Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
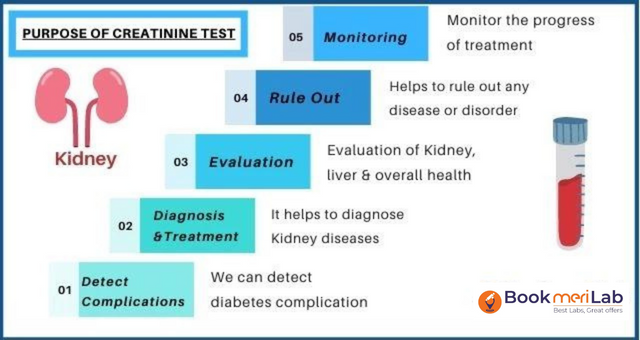
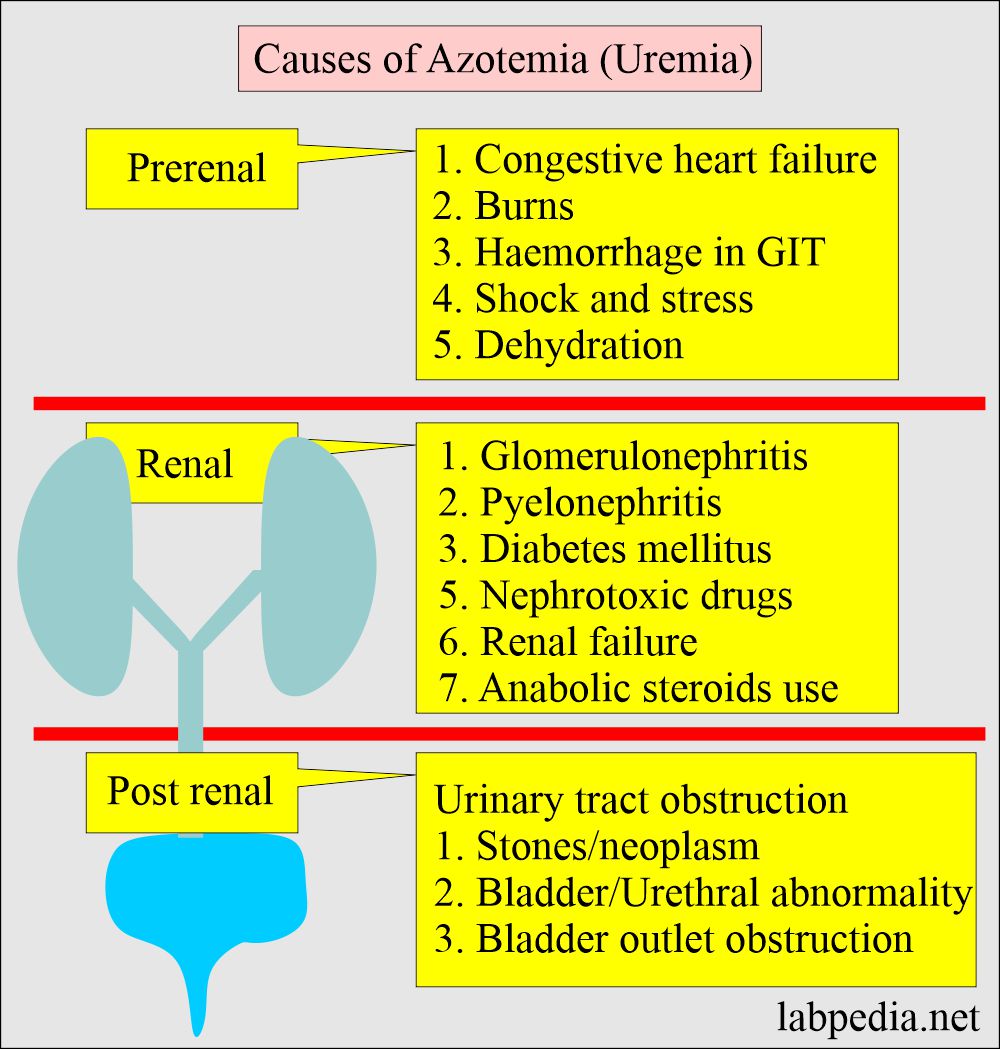
Doses may have to be adjusted to prevent adverse effects, toxicity and increased damage to your kidneys. Steven Coca, professor of medicine and a nephrologist at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, says you should know your estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), the primary measurement of kidney function, and your Blood creatinine increased is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Enbrel, and have Rheumatoid arthritis. Of the 729 patients in this study, a significantly higher serum gabapentin level in those with estimated glomerular filtration rate reduction indicates an inappropriate dosing for their kidney clearance, a problem at the level of gabapentin prescription. Gabapentin is used “off-label” for several conditions. Examples include anxiety, pain, and nerve pain from diabetes (diabetic nephropathy). It can also help treat alcohol use disorder (AUD). As with all medications, gabapentin has possible side effects you should know about. But do these side effects include harm to your liver and kidneys? A high creatinine level in a blood test can be a sign of decreased kidney function or kidney disease. But there are other reasons this level can be high. Some medications can increase the creatinine level without actually hurting the kidneys. Renal dose adjustments for gabapentin and pregabalin are ubiquitously evident in the medical literature. All manufacturers for these branded and generic dosage forms list dosing recommendations relative to creatinine clearance (CrCl) for both medications (Table 1). 1,2 However, the basis of these recommendations has not been well articulated. Of 74,084 gabapentinoid users, 37,383 (50.5%) and 36,701 (49.5%) were dispensed gabapentin and pregabalin, respectively. The outpatient serum creatinine level to estimate baseline eGFR was measured a median of 81 (IQR, 35-161) days before cohort entry. Laboratory tests showed haematocrit 33.4%, serum creatinine 5.1 mg/dl, sodium 134 mEq/l, potassium 3.7 mEq/l and glucose 154 mg/dl. The clinical impression was dizziness and she was observed in the ED. Four hours later, altered consciousness with lethargy was noted. The Glasgow Coma Scale was E2V3M5. There was no focal neurological deficiency. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. This will help prevent any negative effects from the medication, including further kidney damage. You can determine your level of kidney function with a blood test for serum creatinine to calculate an eGFR measurement. An eGFR estimates how well your kidneys are filtering wastes from the blood. Reported increased blood creatinine phosphokinase levels and muscle damage caused by inflammation. Antiepileptic drugs increase risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior in patients taking these drugs for any indication; monitor for emergence or worsening depression, suicidal thoughts or behavior, and/or any unusual changes in mood or behavior. Creatinine renal clearance decreased is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, also take Morphine, and have Post herpetic neuralgia. Gabapentin (GBP) is a drug which is frequently used in diabetic neuropathy. Common adverse effects of GBP include drowsiness, dizziness, ataxia, somnolence, and fatigue. Rhabdomyolysis is an extremely rare side effect of GBP. In this report we describe a case of GBP-induced rhabdomyolysis in a 63-ye The appropriate dosing based on the patient’s actual creatinine clearance is imperative to prevent severe adverse side effects and drug-related toxicity. We report a case of myoclonic activity developed in a patient with chronic kidney disease (CKD) shortly after a gabapentin dose increase. In addition to its effects on troponin-based lab assays and hormone tests, biotin may also cause results of falsely high levels of IgE and falsely low levels of insulin, autoantibodies, vitamin B12, vitamin D, folate, prostate-specific antigen, carcinoembryonic antigen, thyroglobulin, ferritin, DHEA-S, IgM, and hepatitis A, B, and C antibodies. Some of its most common side effects include the following: ataxia, nystagmus, drowsiness, headaches, diplopia, fatigue and myoclonic twitches. 1 All of these effects appear quite often in patients with chronic kidney disease, especially if they are undergoing dialysis and their doses are not adjusted to their glomerular filtration rates. 2 We Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. Majority drugs, including Gabapentin, are eliminated by the kidneys and will accumulate to a toxic level in renally compromised patients as in this case. Per Lexicomp, Gabapentin’s recommended dose in patients with renal impairment is as follows: CrCl >15 to 29 mL/minute: 200 to 700 mg once daily. CrCl 15 mL/minute: 100 to 300 mg once daily.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |