Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
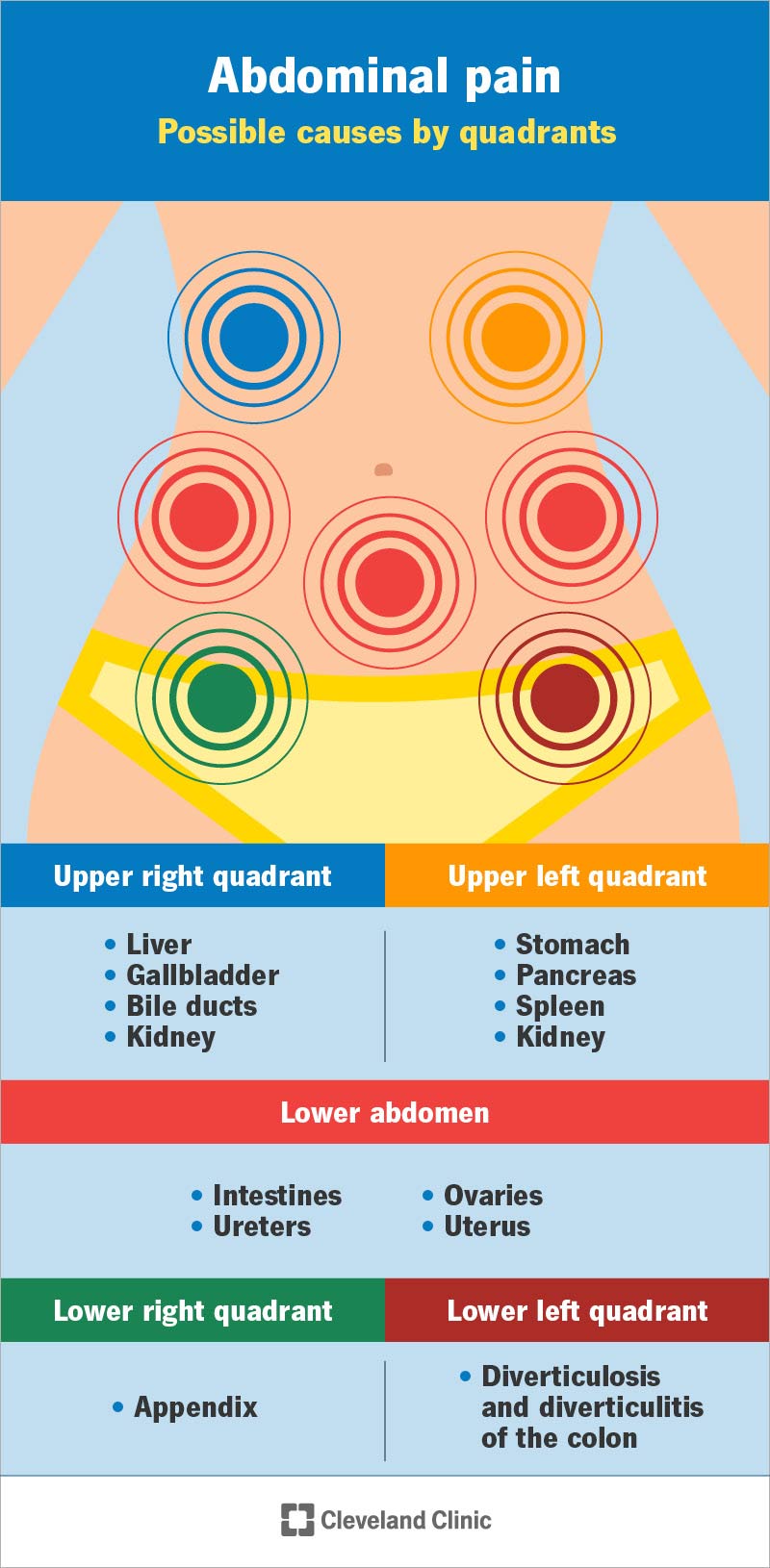
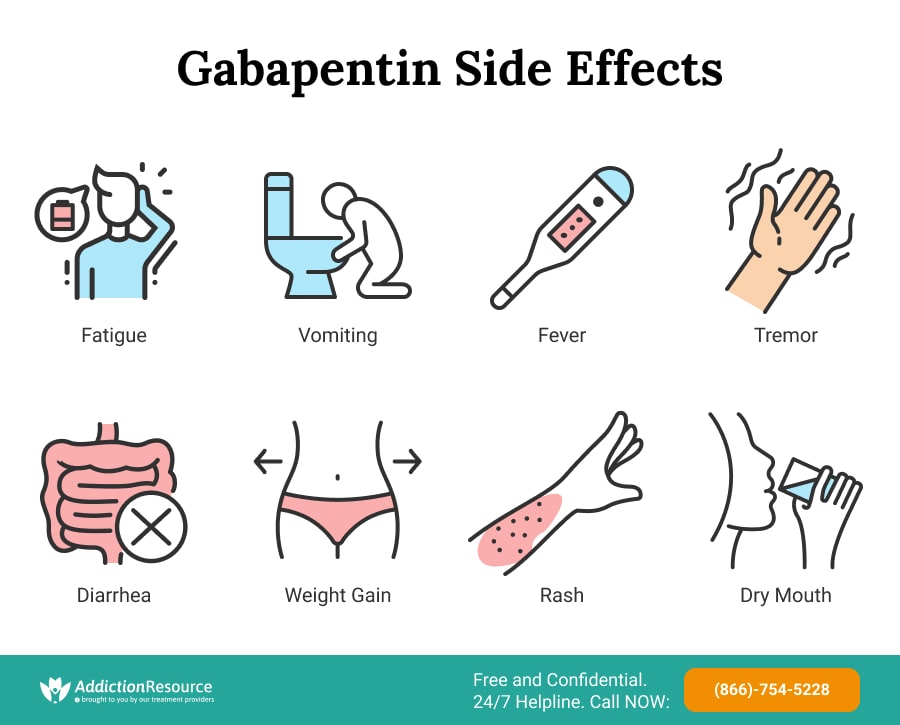
I started recently on Gabapentin to treat abdominal distension and pain from IBS-C. The doctor started me on a very low dose (50 mg), and now that I've been on it for 2 weeks, I'm increasing to 100 mg. Gabapentin is fairly safe when you use it correctly. It does come with some possible side effects, though. People who misuse this drug are also at risk of additional side effects. Gabapentin is Both doses of gabapentin showed antiinflammatory effect and reduced gastric mucus secretion similar to diclofenac. Key words: gabapentin, carrageenan-induced paw edema, gastric mucus. Articles from International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology are provided here courtesy of Oxford University Press. Like all medicines, gabapentin can cause side effects, although not everyone gets them. These common side effects of gabapentin may happen in more than 1 in 100 people. They're usually mild and go away by themselves. There are things you can do to help cope with them: As your body gets used to gabapentin, these side effects should wear off. Gabapentin can cause some rare but serious side effects. While these are uncommon, people should be aware of them and seek medical attention if needed. I also didn’t say I didn’t have this reaction. I have had explosive diarrhea on gabapentin, but not stomach pain. Gabapentin on its own can cause different stomach issues but it’s on the rare side and hard to trouble shoot when we don’t know the amount they are taking, and how long they’ve been taking it How does gabapentin affect the bowels? Gabapentin can cause a variety of GI side effects including diarrhea, constipation, nausea, and abdominal pain. Studies have found that up to 15-25% of people taking gabapentin experience diarrhea while around 5-10% develop constipation. However, other symptoms, such as pain (e.g. abdominal pain, hunger pangs, and nausea), reflux (e.g., heartburn and the return of the stomach acid), and dyspepsia (e.g. abdominal sounds, abdominal bloating, burping, and excessive gas in the stomach), were reduced in both the groups and resulted in the patients' improvement; the severity Gabapentin can cause digestive problems such as nausea, vomiting, and stomach pain in some individuals. These side effects are more likely to occur at higher doses or when starting the medication. Fortunately, there are steps you can take to manage these stomach issues and continue benefiting from gabapentin’s therapeutic effects. Gabapentin may cause stomach side effects like nausea or vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, heartburn, gas, or stomach pain, especially when you are first starting treatment. Taking it with food may help to lessen these side effects. Take your medicine exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Some side effects of gabapentin may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine. Also, your health care professional may be able to tell you about ways to prevent or reduce some of these side effects. More rarely, gabapentin can cause fluid buildup (edema), weight gain, and vision problems. It can also cause diarrhea. More serious (but rare) side effects include suicidal thoughts or behavior, and mood changes in children. Unlike other pain meds like opiods, which work by blocking feelings of pain, gabapentin changes the way the body senses pain. The drug is often prescribed off-label, too, says Patel. (That What Causes Abdominal Pain and Constipation? Constipation causes an accumulation of stool in the intestines. It can also increase gas production, cause intestinal distention (swelling), and put pressure on the surrounding nerves. The pressure, swelling, and gas can stimulate pain receptors, leading to abdominal pain. Upper abdominal pain (−0.68) Lower abdominal pain (−0.63) Postprandial fullness (−0.46) Heartburn (−0.40) Nausea/vomiting (−0.33) There was no significant improvement in bloating. The changes in abdominal pain suggest that much of gabapentin's benefit occurred because of improvement in patients' perceptions of pain. Common side effects of gabapentin include: flulike symptoms such as fever or body aches. Rare but serious side effects of gabapentin include: changes in memory, ability to concentrate, or personality. Gabapentin may cause breathing problems in people who use opioid pain medicines and those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Overall, gabapentin is a medication that is designed to regulate brain activity and alleviate seizures and nerve pain. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting or adjusting the dosage of gabapentin, as it can have potential side effects and interactions with other medications. Sickness (nausea and vomiting) with persistent stomach pain (these could be symptoms of an inflamed pancreas). A skin rash, or any swelling of your mouth or face (these could be symptoms of an allergic reaction). Gabapentin may increase the permeability of the gut lining. This can allow bacteria and toxins to pass through the gut lining and into the bloodstream. This can lead to inflammation and abdominal pain. Allergic reaction: In rare cases, gabapentin can cause an allergic reaction. This can lead to abdominal pain, bloating, and other symptoms. While it is not a pain medication or an opioid, it still has some risk of abuse. Once you get off of gabapentin, it can result in withdrawal. Here are some of the common physical symptoms of gabapentin withdrawal. Physical Symptoms of Gabapentin Withdrawal: Gabapentin withdrawal can manifest neurological, abdominal, heart, and muscle-related
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |