Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
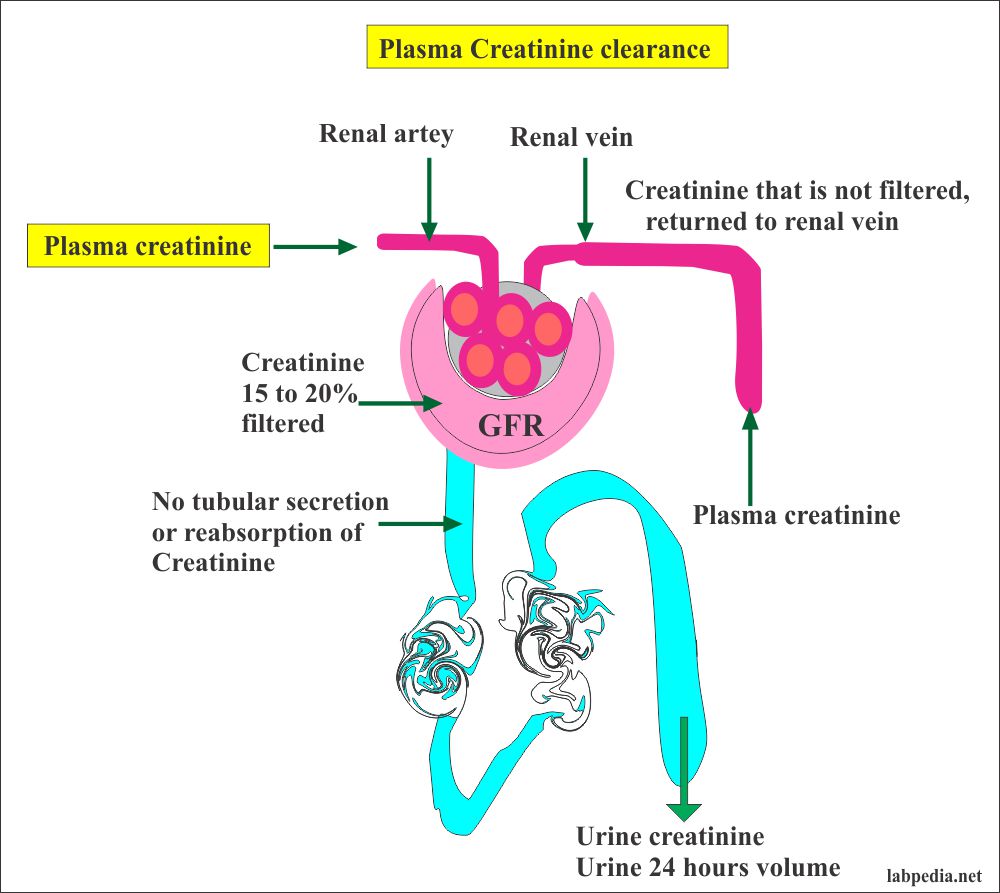 |  |
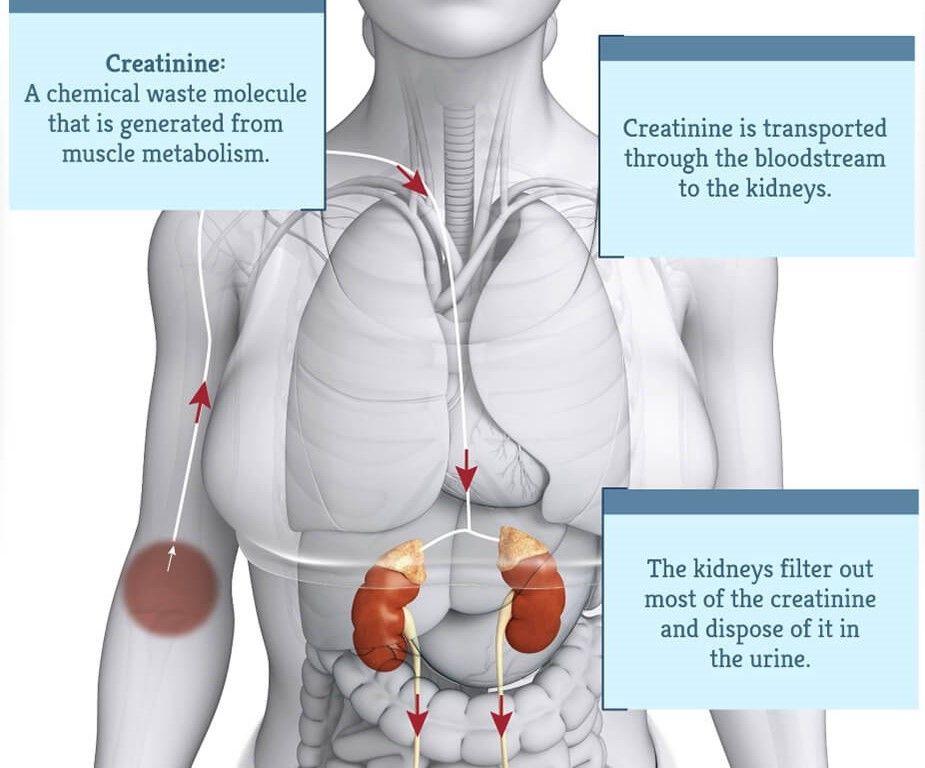
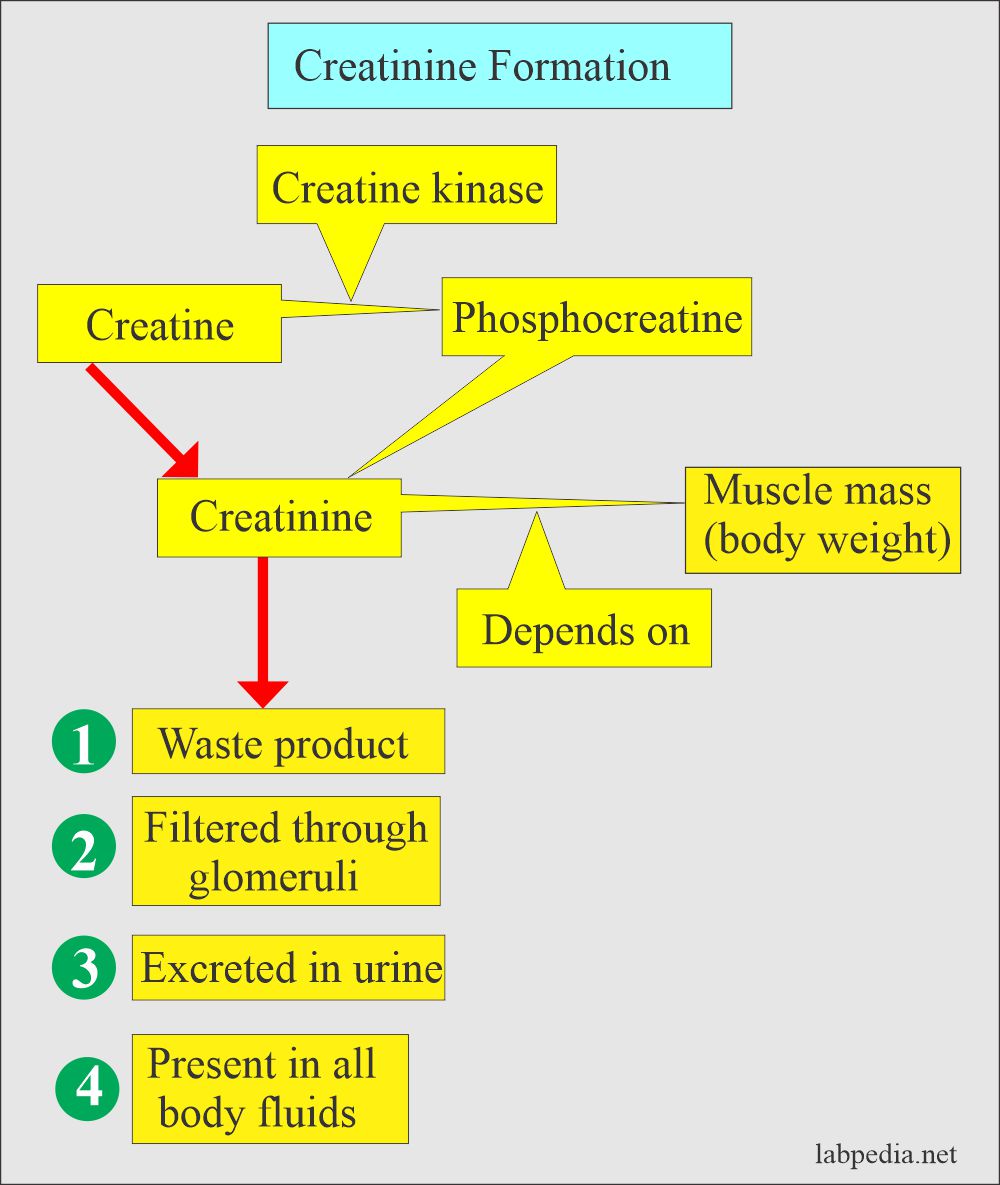
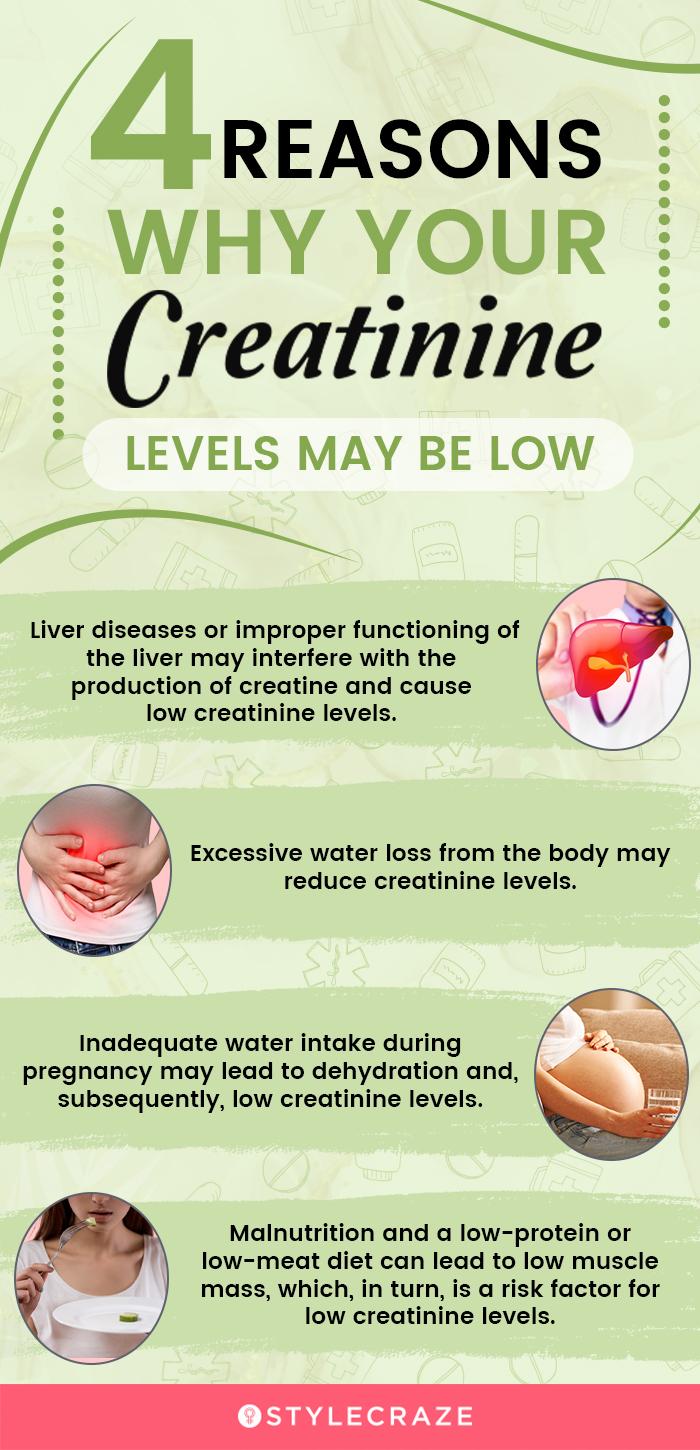
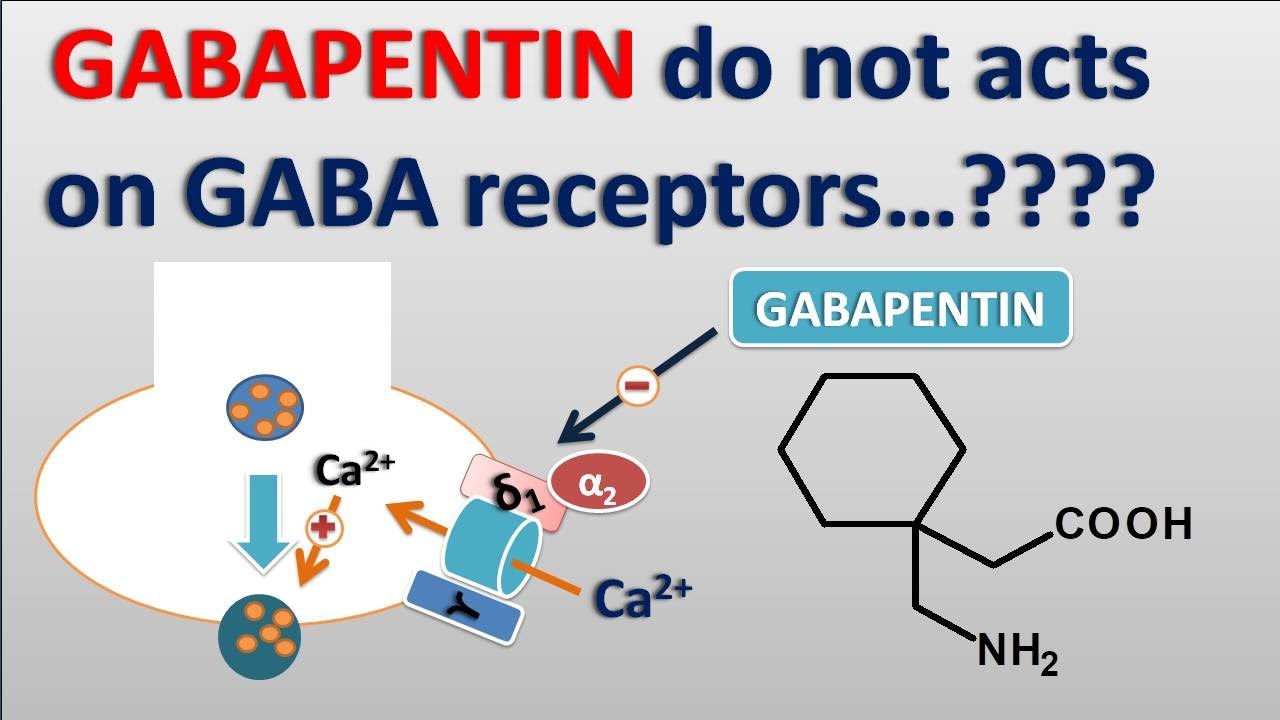
Dose-normalized gabapentin serum concentrations at 3h and 8h were significantly correlated with serum Creatinine and SDMA, measures of kidney function used in IRIS staging. Compliance scores for cats with CKD were significantly increased at 3h versus 8h. Cats with higher serum gabapentin concentrations were more compliant at the 3h mark. .table_layout tbody td{ font-size:0.95em;} Usual Gabapentin Dosing (Adults) Usual initial gabapentin dose: 300mg q8h. Usual maintenance dose: 300-600mg q8h. Maximum dosage/day: 3600 mg Gabapentin Renal Dosing [>60 ml/min]: Give usual dosage : Dosage range: 400-1400mg/day (divided doses - Usually bid) : Dosage range: 200-700mg/day. : 100-300 mg/day. Use lower end of this range for CRCL Gabapentin (GBP) is a drug which is frequently used in diabetic neuropathy. Common adverse effects of GBP include drowsiness, dizziness, ataxia, somnolence, and fatigue. Rhabdomyolysis is an extremely rare side effect of GBP. In this report we describe a case of GBP-induced rhabdomyolysis in a 63-ye Gabapentin is eliminated in urine unmetabolized at a rate proportional to creatinine clearance. 24 In patients with renal impairment, with unaltered gastrointestinal absorption, gabapentin half-life can be prolonged up to 132 hours (without dialysis), 30 placing patients with chronic kidney disease at an increased risk for toxicity. In the presence of cimetidine at 300 mg four times a day (N = 12), the mean apparent oral clearance of gabapentin fell by 14% and creatinine clearance fell by 10%. Thus, cimetidine appeared to alter the renal excretion of both gabapentin and creatinine, an endogenous marker of renal function. This may be due to one of three factors: decreased creatinine secretion, interference with the serum assay, or enhanced creatinine production. Thus, in patients taking one of the drugs described below, an elevation of creatinine without a concomitant elevation of BUN does not likely reflect a true decrease in GFR. DECREASED SECRETION Reported increased blood creatinine phosphokinase levels and muscle damage caused by inflammation. Antiepileptic drugs increase risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior in patients taking these drugs for any indication; monitor for emergence or worsening depression, suicidal thoughts or behavior, and/or any unusual changes in mood or behavior. Check with your doctor immediately if any of the following side effects occur while taking gabapentin: More common in children. Some side effects of gabapentin may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine. Abstract. A bipolar I manic patient was treated successfully by adding gabapentin to perazine and clonazepam. Also initially tolerated well, an increase of creatinine after several weeks of GP (2000 mg) was observed which was reversible after discontinuation of GP. It is suggested that the possibility of renal dysfunction should be kept in mind with the usage of gabapentin. Blood creatinine increased is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Enbrel, and have Rheumatoid arthritis. You can determine your level of kidney function with a blood test for serum creatinine to calculate an eGFR measurement. An eGFR estimates how well your kidneys are filtering wastes from the blood. The National Kidney Foundation encourages you to learn more about the health of your kidneys in order to protect these vital organs when taking Renal dose adjustments for gabapentin and pregabalin are ubiquitously evident in the medical literature. All manufacturers for these branded and generic dosage forms list dosing recommendations relative to creatinine clearance (CrCl) for both medications (Table 1). 1,2 However, the basis of these recommendations has not been well articulated. This case report outlines a significant type of morbidity due to continued use of gabapentin during an episode of acute renal failure. Setting. University teaching hospital. Discussion. Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. The diagnosis, in this case, was supported by the direct association of the recent dose increase of gabapentin in a patient with stage 3b CKD with the recent worsening of his renal function and the improvement of his symptoms after discontinuation of the offending agent, keeping in mind that our patient was not able to take gabapentin for over A high creatinine level in a blood test can be a sign of decreased kidney function or kidney disease. But there are other reasons this level can be high. Some medications can increase the creatinine level without actually hurting the kidneys. In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, gabapentin may be initiated on Day 1 as a single 300 mg dose, on Day 2 as 600 mg/day (300 mg two times a day), and on Day 3 as 900 mg/day (300 mg three times a day). The dose can subsequently be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a dose of 1800 mg/day (600 mg three times a day). Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. In most cases, gabapentin doesn’t hurt the liver or kidneys, though proper dosing is important to prevent side effects. Learn how gabapentin affects the liver and kidneys here. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is an antiseizure medication. It’s also used for nerve pain from shingles. Other long-acting forms called Gralise and Horizant are also available. For adults, your gabapentin dosage varies depending on your medical conditions and which form you’re taking. The maximum dosage is 3,600 mg per day.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |