Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
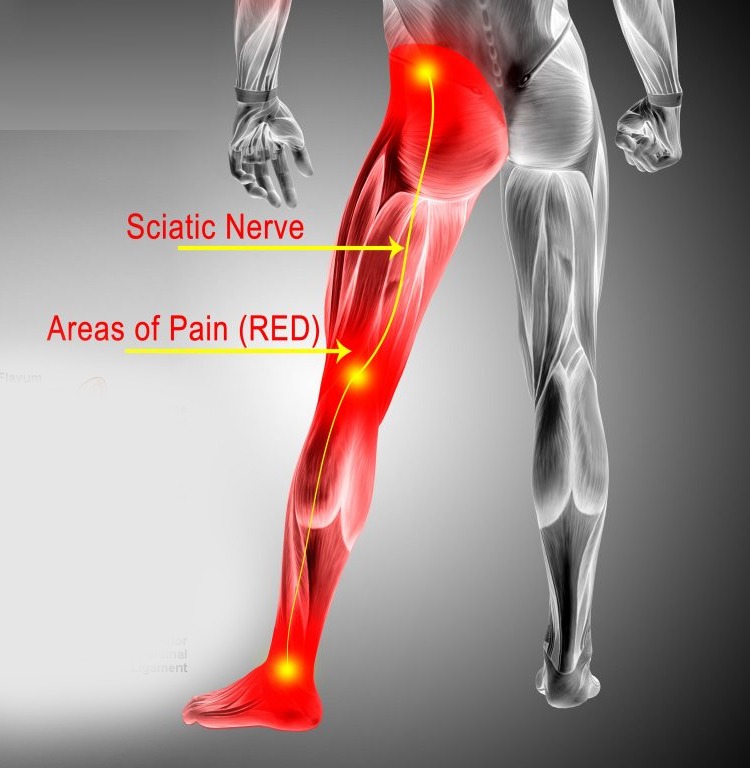
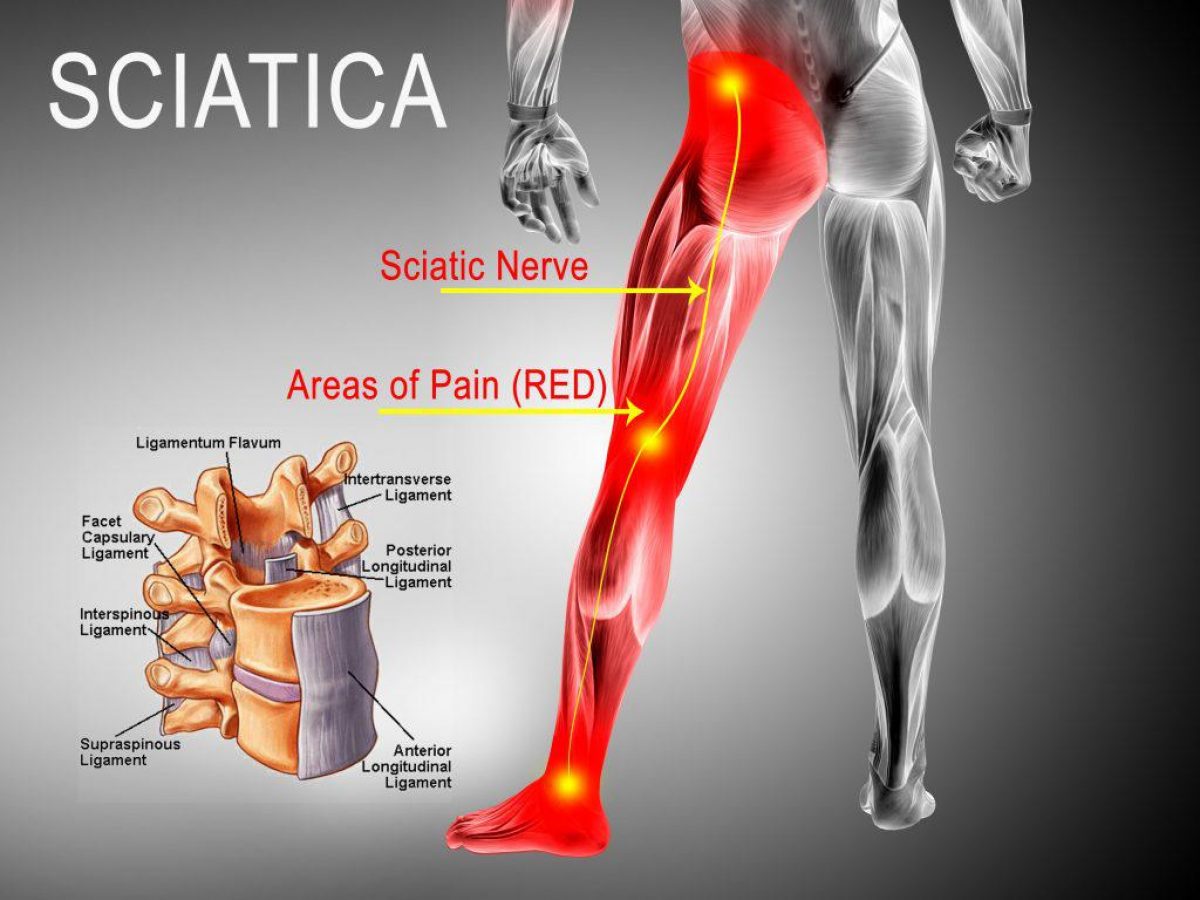
I took gabapentin 300 mg three times a day and it definitely helps if pain is unbearable or have numbness. I still suffer from sciatica put it has gotten better and now I don’t take gabapentin unless I have a bad flare up because my doctor does not recommend it long term since i have sciatica now for 7 months. Healthcare providers often recommend gabapentin as a treatment for nerve pain. In recent years, they have prescribed it to treat back pain. Studies show that it can make a difference in nerve pain due to shingles or diabetes. But the evidence shows that it doesn’t work that well to ease back pain, particularly chronic low back pain. While gabapentin is not a cure for sciatica, it can provide a 1-2 point average reduction in pain scores, allowing better mobility and function. Its favorable side effect profile, lack of drug interactions, and reduced risks of dependency make gabapentin a potentially useful part of a comprehensive sciatica treatment plan. Sciatica is prevalent in 2-5% of the general population and can reach up to 43% in working population cohorts. Factors like poor health, physical stress, obesity, smoking, and occupational workload contribute to its likelihood. The overall outlook for sciatica is positive, with a favorable clinical progression. Analgesic and adjuvant pain drugs are often prescribed for patients with sciatica. 8 Patients with a clinical diagnosis of sciatica are about five times more likely to take drugs than those with low back pain only. 4 Drugs commonly prescribed for the management of sciatica include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), skeletal muscle Both gabapentin (GBP, Neurontin) and pregabalin (PGB, Lyrica) are used to treat chronic sciatica (CS). Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is an important pain-related neurotransmitter, although neither GBP nor PGB affect the GABA receptor. By modulating the release of these neurotransmitters, Gabapentin can help reduce nerve-related pain, such as that experienced in sciatica. Common Uses of Gabapentin Aside from its approved uses for epilepsy and nerve pain, Gabapentin is also sometimes prescribed off-label for conditions such as restless leg syndrome, fibromyalgia, and certain Keywords: Gabapentin, Pregabalin, Sciatica, Pain, Clinical trial, Protocol. Background. Sciatica or sciatic neuralgia, a common form of lumbosacral radiculopathy, is characterised by low back pain which radiates to the leg and which may be accompanied by sensory loss, motor weakness and/or reflex abnormalities. They say it is from crushed discs and surgery would be the best. When my sciatica would act up I could hardly sit, lay down, walk etc. I laid over a large exercise ball chair, I used ice and the pain was awful no matter what I did, but for sure at. 73 I really don't want to go thru surgery. To our knowledge, however, these two case reports are the first to describe sciatica successfully controlled with gabapentin. Because gabapentin has the potential to prevent central sensitization, consideration should be given to prescribing this therapy early in the course of sciatica. Chronic sciatica (CS), like most neuropathic pain states, is often resistant to simple treatment regimens. 1,2 Chronic sciatica is sciatica lasting longer than 3 months. 3 Neuropathic pain states are typically managed by super-adding anticonvulsant drugs onto simple drug regimens. The drugs most commonly used are gabapentin (GBP) or pregabalin Because gabapentin has the potential to prevent central sensitization, consideration should be given to prescribing this therapy early in the course of sciatica. Further research using randomized, placebo-controlled trials are needed to validate the benefit of gabapentin in the treatment of sciatica. Nerve pain medication: Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) may help reduce neck and back nerve pain, especially sciatica. Begin with low doses to avoid daytime drowsiness and fall risk. Muscle relaxants. Tizanidine (Zanaflex) and baclofen (Lioresal) may reduce pain from muscle spasms. Currently, using gabapentin for sciatica is not recommended because its risk of side effects outweigh potential benefits. How does gabapentin work to relieve sciatic nerve pain? In general, gabapentin calms down neurons (nerve cells) to relieve nerve pain. Among the many questions that people with sciatica have is: does gabapentin help sciatic pain? Does gabapentin give immediate pain relief? And how long does it take to start working? In this article, you will learn more about this medication. You will find out about its side effects, how it works, and whether it is right for your sciatica. Gabapentin can help relieve sciatica, intense pain that runs along the sciatic nerve from the lower back through the hips and buttocks (12). Sciatica affects one side of the body and is usually caused by disk herniation or spinal stenosis (12). #### What you need to know Sciatica is commonly seen in primary care. Its prevalence in the general population varies between 3% and 14%, depending on the definition used.1 The prognosis of acute sciatica is generally favourable: data from a prospective study of 183 patients with a median disease duration of 16 days show that in approximately one third of patients, symptoms improve greatly (ie How does gabapentin work for sciatica? Gabapentin belongs to the anticonvulsant class of medications that treat pain due to convulsions or nerve damage, especially in the lower back and legs. It works for sciatic pain in several ways, from binding to calcium channels on nerve endings to calming the nerve signals that are hyperactive due to pain Gabapentin changes the way the brain and body exchange messages. It calms the nerves by blocking pain-causing neurotransmitters, making gabapentin an effective treatment for sciatica and
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |