Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
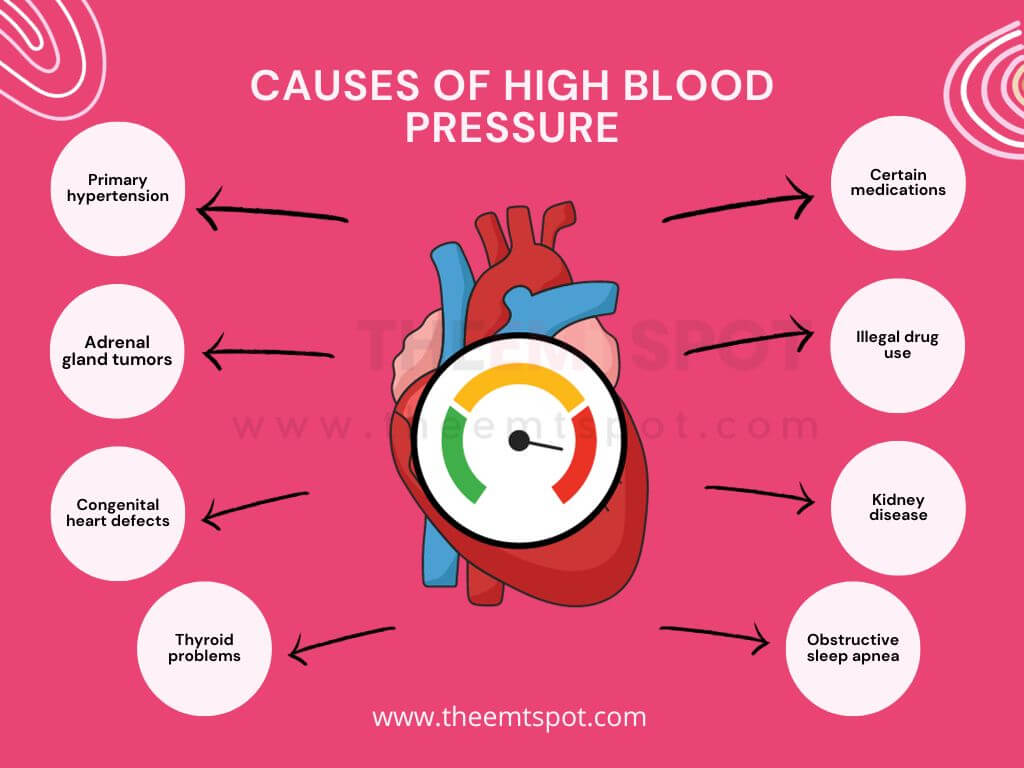
Can gabapentin cause high blood pressure? Yes, abruptly stopping gabapentin can lead to rebound hypertension , a withdrawal symptom. Additionally, while not a direct cause, the cardiovascular risks associated with long-term use can indirectly affect blood pressure. Some side effects of gabapentin may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine. Also, your health care professional may be able to tell you about ways to prevent or reduce some of these side effects. Gabapentin is fairly safe when you use it correctly. It does come with some possible side effects, though. People who misuse this drug are also at risk of additional side effects. Caffeine can cause a short-term spike in blood pressure in people who don't use it all the time. Caffeine helps to keep blood vessels open. This allows blood to easily pass through blood vessels. The relationship between gabapentin and blood pressure is complex, as the drug may exert both hypertensive and hypotensive effects depending on the patient’s clinical context and individual response. In some cases, gabapentin has been reported to cause a decrease in blood pressure, particularly in patients with autonomic dysfunction or those We have explained how gabapentin can cause high blood pressure. However, not every individual taking gabapentin would experience high blood pressure or the same side effects. Other factors can increase one’s risk of high blood pressure besides gabapentin. Now I live my life in bed. But although my BP has been really high every month when I go (he also had me monitor it daily for a month--bad!), he didn't take me off the Gabapentin. So I'm sure you're fine. Gabapentin really helps with my neurological problems, although I can only take it at bedtime. Common side effects of gabapentin include: flulike symptoms such as fever or body aches. Rare but serious side effects of gabapentin include: changes in memory, ability to concentrate, or personality. Gabapentin may cause breathing problems in people who use opioid pain medicines and those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). NSAIDs commonly cause water retention, which can lead to swelling in the legs and ankles. This tends to be more likely in older adults and people with kidney problems. Typically, the swelling will go away once you stop taking the medication. But NSAIDs can also make heart failure worse. And worsening heart failure can cause leg and ankle But sometimes, medications can cause high blood pressure. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), some antidepressants, and some birth control pills can all raise your blood pressure. Steroids, decongestants, and stimulant medications can also cause high blood pressure. Oral and intravenous gabapentin can markedly attenuate blood pressure (BP) in hypertensive rats. The nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS) is the primary integrative center for cardiovascular control and other autonomic functions in the central nervous system. Here are common types of drugs that can make your high blood pressure worse. Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) NSAIDs include both prescription and over-the-counter medication. Atenolol, metoprolol, and propranolol are beta blockers that treat heart problems like irregular heart rates and high blood pressure. But they can increase blood glucose in people with diabetes and cause new Type 2 diabetes in people who didn’t have it before. This seems to happen because the beta blockers reduce how much insulin the pancreas While some studies suggest gabapentin may have therapeutic benefits for individuals with hypertension, it does not typically cause high blood pressure. It is important to monitor blood pressure when taking gabapentin, especially in patients with a history of hypertension, but gabapentin is not a primary driver of elevated blood pressure. Summary: High blood pressure is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Tylenol, and have Rheumatoid arthritis. Not everyone who takes gabapentin will experience changes in blood pressure. However, certain factors may increase your risk, including: * Age: Older adults may be more susceptible to blood pressure changes. * Existing blood pressure issues: If you already have high or low blood pressure, gabapentin may exacerbate these issues. Gabapentin is associated with a risk of dependence and withdrawal. Abrupt discontinuation of the drug may result in symptoms similar to those of benzodiazepine or alcohol withdrawal and may include: Hypertension (high blood pressure). Sweating. Confusion. Incoherent speech. Impaired ability to pay attention. Nausea. Pain. Insomnia. Restlessness Yes, it can cause High Blood Pressure (hypertension) Cardiovascular side effects including hypertension have been reported to occur in more than one percent of patients taking gabapentin. Read more at: I suggest you contact your Dr. asap. Research suggests that gabapentin can lower blood pressure by reducing the body’s production of certain hormones that can increase blood pressure. It may also help to relax blood vessels, making it easier for blood to flow through them. More rarely, gabapentin can cause fluid buildup (edema), weight gain, and vision problems. It can also cause diarrhea. More serious (but rare) side effects include suicidal thoughts or behavior, and mood changes in children.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |