Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
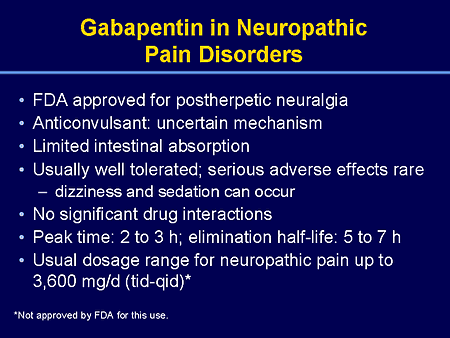 |  |
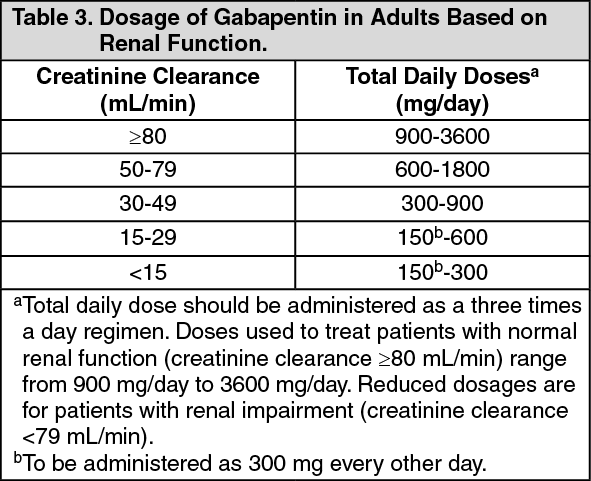
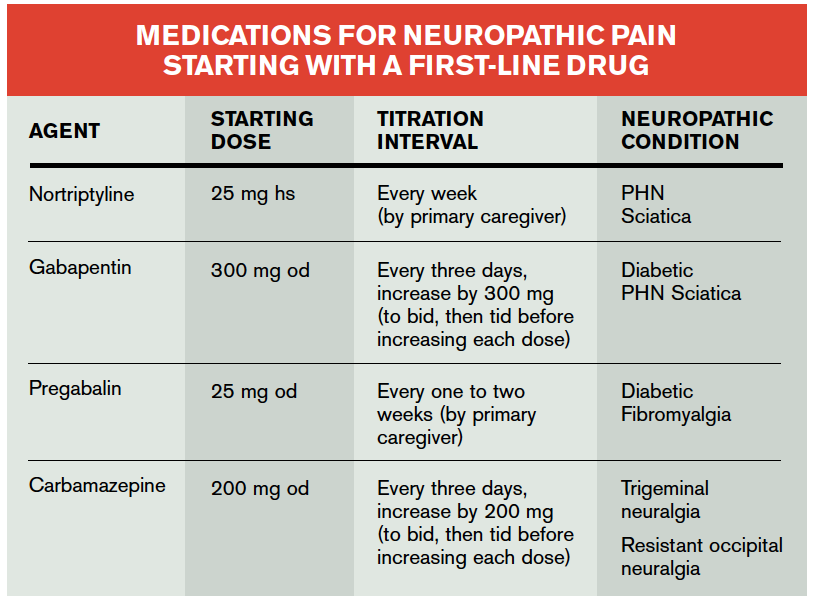
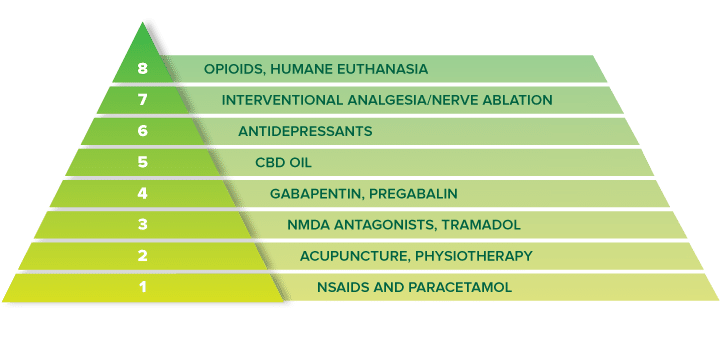
For treating nerve pain, one may recommend three doses of Gabapentin in a day divided into morning, afternoon, and evening doses. One may start with a low dose of 100 mg at night. Slowly increase the dose by adding another 100 mg at noon. Below is a general guideline for dosing: Gabapentin is primarily used for: Neuropathic Pain: Effective in alleviating pain from nerve damage. Postherpetic Neuralgia: Reduces pain following shingles. Seizure Disorders: Acts as an adjunctive therapy for partial seizures. For immediate-release gabapentin (Neurontin), dosing may be initiated with 300 mg on day 1, doubled on day 2 (300 mg twice a day), and tripled on day 3 (300 mg 3 times a day). The dose can then be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a maximum dose of 1,800 mg daily (divided into 3 daily doses). HOW COMMON IS NEUROPATHIC PAIN? • Neuropathic pain is a common condition affecting between 6% and 8% of the population. • An average GP may have between 35 and 70 patients with neuropathic pain. • Much neuropathic pain can be successfully managed within primary care. RECOGNISING AND DIAGNOSING NEUROPATHIC PAIN Common causes of neuropathic What is gabapentin? Gabapentin is a prescription medication known as a gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue. GABA reduces the excitability of nerve cells (neurons) in the brain, which play a role in seizures and the transmission of pain signals. To see if gabapentin works for you, your healthcare provider may prescribe it for four to six weeks or have you take the maximum tolerated dose for at least two weeks. Nerve pain can be recurring and persistent, sometimes lasting three months or longer. Many people stay on gabapentin for long-term management of their nerve pain and take it daily. The usual dose to treat nerve pain in adults is 900mg to 3,600mg a day, split into 3 doses. To prevent side effects, your doctor will prescribe a low dose to start with and then increase it over a few days. Once you find a dose that suits you, it will usually stay the same. Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Gabapentin is from a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. Determining how much gabapentin for nerve pain is appropriate involves understanding standard dosing guidelines. Most healthcare providers start patients on a low dose and gradually increase it based on their response and tolerance. Gabapentin is commonly used to treat and prevent seizures in people with epilepsy or to treat nerve pain (postherpetic neuralgia) that can occur after a viral infection called shingles. The established therapeutic dosing for gabapentin in neuropathic pain trials is 1800-3600 mg/day in 3 divided doses in patients with normal renal function. 3 This means the minimum effective dose is 600 mg 3 times a day. Renal adjustments are recommended in patients with CrCl below 60 mL/min. If you’ve been prescribed gabapentin, Horizant, or Gralise, taking your medication correctly is vital to getting the most out of it. And using the correct dosage will help you minimize, or avoid, side effects. In this guide, we’ll review common gabapentin dosages. Gabapentin is also used as an adjunct to more potent anticonvulsants and for the management of certain types of neural pain. Definition and uses of gabapentin. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat seizures and nerve pain. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant with pain-relieving effects that may be used to treat partial-onset seizures or relieve nerve pain. Research has shown gabapentin binds strongly to a specific site (called the alpha2-delta site) on voltage-gated calcium channels and this is thought to be the way gabapentin works to relieve nerve pain and lower The dose can subsequently be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a dose of 1800 mg/day (600 mg three times a day). In clinical studies, efficacy was demonstrated over a range of doses from 1800 mg/day to 3600 mg/day with comparable effects across the dose range; however, in these clinical studies, the additional benefit of using doses Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. Gabapentin 100mg Dosage for Nerve Pain. One of the most common uses of Gabapentin 100mg is treating neuropathic pain. This type of pain often results from nerve damage caused by conditions such as diabetes, shingles (postherpetic neuralgia), or spinal cord injuries. A 100mg dosage can provide relief for mild to moderate nerve pain, making it a The typical starting dose of gabapentin for sciatic nerve pain for most patients is 300mg once a day. Your physician may increase the dosage up to three times a day. Your physician may increase Initial dose: 300 mg once daily, with gradual increases as needed. Maintenance dose: 900-3600 mg per day, divided into three doses. The duration of treatment depends on the patient’s response. Initial dose: 300 mg on day one, 300 mg twice daily on day two, and 300 mg three times daily on day three. Substance P plays a role in how you perceive pain. Gabapentin dosage for sciatica nerve pain. Gabapentin dosages for sciatica nerve pain typically start at 300 mg to 900 mg by mouth 3 times a day. This dosage is slowly increased by your prescriber depending on your response to the medication. Common side effects of gabapentin
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |