Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 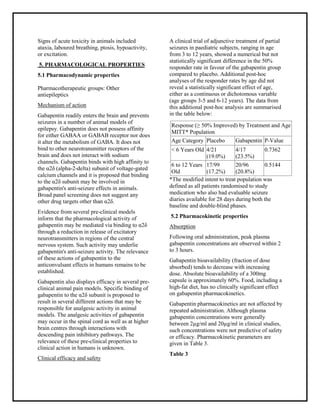 |
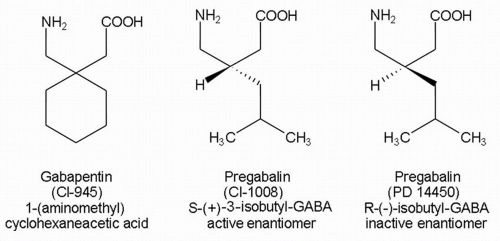
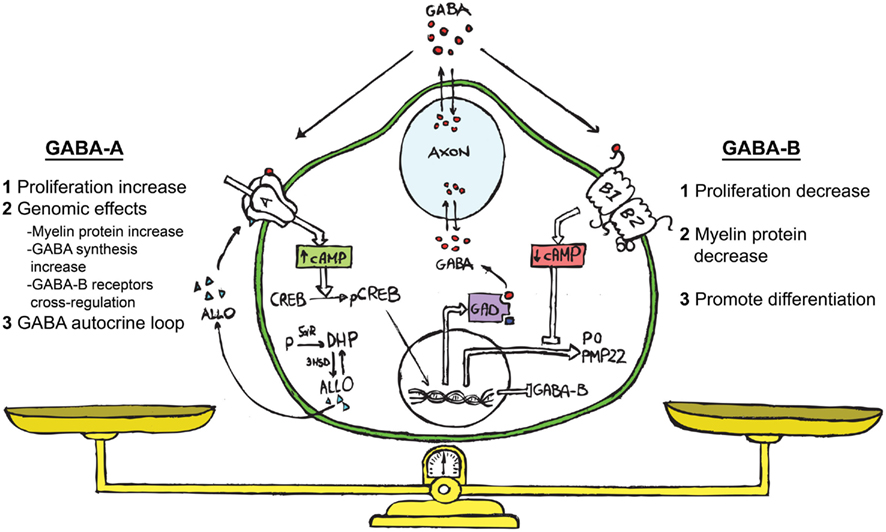
What's the difference between gaba and gabapentin? NT vs Medication: Gaba is a normal neurotransmitter (nt) in the brain and other parts of the nervous system in the body. Gabapentin is a medication that affects GABA in the brain and nervous system. Receptor Interaction: GABA works by binding to GABA receptors in the brain, whereas Gabapentin does not directly interact with these receptors. Therapeutic Use: GABA’s role is primarily within the normal functioning of the brain, while Gabapentin is used to treat various neurological disorders. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter, while gabapentin is a synthetic medication designed to mimic GABA’s effects. GABA is available as a supplement, whereas gabapentin requires a prescription and is used for specific medical conditions like epilepsy and neuropathic pain. In conclusion, understanding the differences between gabapentin and GABA supplements is crucial in determining the most suitable option for managing pain, seizures, or anxiety. Gabapentin targets specific brain activity, while GABA supplements aim to increase overall GABA levels. Gabapentin 901 mg/day to 1500 mg/day → pregabalin 225 mg/day; Gabapentin 1501 mg/day 2100 mg/day → pregabalin 300 mg/day; Gabapentin 2101 mg/day 2700 mg/day → pregabalin 450 mg/day; Gabapentin >2700 mg/day → pregabalin 600 mg/day; This rapid change was generally well tolerated by patients. While both relate to the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), they are fundamentally different in their origin, mechanism of action, and legal status. In short, over-the-counter (OTC) GABA is a dietary supplement, while gabapentin is a prescription medication. Thekey difference between GABA and gabapentinis that GABA is the major inhibitoryneurotransmitterthat helps in the development and maturation of the mammaliancentral nervous system, whereas gabapentin is a medication that can mimic the effect of GABA. Restless legs syndrome (RLS): Gabapentin helps reduce symptoms of RLS, including involuntary leg movements and sleep disturbances. Hot flashes: Recent studies suggest gabapentin may alleviate hot flashes associated with menopause. Gabapentin Vs. GABA: Key Differences. Here’s a table summarizing the key differences between GABA and Gabapentin: We compare the side effects and drug effectiveness of Gaba and Gabapentin. The phase IV clinical study is created by eHealthMe based on reports (from sources including the FDA) of 428,042 people who take Gaba and Gabapentin, and is updated regularly. GABA and gabapentin are often mistakenly used interchangeably, but they are not the same. GABA is an amino acid supplement and neurotransmitter, while gabapentin is a prescription medication. While practitioners may confuse the two, it’s important to understand their differences. GABA and Gabapentin, though distinct entities share a common goal: to promote calmness and regulate neuronal activity. While GABA is a natural neurotransmitter with diverse functions, Gabapentin is a synthetic medication mimicking some of its effects for specific therapeutic purposes. Ativan vs. Gabapentin What's the Difference? Ativan and Gabapentin are both medications commonly used to treat anxiety and seizures, but they work in different ways. Ativan is a benzodiazepine that works by enhancing the effects of a neurotransmitter called GABA in the brain, leading to a calming effect. GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is an amino acid supplement and neurotransmitter; gabapentin is a prescription medication. They are often used interchangeably (as you’ll read below) and should not be! Here are some of the many responses showing how GABA and gabapentin is used interchangeably by a variety of practitioners: The differences between GABA and gabapentin lie in their mechanisms of action in the brain – GABA targets GABA receptors whereas gabapentin interacts with voltage-gated calcium channels. Differences: Pregabalin vs. Gabapentin . One of the primary differences between gabapentin and pregabalin is that the FDA has approved both drugs for some of the same indications but also different ones. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain that inhibits or slows down nerve activity, helping to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. On the other hand, Gabapentin is a medication that is structurally similar to GABA but does not directly bind to GABA receptors. Gabapentin is a GABA analog, meaning that it looks very similar structurally but it is not completely the same. GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter found in the central nervous system (CNS) that regulates its excitability. Gabapentin stimulates GAD at drug concentrations of 1.0 to 2.5 mM (Silverman et al, 1991; Taylor et al, 1992) and inhibits the GABA-catabolizing enzyme, GABA-transaminase (GABA-T) at high concentrations (23-25 mM; Taylor et al, 1992) with relatively weak effects on GABA-T at lower concentrations of 10 mM (Goldlust et al, 1995). Pregabalin and gabapentin are known as gabapentinoids. They’re structurally similar to a chemical called GABA. GABA is an important “inhibitory” neurotransmitter (chemical messenger) in the body. This means it decreases the activation of your nerve cells, and has a calming effect. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |