Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
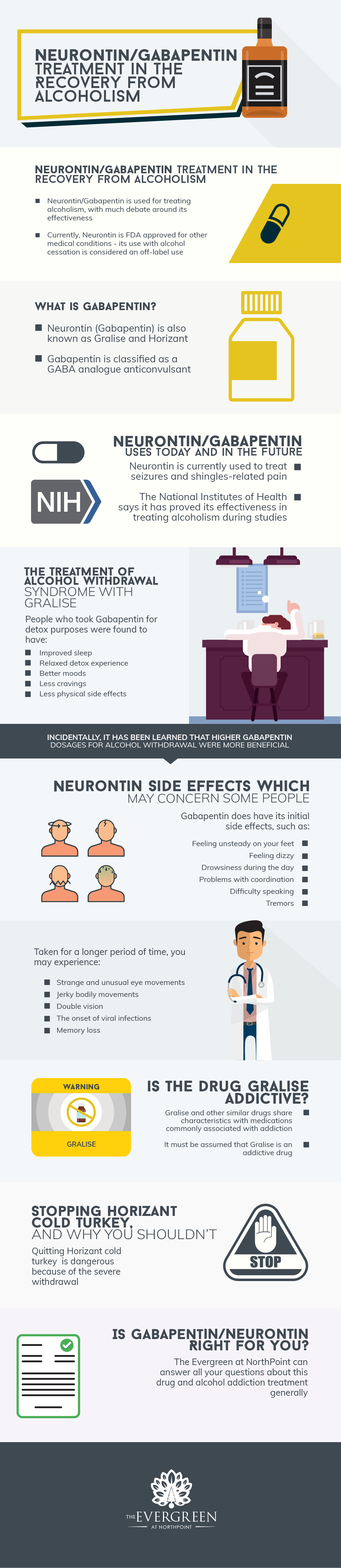
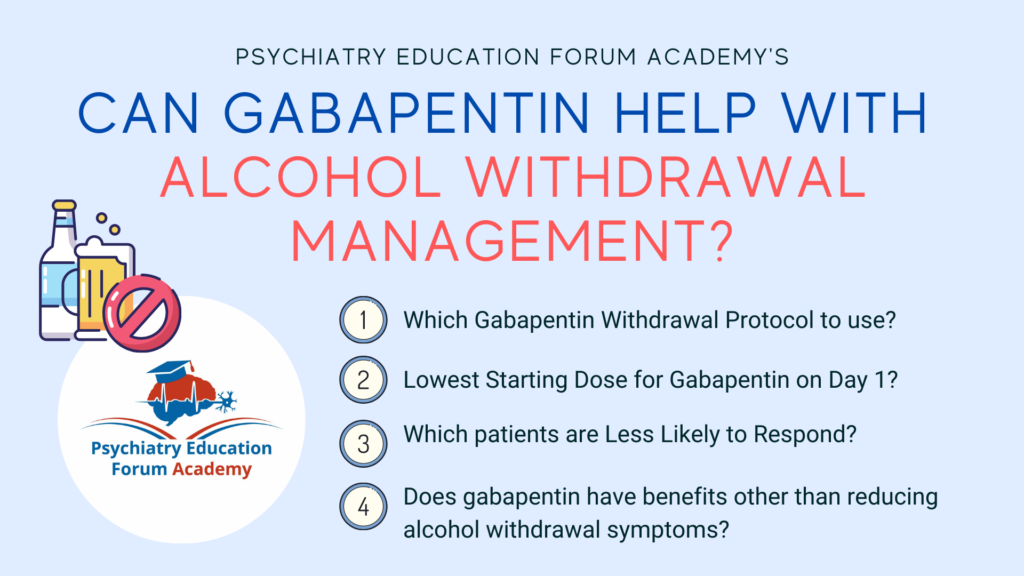
Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29,30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32,33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or Method: A total of 150 alcohol-dependent individuals were randomly assigned to a 16-week course of naltrexone alone (50 mg/day [N=50]), naltrexone (50 mg/day) with gabapentin (up to 1,200 mg/day [N=50]) added for the first 6 weeks, or double placebo (N=50). All participants received medical management. • You should not take gabapentin if you are pregnant, planning on getting pregnant or are breastfeeding. • Taking medicine for an alcohol use disorder is not substituting one drug for another. How should I take gabapentin? • The recommended dose of gabapentin for the treatment of alcohol use disorder is 300–600 milligrams (mg) three While gabapentin is not yet an FDA-approved treatment for alcoholism, a number of studies support the its use withdrawal and cravings: In a 12-day study detoxifying with either gabapentin or lorazepam (a benzodiazepine prescribed with the brand name Ativan), the former was less likely to drink – and had less craving, anxiety, and sedation. Gabapentin can help with alcohol withdrawal by counteracting the physiological effects of the syndrome. Evidence indicates that symptoms of alcohol withdrawal syndrome stem People whose anxiety levels are very high during alcohol withdrawal may get relief from their symptoms by taking gabapentin, which has minor anxiolytic (anxiety-reducing) properties. This medicine can work very well at boosting emotional regulation by affecting brain neurotransmitters. This explains its use in treating nerve-related pain such as shingles, as well as epileptic seizures. In fact, seizures are among the more extreme reactions people can have to alcohol withdrawal, and can be prevented by taking gabapentin. For alcohol use disorder (AUD), gabapentin is considered “off-label.” An off-label medication is a drug You can take gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal. Many healthcare providers treat acute alcohol withdrawal by prescribing gabapentin, which can be taken in an outpatient setting. Gabapentin promotes the release of brain-sedating chemicals, such as gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Gabapentin has been shown to be safe and effective for mild alcohol withdrawal but is not appropriate as mono-therapy for severe withdrawal owing to risk of seizures. During early abstinence, gabapentin may improve sleep, cravings, and mood—factors associated with relapse. Given gabapentin’s effectiveness for acute alcohol withdrawal problems, a research team at the Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC) explored whether AUD patients who exhibit more severe withdrawal symptoms might experience greater improvements with gabapentin than those who experience fewer symptoms. Gabapentin has been found to help with alcohol withdrawal symptoms, including easing alcohol cravings, as well as reducing alcohol consumption and maintaining abstinence after withdrawal. 4,5,6 Using gabapentin for withdrawal constitutes one example of off-label use of the drug. 4 Gabapentin can significantly reduce the severity of withdrawal symptoms, making the detoxification process more comfortable for patients. Patients may experience a reduction in the urge to consume alcohol, which can be a pivotal factor in preventing relapse. ⦁ Gabapentin is advantageous for withdrawal because (unlike benzos) it can be continued for long-term treatment to prevent future alcohol relapse Moderate Outpatient Withdrawal With Benzodiazepines Clonazepam (Klonopin) is usually the first-choice benzodiazepine for outpatient withdrawal due to a lower likelihood of causing euphoria. Gabapentin can cause a serious condition called multiorgan hypersensitivity or Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) syndrome. If experiencing symptoms such as rash, fever, swollen lymph nodes, or liver problems, medical attention should be sought immediately. Important considerations when taking gabapentin We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. One of the main concerns of stopping gabapentin when not using for seizures, is the occurrence of withdrawal symptoms. Withdrawal symptoms of gabapentin can mimic those of alcohol withdrawal symptoms including the following: Anxiety; Irritability and agitation Insomnia Nausea and diarrhea; Sweating; Pain; Palpitations; Headache Flu-like symptoms A study published this week concluded that gabapentin can relieve alcohol withdrawal symptoms but is most effective for people with a history of more severe symptoms after a few days Some research shows that gabapentin has promise as an alcohol withdrawal treatment, possibly in combination with other medications. Gabapentin can: Help stop the impulse to Some people can become addicted to gabapentin. If this happens, you’ll have withdrawal symptoms after you stop taking the medicine. When you stop taking gabapentin, you'll need to reduce your dose gradually to avoid withdrawal symptoms. Do not stop taking gabapentin without talking to your doctor.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |