Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
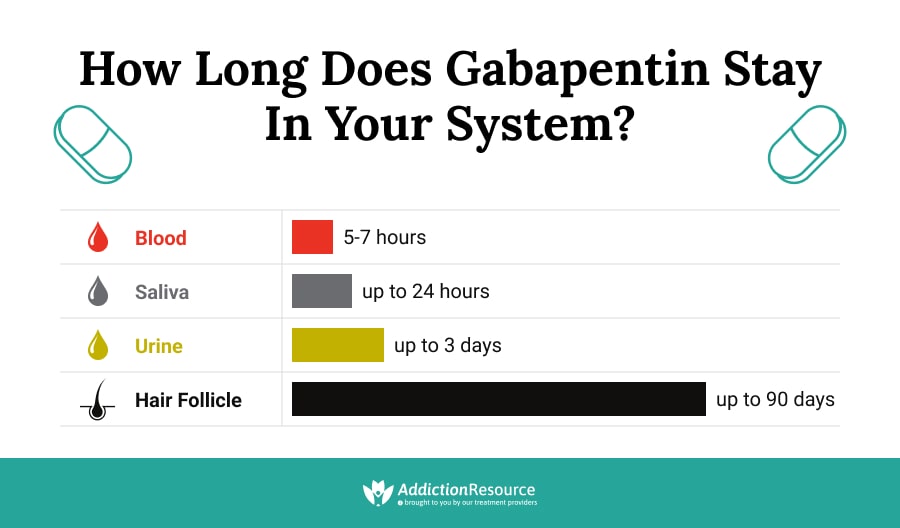 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
Look no further than gabapentin! Known for its pain-killing abilities, gabapentin is a medication that can effectively alleviate various types of pain. How does gabapentin work? Gabapentin works by affecting the chemicals and nerves in the body that are involved in pain signals. By blocking these signals, gabapentin can provide significant pain In animal models of analgesia, gabapentin prevents allodynia and hyperalgesia. Michael Verret et. al.; Perioperative Use of Gabapentinoids for the Management of Postoperative Acute Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Anesthesiology 2020; 133:265–279 doi: Gabapentin alleviates pain by modulating nerve signals, providing relief for various chronic pain conditions. Gabapentin, originally developed to treat epilepsy, has gained recognition for its effectiveness in managing various types of pain. This medication works by altering the way the brain and nervous system respond to pain signals. Gabapentin for dogs can be prescribed to help with seizures, pain, and anxiety in dogs, as it may help treat chronic pain and neuropathic pain. According to Dr. Tamara Grubb, a board-certified veterinary anesthesiologist, gabapentin decreases the release of excitatory neurotransmitters , which serves to decrease pain and seizures. Gabapentin for dogs is commonly prescribed for pain, anxiety, or seizures. but there are some known side effects to be aware of. Gabapentin for dogs is commonly prescribed for pain, anxiety Veterinarians prescribe gabapentin for dogs primarily to manage chronic pain, especially neuropathic pain, and to control seizures. It’s often used in conjunction with other medications to enhance pain relief. 1. Gabapentin For Pain Relief in Dogs Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant with pain-relieving effects that may be used to treat certain seizure disorders or relieve nerve pain. Common side effects include dizziness or drowsiness and it may cause a withdrawal syndrome on discontinuation so should not be stopped abruptly. Common side effects of Gabapentin may include dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue, and coordination problems. It is important to discuss any potential side effects with your healthcare provider. 3. How long does it take for Gabapentin to start working? The onset of action of Gabapentin can vary depending on the individual and the condition being Gabapentin: Alternatives. Otheralternarive drugs that kill pain include anti-inflammatories, and certain antidepressants that are effective for neuropathic pain. These include duloxetine (duloxetine), milnacipran (Savella), and venlafaxine (Effexor). All three of these drugs are used in combination with or without opioids. Gabapentin: Addictive? How does gabapentin work to kill pain? Gabapentin is a human drug that is used to treat some seizures and nerve related pain. It is in the treatment of this neuropathic pain in dogs as well as cats that we'll be looking at today. The CDC’s controversial 2016 opioid guideline, for example, calls gabapentin and pregabalin “first-line drugs” for neuropathic pain. In a new draft report being funded by the CDC, researchers say gabapentin showed only “small improvements” in pain for people with diabetic peripheral neuropathy and fibromyalgia. The study by the Agency Gabapentin may cause breathing problems in people who use opioid pain medicines and those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Older adults who take gabapentin also are at higher risk of breathing problems. Gabapentin is approved to treat seizures and postherpetic neuralgia, a type of nerve pain from shingles. It is thought to work by changing how nerves send messages to your brain. It is also used off-label to treat other neuropathic pain conditions. Antacids containing aluminum with magnesium can decrease gabapentin absorption. When having to give antacids allow for 2 hours before or after administration of gabapentin. Gabapentin is fairly short acting, but effects may last longer in rats with renal impairment. Adverse Reactions. CNS: Mild sedation (sleepiness), ataxia (poor coordination) Gabapentin works by affecting chemicals and nerves in the body that are involved in the cause of seizures and in some types of nerve pain. Gabapentin is not a federally-controlled drug substance and does not contain an opioid (narcotic) medication. Gabapentin reduces neuropathic pain by < 1 point on a 0-10 point scale and benefits about 15% of carefully selected patients (NNT=6-8). A similar proportion of people suffer harm (NNH=8). A test of benefit/harm can be made after 1-2 days at a low dose (100-900 mg/day). Benefit is unlikely to increase with higher doses or longer treatment. Gabapentin is a medication that treats nerve pain by calming overactive nerves in your body. It may also prevent and control seizures in people with epilepsy. You can take this medication by mouth with a glass of water. Gabapentin can help relieve nerve pain in some people with postherpetic neuralgia (nerve pain after shingles) and peripheral diabetic neuropathy (nerve pain in the feet in people with diabetes). Can Taking Too Much Gabapentin Kill You? Taking too much gabapentin is rarely fatal on its own, but it can be deadly if the gabapentin is taken with other substances, like alcohol or opioids . For this reason, it’s important to only use gabapentin as prescribed and avoid taking it with other substances, especially illicit drugs.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |