Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_What-to-Know-About-Gaba_Illustrator_Jessica-Olah_Final-ea5963205783442fa62455edbc5851ef.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
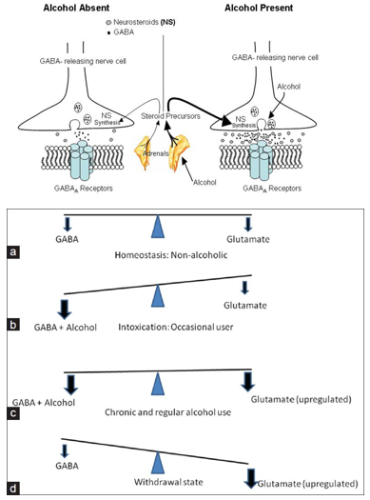
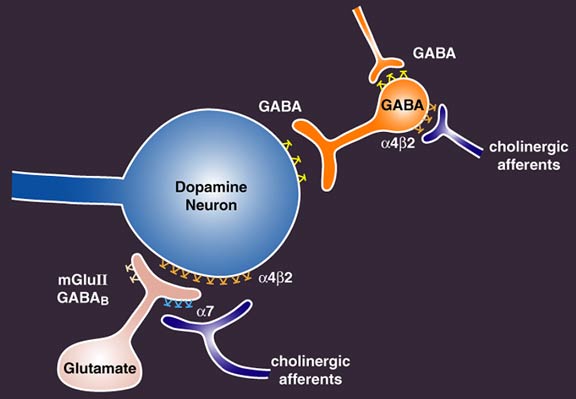
Although GABA concentration changes were small both within day (average 5.6%) and between day (average 4.8%), gabapentin administration was associated with an average increase in GABA concentration of 55.7% (6.9-91.0%). Importantly, drug-induced change in GABA levels was inversely correlated to the individual's baseline GABA level (R²=0.72). The differences between GABA and gabapentin lie in their mechanisms of action in the brain – GABA targets GABA receptors whereas gabapentin interacts with voltage-gated calcium channels. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. GABA and Gabapentin, though distinct entities share a common goal: to promote calmness and regulate neuronal activity. While GABA is a natural neurotransmitter with diverse functions, Gabapentin is a synthetic medication mimicking some of its effects for specific therapeutic purposes. Gabapentin has come into clinical use as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of epilepsy. Designed to mimic gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), its mechanism of action remains elusive. In vivo measurements of GABA in human brain were made using 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy. We used a 2.1-T magneti Gabapentin is a medication that mimics GABA’s effects in the brain, while GABA supplements are intended to increase the natural levels of GABA in the system. Gabapentin is usually more potent and effective for specific medical and behavioral problems that require medication management, as compared to supplements. GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter found in the central nervous system (CNS) that regulates its excitability. On the other hand, gabapentin was created to mimic some of the effects of GABA but it does not appear to affect the same receptors in the brain. Gabapentin works by mimicking the effects of GABA, a neurotransmitter that helps to reduce neuronal excitability in the brain. This mechanism of action makes it effective in controlling seizures and reducing nerve pain. They make gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)—which slows the activity of neurons in the brain-—more potent. For that reason, they are used to calm anxiety and help people sleep. If you take one of these drugs. It's always good to review the potential benefits and harms of these medications with your doctor. Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on glutamate are not known. While GABA and gabapentin share structural similarities, they are fundamentally different in their functions and applications. GABA is a neurotransmitter that directly inhibits neuronal activity, whereas gabapentin is a GABA analog that modulates calcium channels to achieve its therapeutic effects. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain that inhibits or slows down nerve activity, helping to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. On the other hand, Gabapentin is a medication that is structurally similar to GABA but does not directly bind to GABA receptors. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter, while gabapentin is a synthetic medication designed to mimic GABA’s effects. GABA is available as a supplement, whereas gabapentin requires a prescription and is used for specific medical conditions like epilepsy and neuropathic pain. Some medications work to increase GABA levels or interact with GABA receptors, while others are GABA agonists, meaning they act like GABA in the body. Perhaps the most well-known are the gabapentinoids , a group of medications that include gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise) and pregabalin (Lyrica). Recommended doses range from 20 mg to 40 mg daily, preferably dissolved under the tongue. However, it's crucial to emphasize that GABA supplementation should not be viewed as a substitute for professional medical advice in addressing prostate problems. GABA's therapeutic potential has been harnessed in the treatment of various medical conditions. compound that was initially synthesized to mimic the chemical structure of GABA by addition of a cyclohexyl to concentrations of 10mM (Goldlust et al, 1995). Gabapentin increased GABA turnover In the present review we show that although gabapentin is not a GABA mimetic, it has great utility as an add-on therapy for epilepsy and as a first-line treatment for neuropathic pain. Gabapentin, although a GABA analogue, does not mimic GABA's action on its receptors. Studies have shown that gabapentin does not act as an agonist at GABA(B) receptors, nor does it displace GABA from its binding sites. Take-home message: - gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) is a major neurotransmitter that regulates much of our brain function. It was previously thought that ingested GABA could not cross the blood-brain barrier, but new research suggests that it may be able to. - Drugs that mimic the action of GABA are numerous, work in a variety of ways, and can have effects ranging from treating epilepsy to Gabapentin (Neurontin) Carisoprodol (Soma) Diazepam (Valium) Alprazolam (Xanax) Lorazepam (Ativan) There are also herbs and amino acids available without a prescription that can be used as GABA surrogates: Valerian root. Ashwagandha. Taurine. Brahmi. Bacopa. Glutamine: GABA’s Precursor
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_What-to-Know-About-Gaba_Illustrator_Jessica-Olah_Final-ea5963205783442fa62455edbc5851ef.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |