Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
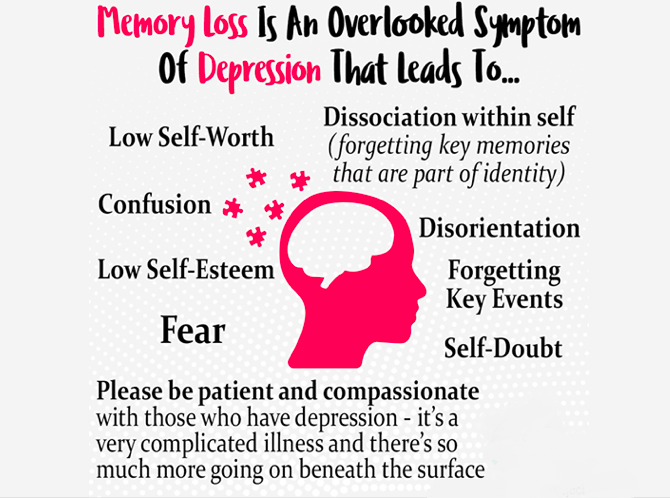 |  |
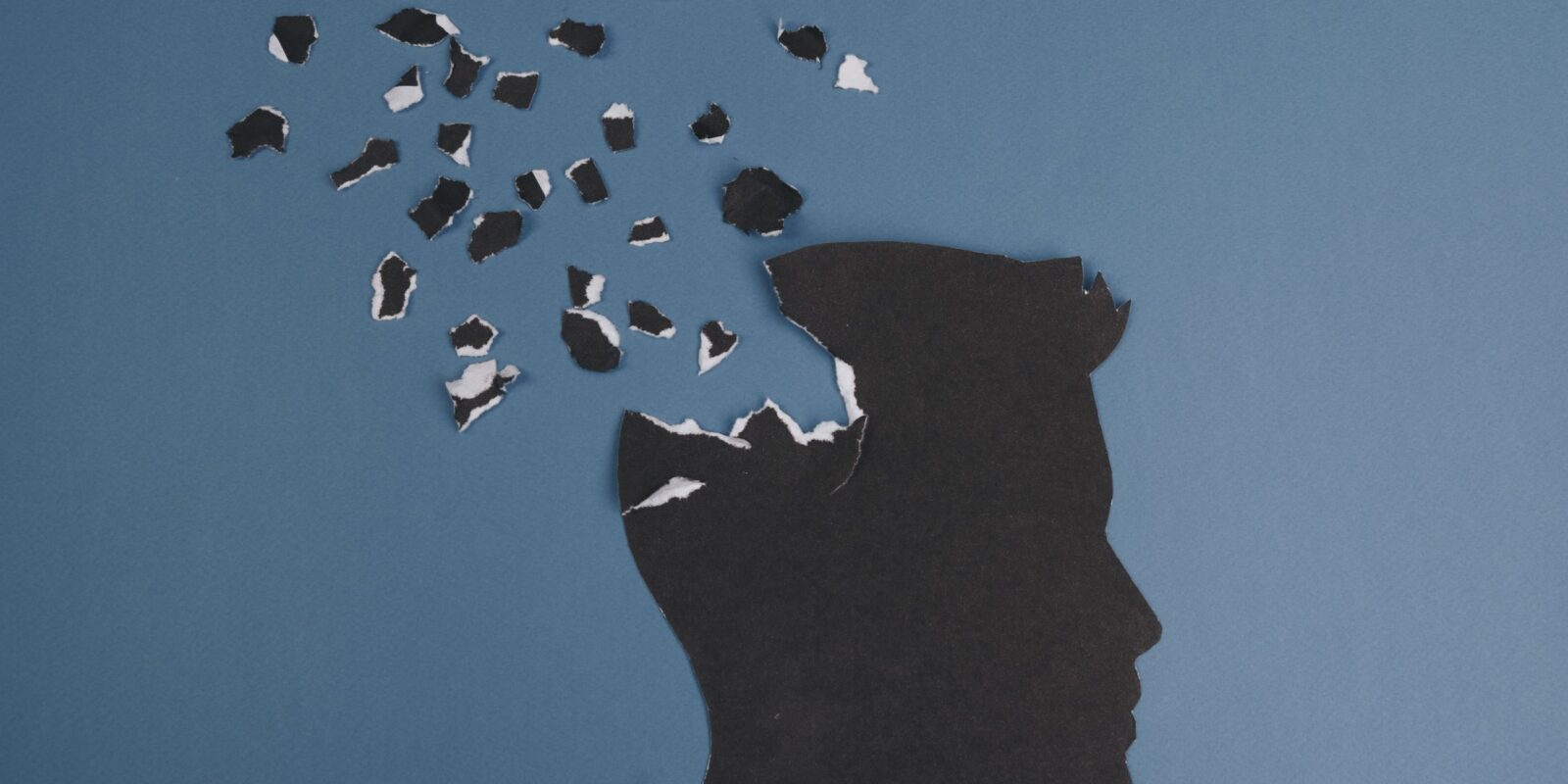
Gabapentin new users with normal cognition at the visit of gabapentin initiation (i.e., index visit) were included. New-users were matched on year of first enrollment and time of gabapentin initiation since enrollment to randomly select nonusers with replacement. Moreover, the stratification analysis revealed that the risk of dementia associated with gabapentin or pregabalin exposure was significant in all age subgroups; however, it was higher in younger patients (age <50) than in the older patients (hazard ratio, 3.16; 95% CI, 2.23–4.47). Such drugs are on the list because they share troubling side effects—confusion, clouded thinking, and memory lapses—that can lead to falls, fractures, and auto accidents. What the studies found It's important to note that neither of these studies was a randomized controlled clinical trial, so neither proved that either type of drug causes Neurontin (gabapentin) is associated with memory loss in a dose dependent fashion, meaning the higher doses you take, the more chance there is of having some sort of memory loss, or cognitive impairment. While the evidence suggests that gabapentin alone does not cause memory loss, it can lead to brain fog or minor confusion. However, combining gabapentin with other drugs like baclofen can result in significant memory loss and impairment. The results from this study showed that gabapentin therapy was associated with decline in memory, executive function, and attention after 1 week of gabapentin treatment (Shem et al., 2018). Some studies report that gabapentin can cause erectile dysfunction in men. However, older studies also report cases of sexual dysfunction and loss of libido in women. Additionally, the side Overall, the risk of being hospitalized with altered mental status after initiating gabapentin remains low, but may be reduced through the judicious use of gabapentin, use of the lowest dose to control pain, and vigilance for early signs of altered mental status. Gabapentin, widely used for nerve pain and seizures, can cause memory issues in some users, such as forgetfulness or difficulty concentrating. Compared to pregabalin, which shares a similar mechanism, gabapentin’s cognitive effects are often considered milder, though this varies by individual. Gabapentin’s impact on aging bodies differs significantly from its effects on younger patients. From physical symptoms like dizziness and edema to cognitive changes and emotional shifts, the medication’s side effects can profoundly influence an older adult’s quality of life. Explore the details of gabapentin use in older adults. For healthcare professionals. Applies to gabapentin: compounding powder, oral capsule, oral solution, oral tablet, oral tablet extended release. General adverse events. The most common adverse reactions associated with the use of this drug were dizziness, somnolence, and peripheral edema. Dizziness is the No. 1 side effect of gabapentin. In studies, almost 30% of people taking gabapentin for postherpetic neuralgia, and over 15% of people taking it for seizures, experienced dizziness. Gabapentin is also used to manage a condition called postherpetic neuralgia, which is pain that occurs after shingles. Gabapentin works in the brain to prevent seizures and relieve pain for certain conditions in the nervous system. It is not used for routine pain caused by minor injuries or arthritis. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant. Rare but serious side effects of gabapentin include: changes in memory, ability to concentrate, or personality. Gabapentin may cause breathing problems in people who use opioid pain medicines and those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Older adults who take gabapentin also are at higher risk of breathing problems. Regular cognitive assessments and dosage adjustments may be necessary for individuals taking gabapentin to manage memory problems. Further research is needed to better understand the effects of gabapentin on memory and cognitive function. Prevalence of Dementia and Memory Loss To truly grasp the cognitive effects of gabapentin, we need to don our neuroscience hats and dive into the brain’s inner workings. Gabapentin doesn’t play by the rules of most medications. Instead of directly latching onto neurotransmitters, it sneaks in through a back door, binding to calcium channels in our neurons. Cognitive impairment and confusion: Some older adults may experience difficulties with memory, concentration, or thinking clearly while on gabapentin. This can be especially troubling for those already dealing with age-related cognitive changes. Seniors with a baseline erectile dysfunction problem can worsen their symptoms. Gabapentin could make you gain weight because it can increase appetite and hunger. But how does gabapentin affect appetite? A recent study reveals that it might be related to a slight change in the gut-brain axis. Here, we’ll delve into seven types of drugs that may cause memory loss and explore alternative treatment options. Short- vs. long-term memory There are two key types of memory: short- and long-term, says Jessica Merrey, the lead clinical pharmacy specialist at Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |