Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/is-this-normal-how-long-will-it-last-80197_final-01-61e907a86b19467487b731d369f8c978.png) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
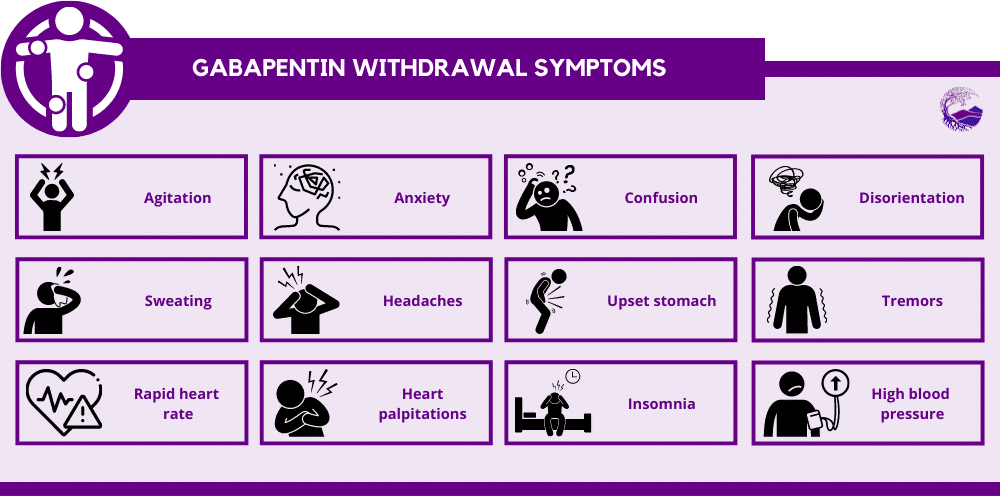
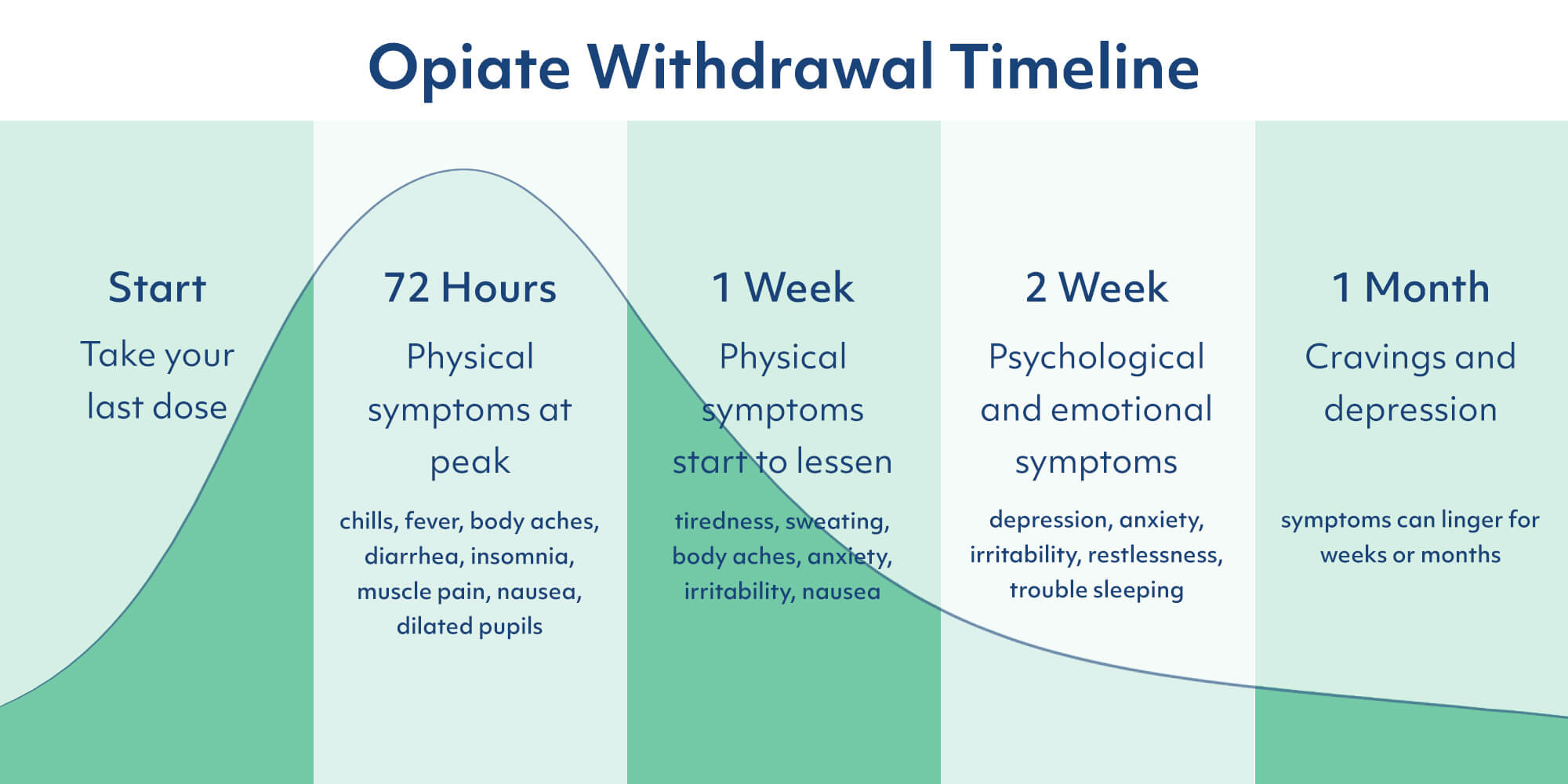
Gabapentin supplements can also help in the withdrawal phase, but the effect is lesser than the medicinal form of Gabapentin. What improvement does Gabapentin make? The usage of Gabapentin during the opiate withdrawal phase brings the following changes. In the words of key informant 7, gabapentin may help alleviate, “restless legs the headaches, the nerve pain, the achiness, all the stuff,” associated with withdrawal. Similarly, gabapentin was described by key informant 8 as helping clients to mentally cope with withdrawal symptoms. Several additional key informants reported analogous Benzodiazepine withdrawal can be a long and difficult process, but there are steps that physicians can take to help their patients survive the process. Tapering the drug slowly and switching to a long half-life benzodiazepine may be helpful, as may adjunctive medications and coping skills. Encouraging acceptance and finding a support system can also be key to surviving benzodiazepine withdrawal. Data from early clinical trials showed that gabapentin could reduce withdrawal symptoms and, when compared with placebo, was associated with reductions in opioid use. 1 However, more recent studies and research has demonstrated that gabapentin did not produce better results than a placebo when used for withdrawal symptoms. 1 gabapentin uses What the Evidence Says: Does Gabapentin Help with Opioid Withdrawal? Evidence on gabapentin’s effectiveness in opioid withdrawal is often conflicting. Let’s dig deeper. Evidence in Favor A clinical trial on 27 patients revealed that a 1600 mg/day dose of gabapentin (when used with methadone) reduces withdrawal symptoms. Researchers found a total daily dose of 600 mg to 1,800 mg of gabapentin reduced withdrawal symptoms. this is a promising new method to help patients undergoing benzodiazepine withdrawal to Some doctors use gabapentin and other medications to help treat alcohol withdrawal and alcohol use disorder. What Is Gabapentin? Gabapentin is a medication used for epilepsy seizures, restless leg Case reports have shown that gabapentin withdrawal often lasts for 5 to 10 days, but some people have taken as long as 18 weeks to completely taper off gabapentin while managing withdrawal symptoms. Symptoms may start within 12 hours to 7 days after stopping gabapentin and may be severe. One possible form of help in decreasing alcohol withdrawal symptoms is gabapentin, a medicine mostly used to control seizures and neuropathic pain. Here, we explore the function of gabapentin in relation to alcohol withdrawal: how it works, the many conditions it treats, and the important things to keep in mind when thinking about taking it Gabapentin Withdrawal Timeline. Understanding the timeline of Gabapentin withdrawal can help you anticipate and manage the challenges that come with it. Withdrawal from Gabapentin is typically divided into three phases: early withdrawal, acute withdrawal, and protracted withdrawal. Each phase has its own set of symptoms and duration, and Add-on gabapentin with a dose of 1600 mg/d is effective in reducing some of the withdrawal symptoms in patients addicted to opiate undergoing methadone-assisted detoxification. Gabapentin may be prescribed to ease withdrawal symptoms as a part of someone’s comprehensive, customized treatment plan. In addition to supporting a safe and comfortable withdrawal, detox also prepares patients for continued addiction treatment. Specifically, it is useful in treating withdrawal and maintaining abstinence in people struggling with alcohol, benzodiazepine, and opioid addiction. A research review from Pharmacology & Pharmacy indicates that multiple studies show gabapentin as a positive support to alcohol detox and withdrawal. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is a prescription anticonvulsant medication that is prescribed to treat neuropathic (nerve) pain and seizures.[1] Although gabapentin abuse is not as common as other forms of prescription drug abuse, studies have documented increasing reports of people misusing the medication with other drugs like alcohol, benzodiazepines, and opioids.[2] Since gabapentin withdrawal symptoms are similar to those seen in withdrawal from other substances, lorazepam was thought to be a potential treatment for gabapentin withdrawal symptoms. However, several case reports have shown benzodiazepines to be ineffective at reducing gabapentin withdrawal symptoms. Gabapentin can help manage certain withdrawal symptoms, such as pain and anxiety, allowing individuals to better tolerate the detoxification process. Notably, adjusting the use of gabapentin to suit individual needs and modifying the dosage accordingly is essential.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/is-this-normal-how-long-will-it-last-80197_final-01-61e907a86b19467487b731d369f8c978.png) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |