Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
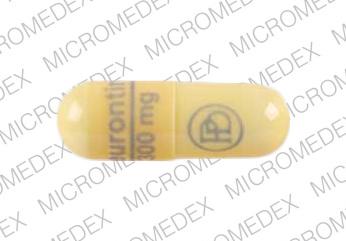
The best pain reliever for a tooth ache, or really any transient pain is ibuprofen. (I worked with a dentist for 15 years.) If you don't already take Gabapentin, no one is going to prescribe it for you for a tooth ache. In Miami, tooth decay is a significant public health issue, partly fueled by excessive sugar consumption. Gabapentin, primarily used to treat nerve pain, surprisingly also affects oral health. Some studies suggest its use may exacerbate tooth decay. This highlights the need for more research on Gabapentin's role in dental health. Customer: Can I use Gabapentin for toothache pain? Doctor's Assistant: The Dentist can help. Just a couple quick questions before I transfer you. When did the pain start? Is it localized in a particular part of your body? Customer: It’s been going on for a week and it’s in the front of my mouth. Doctor's Assistant: What type of pain is it Source: Pain service Reference No: 5312-3 Issue date: 27/10/21 Review date: 27/10/24 Page 1 of 3 Gabapentin and its use in pain management Why do I need gabapentin? Gabapentin is a drug used to treat nerve pain. This type of pain is often not relieved by normal painkillers. It can be used in combination with other painkillers to improve “We hypothesized that using a combination of the non-opioid pain medications and adding gabapentin to the mix for pain would be an effective strategy to minimize or eliminate opioids for dental pain,” said Yanfang Ren, DDS, PhD, MPH, professor and clinical chief, Howitt Urgent Dental Care. How Gabapentin Works to Provide Toothache Relief? Gabapentin primarily targets the calcium channels in nerve cells, inhibiting the release of excitatory neurotransmitters. By doing so, it decreases the hyperexcitability of nerves, reducing the intensity of pain signals. Gabapentin is a medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain, which is pain caused by nerve damage. Its efficacy in managing various types of pain has been well-documented, but its role in alleviating tooth pain, particularly postendodontic pain, is less clear. Dentists frequently prescribe opioids for dental pain and contribute substantially to new and persistent opioid use. 1 Although the American Dental Association recommends nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for managing pain, 2 opioids continue to be used more than nonopioids. 3 This may partly be explained by the lack of alternatives to opioids, especially when NSAIDs or Known as an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat epilepsy and nerve pain, gabapentin has been gaining popularity as a remedy for wisdom tooth pain. In this article, we will explore whether gabapentin is truly effective in alleviating the agony caused by emerging wisdom teeth. This study showed that pretreatment with a single dose of pregabalin and gabapentin both had greater analgesic effects than a placebo. They can be effectively used to reduce postoperative endodontic pain. Keywords: Gabapentin, Postoperative Pain, Pregabalin, Prophylaxis, Root Canal Therapy. INTRODUCTION Gabapentin is a prescription antiepileptic medication commonly used to treat postherpetic neuralgia, a type of nerve pain, and other neuropathic pain conditions. Learn more about how long it takes to treat nerve pain and what to expect when you're prescribed it. In a new study at the University of Rochester Medical Center’s Eastman Institute for Oral Health (EIOH), researchers found that gabapentin, when combined with ibuprofen or acetaminophen, was more effective than opioids in relieving pain after tooth extractions. Gabapentin is a medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain, which is pain caused by nerve damage. However, its application in dental pain, particularly postendodontic pain, has been explored in recent studies. A combination of analgesics prescribed with gabapentin after dental procedures was shown to be just as effective for treating pain as opioids, researchers reported in JAMA Network Open. Gabapentin didn’t do anything for my tooth pain. However I HIGHLY recommend taking 2 Tylenol and 2 Motrin at the same time. It knocks my tooth pain completely out. Gabapentin, in combination with other analgesics, can help manage toothache pain. Gabapentin, an anticonvulsant drug, has been found to be beneficial in managing dental pain, particularly when used in combination with other analgesics. Here are some of the benefits of using gabapentin for dental pain: Despite its primary use for nerve-related issues, gabapentin has garnered attention for its potential effectiveness in managing tooth pain. Tooth pain can arise from various sources: infections, inflammation, or even dental procedures. PubMed Central (PMC) is a free digital repository that archives publicly accessible full-text scholarly articles in the biomedical and life sciences. At that dose, it's possible the neurontin would soothe the trigeminal nerve pain that is likely causing your toothache (esp if you have a headache, too), but the length of time to get to the necessary dose - and the possibility it may not work at all on you depending on your chemistry - means the medication is not appropriate for tooth pain
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |