness in dogs. This effect is usually most noticeable in Can Gabapentin Cause Seizures in Dogs? Gabapentin itself is not a typical cause of seizures in dogs. Instead, seizures may occur due to improper use, particularly abrupt discontinuation of the medication. This happens because Gabapentin works to suppress overactive nerve signals. While gabapentin can be a valuable tool for managing pain, seizures, and anxiety in older dogs, careful consideration and monitoring are necessary. This article will delve into the specifics of gabapentin use in senior dogs, providing a detailed look at its effects, safety profile, and potential side effects. Gabapentin has anticonvulsant properties that make it beneficial for adjunctive therapy for dogs with refractory seizures or those whose current medication regime is no longer effective enough. Gabapentin is also an analgesic, meaning it provides relief for chronic pain and neuropathic pain. For dogs, it’s used to treat seizures, anxiety, and nerve pain. It works by blocking calcium channels in the brain to suppress overly stimulated neurons that cause anxiety, nerve pain, and In dogs with epilepsy, a sudden Gabapentin discontinuation is likely to trigger withdrawal seizures. The vet will help create the best plan for weaning your dog off in terms of decreased dose and administration frequency. The same dose tapering plan should be used for dogs using Gabapentin for pain. Never stop Gabapentin abruptly if it's being used to treat seizures in your dog, as it can cause withdrawal seizures. Final thoughts. Although classified as an anti-seizure drug, Gabapentin is valuable as part of an any anti-pain and anti-anxiety management plan for your dog. Gabapentin is a safe and efficient treatment option for dogs.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
:strip_icc()/If-your-dog-has-a-seizure-1117423_final-a65066098f2742daa2427e19fc454e2a.jpg) |  |
 |  |