Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
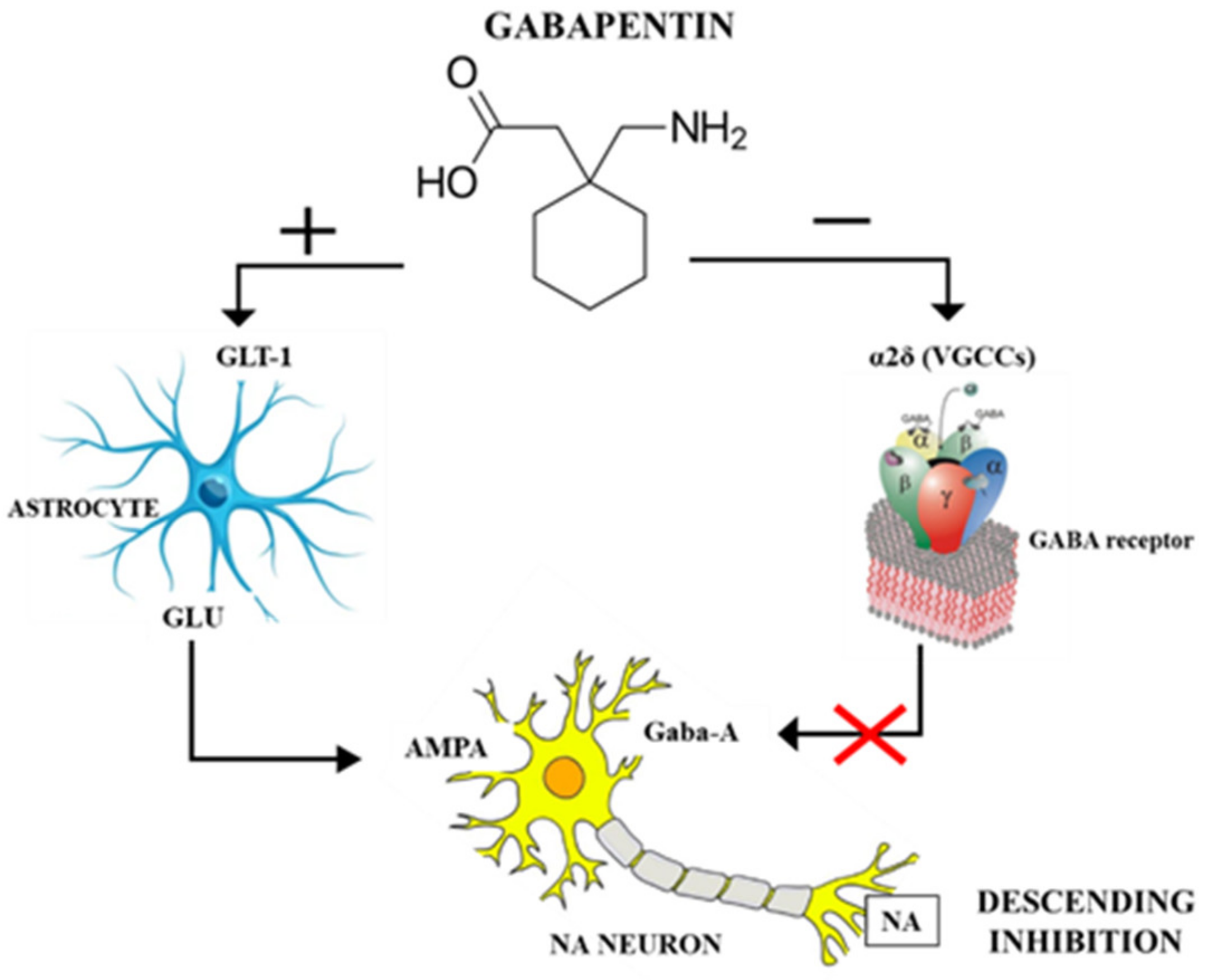
How Does Gabapentin Affect Sleep? Will gabapentin help you sleep? You may wonder. According to research, there are excellent treatment effects of gabapentin for primary insomnia. The treatment is possible in various ways. One, gabapentin has great anti-anxiety and calming effects, making it very helpful in treating sleep disorders and insomnia. The impact of Gabapentin and REM Sleep: Effects, Benefits, and Potential Risks is an area of ongoing investigation, as changes in REM sleep can affect various aspects of cognitive function and emotional processing. When it comes to the potential impact of gabapentin on sleep apnea symptoms, the evidence is mixed. Gabapentin is considered highly effective for the treatment of insomnia for a few reasons. First and foremost, it improves sleep quality by reducing spontaneous arousal in the brain. It also increases total sleep time thanks to fewer awakenings and its ability to help individuals go to sleep faster. Some studies have found that gabapentin may increase slow-wave sleep, also known as deep sleep, which is crucial for physical restoration and cognitive function. Additionally, it may reduce sleep fragmentation, leading to fewer nighttime awakenings and improved sleep continuity. Preliminary evidence indicates that gabapentin can attenuate insomnia, bolster sleep quality, and increase total sleep duration. Moreover, gabapentin has been shown to increase slow-wave sleep (SWS), promote sleep maintenance, and decrease unwanted awakenings throughout the night. Chronic neuropathic pain (NP) is debilitating and impacts sleep health and quality of life. Treatment with gabapentinoids (GBs) has been shown to reduce pain, but its effects on sleep health have not been systematically evaluated. The objective of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to asse While gabapentin may help improve sleep for some people (especially if you have another health condition that worsens sleep), it’s unlikely to be the first medication your healthcare provider recommends. Can gabapentin help you sleep? Yes, it can. As reported in a small study that was published in the March-April 2010 edition of the journal Clinical Neuropharmacology, “Gabapentin enhances slow-wave sleep in patients with primary insomnia. It also improves sleep quality by elevating sleep efficiency and decreasing spontaneous arousal.” Research suggests that gabapentin may increase slow-wave sleep, also known as deep sleep, which is crucial for physical recovery and memory consolidation. This effect could be particularly beneficial for individuals who struggle to achieve restorative sleep due to pain or anxiety. Some research suggests that gabapentin might alter the distribution of sleep stages throughout the night, potentially affecting the duration and quality of REM sleep. Research findings on gabapentin’s effects on REM sleep have yielded mixed results, highlighting the complexity of sleep pharmacology. Purpose: The older antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) have a variety of effects on sleep, including marked reduction in rapid-eye-movement (REM) sleep, slow-wave sleep (SWS), and sleep latency, and an increase in light sleep. The effects of the newer AEDs on sleep are unknown. Our purpose was to study the effect of gabapentin (GBP) on sleep. The main adverse effects reported with gabapentinoids are sleepiness, dizziness, headache, nausea, and vomiting. Due to the structural similarity between gabapentin and baclofen (a centrally acting GABA-B agonist), gabapentin was reported to produce “baclofen-like” effects [1] (Figure 1A). How does sleepwalking caused by gabapentin affect sleep quality and overall well-being? Sleepwalking, also known as somnambulism, is a sleep disorder characterized by complex motor behavior or actions during sleep. It most commonly occurs in children, but can also affect adults. This study is the first to systematically assess the clinical value of gabapentin for the treatment of sleep disorders. We found that regardless the type of sleep outcomes, gabapentin displayed stable treatment efficacy for sleep disturbance in patients with medical illness. Take gabapentin one to two hours before bedtime. This timing allows for proper absorption, improving sleep quality. Studies show 250 mg or 400 mg doses taken 30 minutes to two hours before bed can extend sleep duration effectively. Gabapentin works by affecting neurotransmitters in the brain, which helps to calm neural activity. Does Gabapentin make you sleepy? What does the research say? Drowsiness is one of the most commonly reported Gabapentin side effects, which is why it is sometimes prescribed as a sleep aid. Research has explored its effects on sleep in people with primary insomnia and insomnia linked to other health conditions. Gabapentin for primary insomnia Although drugs with sedative properties may increase the risk of airway collapse during sleep, their acute effects on the apnea-hypopnea index in older adults are under-reported. We investigated the acute effects of gabapentin (GABA) on sleep breathing in older men without sleep apnea. A double-blin Most studies show that gabapentin improves slow wave sleep (“deep sleep”) and total sleep time. Two small studies showed that gabapentin may help people with primary insomnia and occasional sleep disturbance improve total sleep time and wakefulness in the morning. The main adverse effects reported with gabapentinoids are sleepiness, dizziness, headache, nausea, and vomiting. Due to the structural similarity between gabapentin and baclofen (a centrally acting GABA-B agonist), gabapentin was reported to produce “baclofen-like” effects [1] (Figure 1A).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |