Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
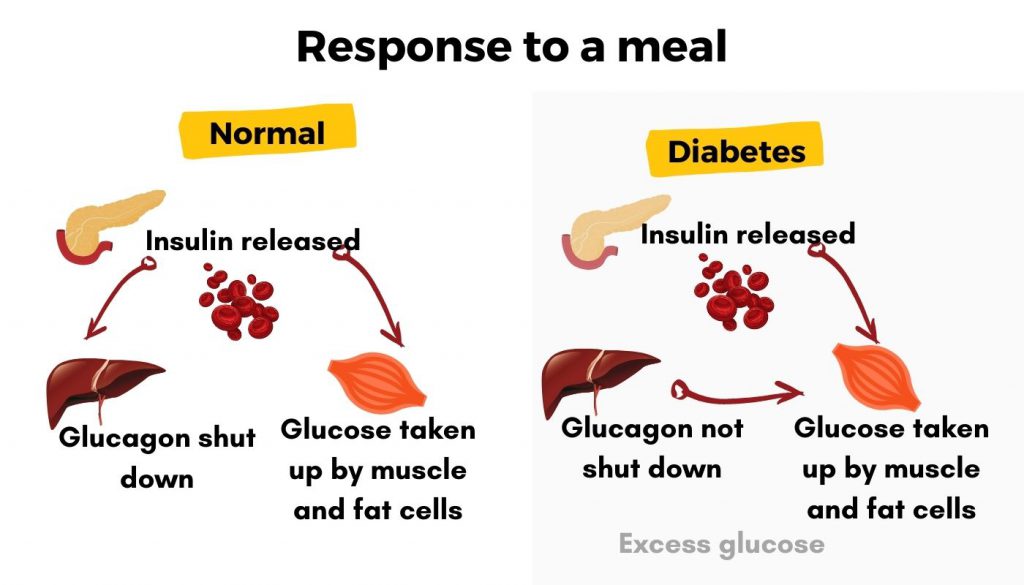
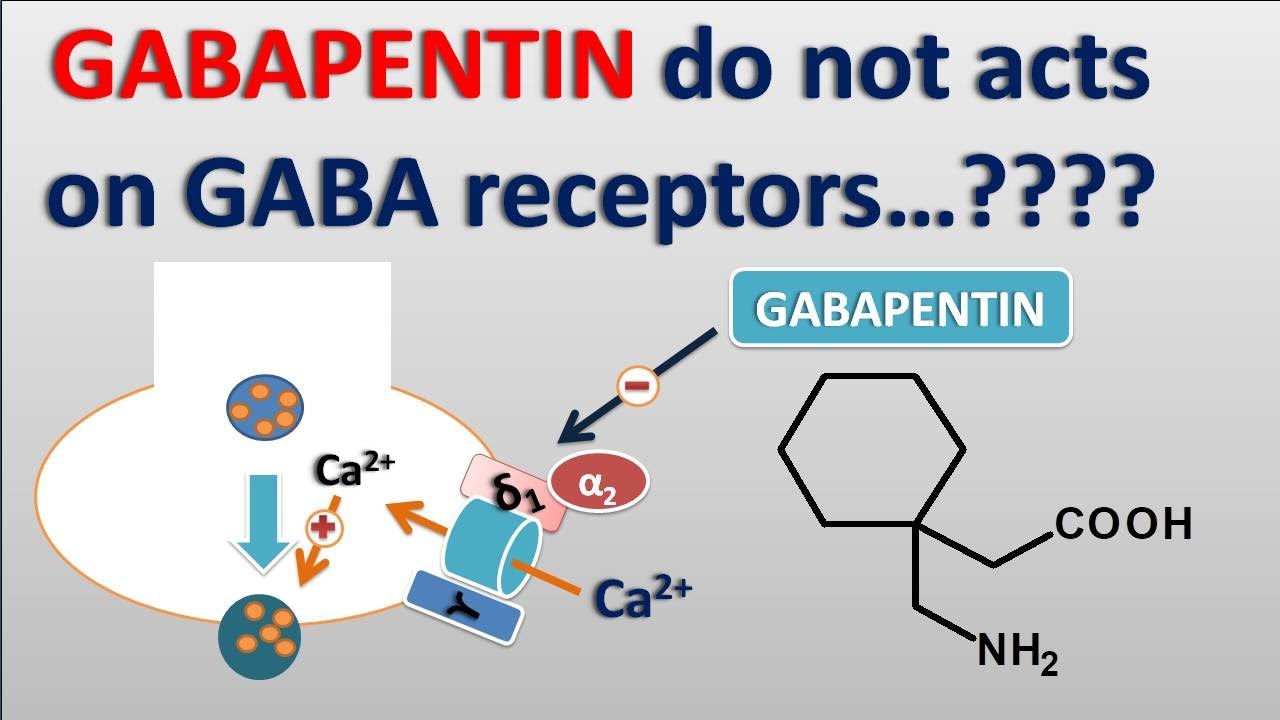
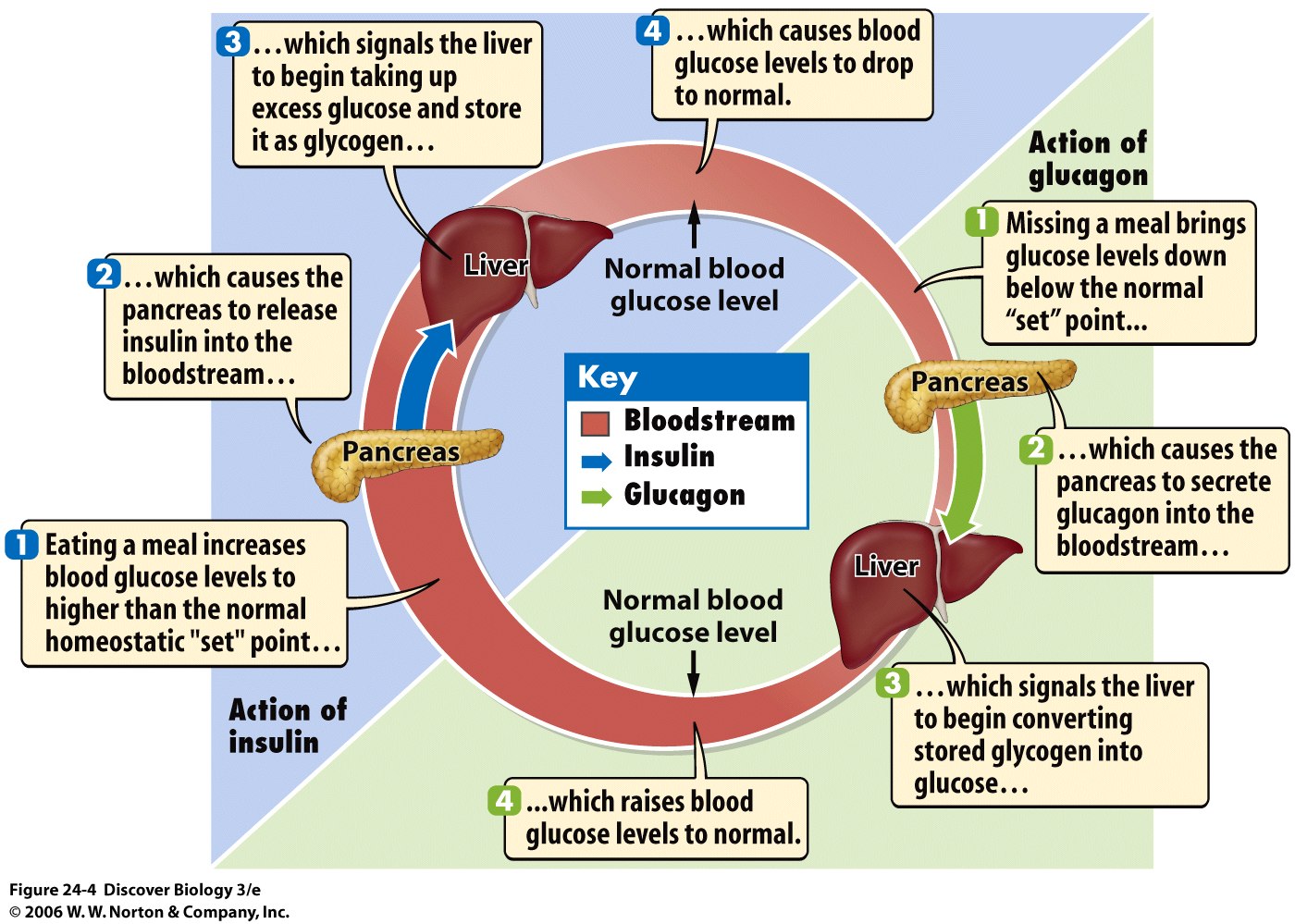
Summary: Blood glucose abnormal is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Metformin, and have Type 2 diabetes. Gabapentin and severe hypoglycaemia Introduction Gabapentin (Neurontin ®) is indicated for the treatment of partial epilepsy and peripheral neuropathic pain, such as diabetic neuropathy and post-herpetic neuralgia and was granted marketing authorization in the Netherlands in 1999. Gabapentin is structurally related to Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant (antiseizure) medication approved by the FDA to treat several conditions. Doctors sometimes prescribe gabapentin "off-label" to treat other conditions as well. A 2022 report stated that gabapentin was among the 10 most commonly prescribed medications in the U.S. What is gabapentin and what is it used for? Common adverse effects from gabapentin include somnolence, sedation, and dizziness. Hyperglycemia is listed as a possible adverse drug reaction in the labeling. Case reports describe hypoglycemia in patients with diabetes, peritoneal dialysis, and/or incomplete medication records. OTC medicines that can raise your blood sugar include: Cough syrup. Ask your doctor if you should take regular or sugar-free. How Do You Decide What to Take? Even though these medicines can Older adults who take gabapentin also are at higher risk of breathing problems. Because gabapentin can enhance the psychological effect of opioids, it has the potential to be abused and has contributed to drug overdose deaths. Drugs such as gabapentin have been linked in rare cases to an increased risk of suicidal thoughts or behaviors. Additionally, gabapentin has been shown to affect the release of certain neurotransmitters such as glutamate, which can have an indirect impact on blood sugar regulation. The precise mechanisms by which gabapentin affects blood glucose levels are still being studied, and further research is needed to fully understand this connection. Gabapentin has not been reported to raise blood sugar, however it would be best to consult a pharmacist/doc who would have prescribed the med. Take care, be well & safe! Votes: +0 As evident from the literature, Gabapentin exhibits its effect as an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent, the combined effect of which resulted in decreased blood glucose levels; however, it Gabapentin appears to have effects on several voltage-gated calcium channels. Hypoglycemia may be due to gabapentin binding to the alpha<sub>2</sub>delta subunit of the calcium channels in the pancreas. Future research should investigate gabapentin and the potential for hypoglycemia. CONCLUSIONS: Hypoglycemia is a rarely acknowledged adverse effect of gabapentin overdose and requires urgent intervention as it could be initially resistant to simple glucose replacement and may lead to serious consequences. In this case, blood glucose levels responded only to high concentration dextrose infusion (D10) with concomitant tube feeds. High blood sugar is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Lantus, and have Depression. Gabapentin appears to have effects on several voltage-gated calcium channels. Hypoglycemia may be due to gabapentin binding to the alpha 2 delta subunit of the calcium channels in the pancreas. Future research should investigate gabapentin and the potential for hypoglycemia. While there is evidence suggesting that gabapentin can potentially raise blood sugar levels in some individuals, particularly those with pre-existing diabetes, there are also multiple reports of gabapentin causing hypoglycemia. Began some medical journal research and found an obscure paper indicating that, in rare instances, gabapentin may cause lowering of blood sugar. Since then my oral blood sugar medication requirements have dropped significantly. Gabapentin has been associated with both hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia in different patient cases. The drug's interaction with GABA receptors and voltage-gated calcium channels may influence insulin secretion, leading to these varying effects on blood sugar levels. Hypothetically, gabapentin-induced GABA A receptor activation could stimulate insulin release resulting in hypoglycaemia. Alternatively, direct binding to the alpha 2 -delta 2 receptor of the voltage-gated calcium channels could also provide a pharmacological explanation. The short answer is: yes, it is possible, though not very common, for gabapentin to raise your blood sugar. Studies have shown that approximately 1.2% of patients treated with gabapentin may experience hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) compared to 0.4% with a placebo. The SmPC of gabapentin mentions blood glucose fluctuations in diabetic patients as a potential adverse drug reaction with unknown frequency [1]. The current observation describes the association between gabapentin and severe Despite adequate pain control achievement following gabapentin initiation, blood glucose values continued to rise. From a search of the medical literature, 2 articles speak to the effect of gabapentin on blood glucose levels.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |