Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
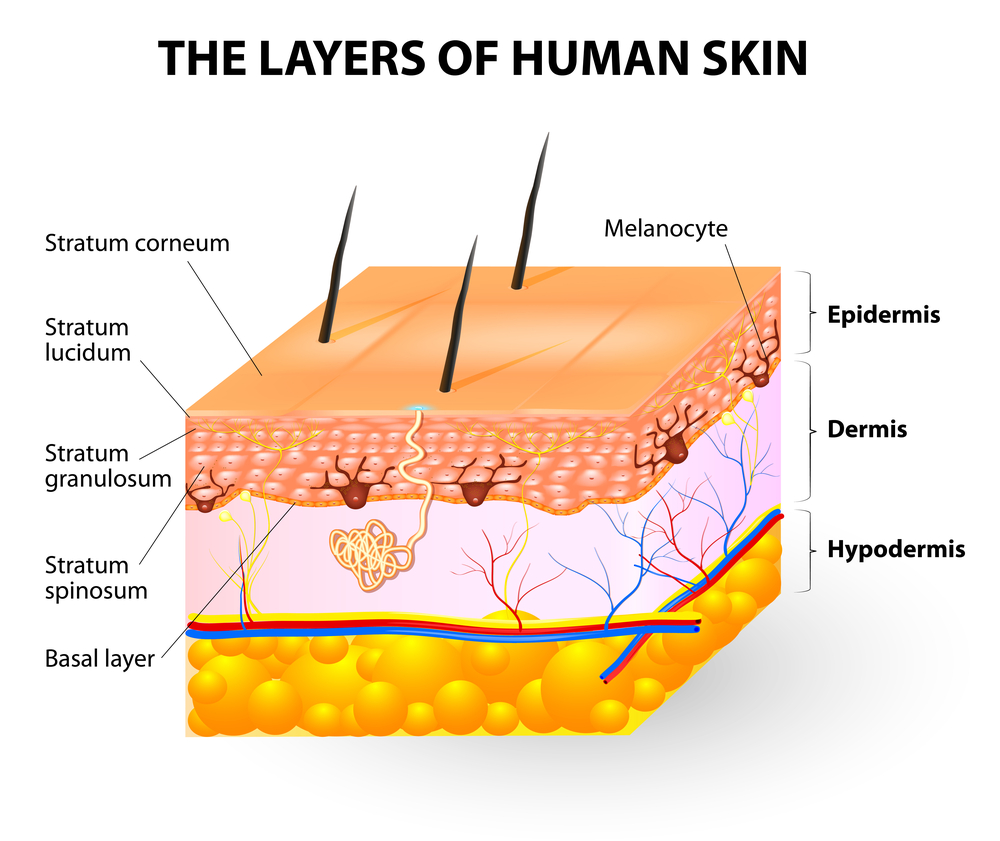
When it comes to drug absorption through the skin, there are three main routes: passive diffusion, active transport, and intracellular penetration. Each route plays a role in how drugs permeate the skin and enter the bloodstream. Passive Diffusion. Passive diffusion is the most common route of drug absorption through the skin. When topical products are formulated, a critical factor to consider is the ability of the drug molecule to enter and cross the skin, or other biological barrier, whether intended for local or Lidocaine released from a patch penetrates through the skin and, to a negligible degree, is absorbed into vessels; therefore, it does not induce circulatory complications and there is no need to monitor circulatory system function. Rapid penetration to peak flux was detected for gabapentin and baclofen at approximately 1 hour after application. Clonidine HCl also had a rapid penetration to peak flux occurring approximately 1 hour after application and had a secondary peak at approximately 40 hours. Flux of the drug appeared to be concentration-dependent with no permeation occurring at 1% strength. Whereas, 5% and 10% strengths in Lipoderm Cream permeated the skin rapidly, the same concentrations in Emollient Cream and VersaBase Gel required 60-minutes and 120-minutes lag times, respectively. When handling the skin patch, be careful not to touch the adhesive (sticky) surface with your hand. The adhesive part of the system contains some fentanyl, which can be absorbed into your body too fast through the skin of your hand. If any of the medicine does get on your hand, rinse the area right away with large amounts of clear water. The most rapid and greatest penetration and retention of gabapentin in the skin occurred with a poloxamer lecithin organogel base. Lipobase and Lipoderm bases produced slow and smaller penetration and retention of gabapentin as compared to poloxamer lecithin organogel base. Our data suggests that gabapentin can permeate the human SC if applied to the skin in a vehicle with sufficient thermodynamic activity. This data correlates with the findings of [ 11 , 15 , 16 ] ( Table 2 ), all of whom investigated skin permeation using in vitro porcine or rodent skin models. Toxicity : Some illegal drugs contain harmful substances or contaminants that can cause toxicity when absorbed through the skin. These toxins can have detrimental effects on various organs and systems in the body. Addiction : The absorption of illegal drugs through the skin can still lead to addiction, as the drugs enter the bloodstream and Gabapentin, a commonly prescribed medication for cats, can be challenging to administer. However, there are alternatives to consider that can make the process easier. One possibility is using transdermal patches and gels. These products allow for the medication to be absorbed through the skin, eliminating the need for oral administration. Yes, an e-juice can be absorbed through the skin. While we do not recommend using nicotine products on your skin, eLiquid can spill and be absorbed into your bloodstream. The amount of nicotine that will get in will depend on how much liquid you apply to your skin, how long it stays there, and how much nicotine is in the liquid. Due to the permeability barrier of the skin (in particular, the outermost layer, called the stratum corneum), there are very few drugs that can be absorbed through intact skin. Nicotine is one of the few that can be delivered transdermally. It is able to diffuse through the stratum corneum in part because it is a small molecule (162 Da) that is When it comes to drug absorption through the skin, there are three main routes that substances can take: passive diffusion, active transport, and intracellular penetration. Understanding these routes is essential for comprehending how drugs can be effectively delivered through the skin. Passive Diffusion. Passive diffusion is the most common Remember the dose-dependent absorption issue with gabapentin. As you get to higher dosages, there is the potential that you Gabapentin and Renal Function - Case Scenario - Med Ed 101 - [] Here’s another clinical pearl regarding gabapentin effectiveness and how this drug’s absorption can vary based upon the dose. Skin concentrations increased with a longer 1-hour pre-treatment. Minimal skin and deeper tissue levels were found following a 4-hour pre-treatment. These results suggest that topical gabapentin may be antinociceptive in a rodent formalin model at specific doses and pre-treatment intervals. The concentration of gabapentin in the gel has been optimized to ensure adequate absorption through the skin while minimizing the risk of local irritation. In this study, we developed an optimal niosomal formulation for gabapentin and assessed its cytotoxicity effect on normal cells and a colon cancer cell line. Methods: Several niosomal One ml of cosolvent system containing 5 mg of gabapentin or drug - loaded microemulsion was applied onto skin surface facing the donor compartment that was covered with a glass lid. The way each drug works and is absorbed transdermally varies considerably. Hair, differences in skin, skin infections, effects of illness, or hydration status, can all influence the body’s ability to use a drug applied on the skin. If your pet is placed on a transdermal medication and fails to improve, the drug may need to be administered orally. Oral gabapentin is taken by mouth and is the most common method of administration. It can be given as a tablet, capsule, or liquid, depending on the cat’s preferences and ease of administration. Transdermal gabapentin, on the other hand, is absorbed through the skin and is applied as a gel or cream.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |