Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_What-to-Know-About-Gaba_Illustrator_Jessica-Olah_Final-ea5963205783442fa62455edbc5851ef.jpg) | 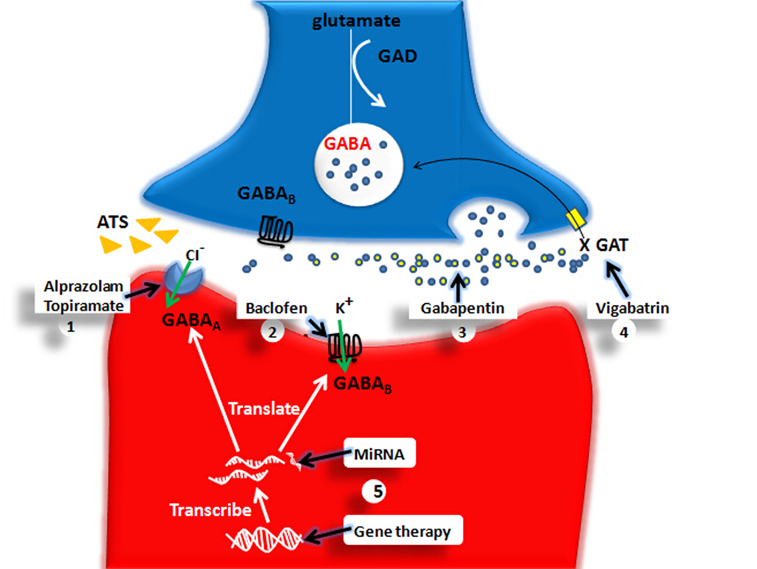 |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
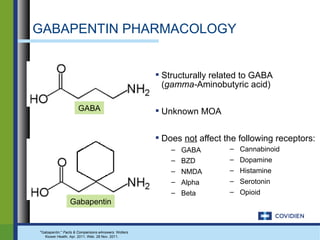
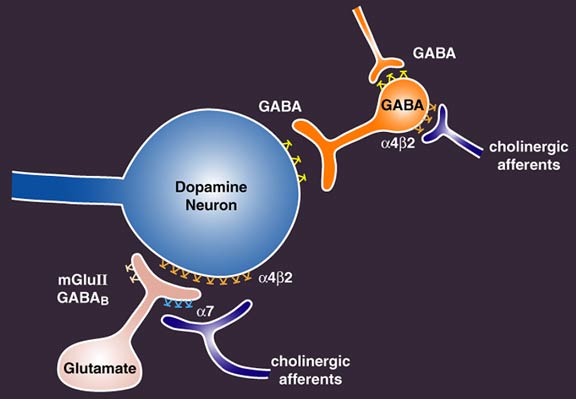
Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on glutamate are not known. Several studies have reported that gabapentin has a deleterious effect on cognition (Leach et al., 1997; Meador et al., 1999; Shem et al., 2018). A prospective observational cohort study has reported that gabapentin initiators with spinal cord injury had a cognitive decrease using neuropsychological tests. The short answer is that, yes, gabapentin can be detrimental to brain health for some individuals, depending on various factors such as dosage, duration of use, and pre-existing conditions. Let’s delve deeper into the specifics. How Gabapentin Affects the Brain Neurochemical Mechanisms In people with partial seizures, gabapentin works by decreasing abnormal activity in the brain. Experts believe gabapentin may cause brain cells to produce more of a chemical called GABA, which reduces abnormal electrical activity of brain cells. Why the drugs affect your mind. Both anticholinergics and benzodiazepines affect the activity of neurotransmitters—chemical messengers that work in the central nervous system—but the drugs work in slightly different ways. Anticholinergic drugs block the action of acetylcholine. In the brain, acetylcholine is involved in learning and memory. Some patients find that activities like yoga or meditation can help balance out some of the psychological effects of gabapentin. In some cases, considering alternative medications may be necessary. If the psychological side effects of gabapentin are proving too challenging, your doctor might suggest trying a different medication. Understanding Gabapentin-Induced Respiratory Depression How Gabapentin Affects Breathing. Gabapentin and its close relative, pregabalin, are known as gabapentinoids. While not opioids, these drugs can depress the central nervous system, which includes the area of the brain that controls breathing. Gabapentin effects on glutamate are not known. We conducted a gabapentin (900 mg) challenge in healthy human subjects to confirm and explore its effects on GABA and glutamate concentrations, respectively, and to test the ability of single voxel localized proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (¹H-MRS) to reliably measure GABA and glutamate in Because gabapentin easily crosses the placental barrier, it could potentially interfere with a fetus' rapidly developing brain just when global synapse formation is proceeding at breakneck speed. "It's a bit scary that a drug that can so powerfully block synapse formation is being used in pregnant women," Barres said. While some studies suggest that gabapentin may indirectly increase dopamine levels in certain brain regions, others have found no significant effect or even a potential decrease in dopamine activity. One study conducted on rats found that gabapentin administration led to an increase in dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens, a key area of Gabapentin has been successfully used to treat some of the effects of brain damage. However, prolonged use can cause serious side effects. This article will summarize the use of gabapentin for brain damage and discuss which symptoms it can help relieve. gabapentin’s effects on GABA and glutamate synthetic and metabolizing enzymes reveals a complex pattern of activity and provides an incomplete explanation for its anticonvulsant How does gabapentin affect serotonin? Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic medication, also known as an anticonvulsant. It works by stabilizing electrical activity in the brain. Gabapentin is thought to affect neurotransmitters, including serotonin, in a similar way to other anti-epileptic medications. Explore gabapentin's effects on mental function, memory, and cognition. Learn about managing side effects and balancing therapeutic benefits with potential risks. A report from ISMP QuarterWatch (March 27, 2019) warns about the inappropriate use of GABA drugs like gabapentin and pregabalin. Mental impairment, confusion and memory loss are recognized side effects. Some people use the term fuzzy thinking to describe the brain impact. Gabapentin use has been associated with memory loss and cognitive decline. Studies suggest that the risk of dementia may be higher in patients treated with gabapentin. It is important for patients and healthcare providers to be aware of the potential cognitive side effects of gabapentin. Avoid taking gabapentin with other medications and substances that slow down the brain. Examples include opioids, benzodiazepines, and alcohol. These combinations can lead to dangerously slowed breathing. GoodRx Health. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is FDA approved to treat certain types of seizures. While the evidence suggests that gabapentin alone does not cause memory loss, it can lead to brain fog or minor confusion. However, combining gabapentin with other drugs like baclofen can result in significant memory loss and impairment. Overall, the risk of being hospitalized with altered mental status after initiating gabapentin remains low, but may be reduced through the judicious use of gabapentin, use of the lowest dose to control pain, and vigilance for early signs of altered mental status. Research has shown that gabapentin exerts a modulating effect at neuronal receptor sites, inhib- iting the release of the neurotransmitters dopamine (5), serotonin and norepinephrine (6) and resulting in in- creased GABA concentrations in various locations throughout the brain (7).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_What-to-Know-About-Gaba_Illustrator_Jessica-Olah_Final-ea5963205783442fa62455edbc5851ef.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |