Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
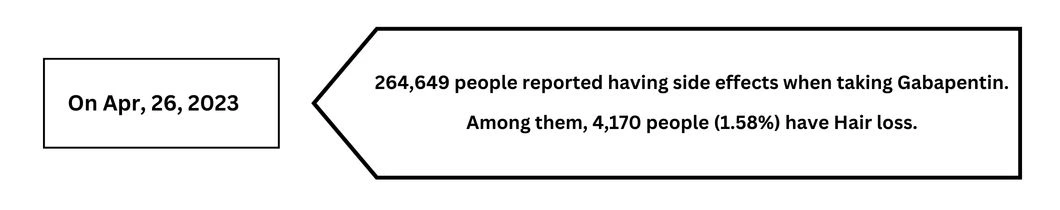
11. Can Gabapentin Cause Brain Fog? Yes, gabapentin can cause brain fog or mild confusion in some individuals. Though long-term studies do not show memory loss or impairment, it is a potential side effect to be aware of. 12. Can you take Gabapentin and Tylenol together? Yes, Tylenol (acetaminophen) and gabapentin can be taken together without Along with its needed effects, gabapentin may cause some unwanted effects. Although not all of these side effects may occur, if they do occur they may need medical attention. Check with your doctor immediately if any of the following side effects occur while taking gabapentin: According to Patel and Saxon, gabapentin is usually well-tolerated when taken as directed. Still, it's important to be aware of these gabapentin side effects. You always feel woozy and Not having enough fluids can cause tremors, dizziness, and anxiety. Drinking plenty of water each day can help avoid these problems. Excessive Caffeine Intake. Too much caffeine can also make you feel jittery. Caffeine speeds up your heart rate and makes you feel anxious. If caffeine makes you jittery, try drinking less or choosing decaf. Gabapentin has been successfully used to treat some of the effects of brain damage. However, prolonged use can cause serious side effects. This article will summarize the use of gabapentin for brain damage and discuss which symptoms it can help relieve. What Is Gabapentin Used For? Gabapentin is most commonly prescribed for nerve pain such [] Gabapentin commonly causes feelings of depression, hostility and anxiety. Gabapentin has been associated, rarely, with hallucinations and suicidal thoughts. Does gabapentin make you jittery? Gabapentin can make you jittery. It is known to cause trembling, shaking, and tremors, though this side effect is only thought to affect 10% of users. The drug affects the nervous system, which could be the reason for this side effect. The memory issues you are experiencing may be very well due to the extremely high dose of gabapentin you are taking. Fortunately, memory loss and other side effects associated with gabapentin are not considered permanent and should resolve upon discontinuation of therapy or with a dose decrease. Gabapentin is fairly safe when you use it correctly. It does come with some possible side effects, though. People who misuse this drug are also at risk of additional side effects. Most people are swallowing gabapentin for conditions that the FDA has never approved and for which there may be modest scientific support. We would not get overly concerned with this off-label prescribing if this drug were perfectly safe. But gabapentin side effects are not trivial, as you will read. Weight Gain: Gabapentin doesn’t make you gain weight, but it can make you feel hungrier, causing you to gain weight. Eating a balanced diet and healthy foods that help you feel full can help prevent weight gain. Memory Issues: Gabapentin is associated with memory decline and can cause confusion in some older patients. Both gabapentin and alcohol can cause central nervous system depression, leading to increased sedation and impairment. It’s important to be cautious about alcohol consumption while taking gabapentin, and individuals should follow their healthcare provider’s advice and recommendations. Can You Take Gabapentin While Pregnant? 1. Can gabapentin cause chest pain? 2. Is gabapentin a common cause of breathing problems? 3. Can gabapentin make you feel like you’re choking? 4. Does gabapentin affect lung function in the long term? 5. Is gabapentin harder on the lungs than opioids? 6. What other medications can worsen gabapentin’s effect on breathing? 7. Gabapentin is used to help control partial seizures (convulsions) in the treatment of epilepsy. This medicine cannot cure epilepsy and will only work to control seizures for as long as you continue to take it. Gabapentin is also used to manage a condition called postherpetic neuralgia, which is pain that occurs after shingles. Key Takeaways: Gabapentin and Sleepiness Drowsiness Duration: Gabapentin can cause drowsiness lasting 4-8 hours. Dosage Matters: Higher doses typically lead to more pronounced sedation effects. If you are discontinuing gabapentin, or even merely lowering your dose, it is important to discuss how to do so safely with your doctor. Tapering regimens are not 'one-size-fits-all', and your doctor can recommend a specific protocol for your particular medical situation. References. Elsevier ClinicalKey: Gabapentin (Accessed 2/06/19) Gabapentin may make you feel a little drowsy, dizzy, or clumsy when you first start taking it. You may feel like your thinking is slower. These are common side effects of gabapentin, but they usually get better as your body adjusts to the medication. What you have described is so very possible I have been on gabapentin for a long time, up to 3600mg daily I have been reading so much about this drug recently and decided to wean off it because of the long-term side effects, including causing a decline in cognitive effect as well as other concerning issues and am having a terrible time coming off it regardless of my doctor said it was not Taking gabapentin can make you sleepy. According to studies, about 20% of people taking gabapentin experience drowsiness or fatigue. It may be even more likely, affecting 20% to 30% of people, with Horizant. However, tiredness is less common with Gralise, occurring in about 5% of people taking it. What many people don’t realize is that taking gabapentin can result in various side effects. Here are some gabapentin side effects that could occur. 1. Abnormal eye movements. People taking gabapentin have reportedly experienced involuntary and continuous eye movements.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |