Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_What-to-Know-About-Gaba_Illustrator_Jessica-Olah_Final-ea5963205783442fa62455edbc5851ef.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
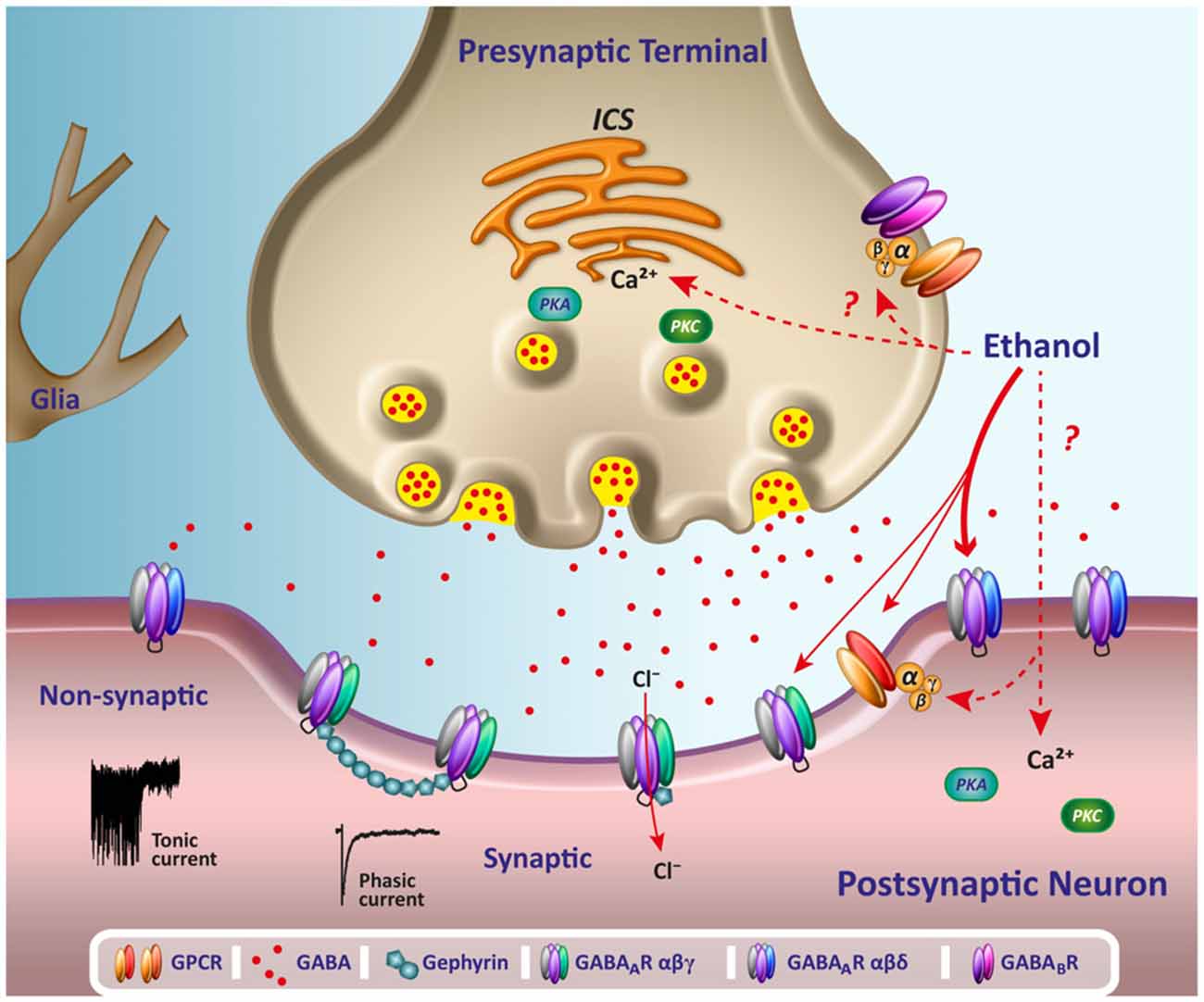
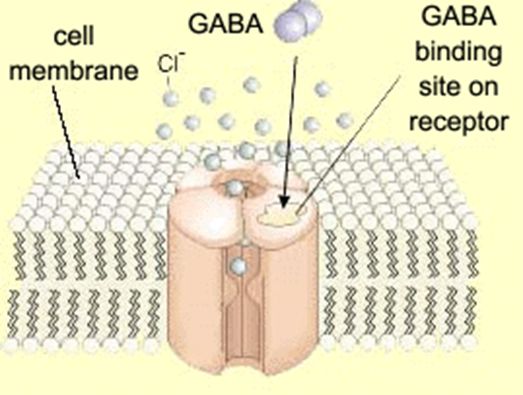
Research regarding gabapentin's effects on GABA and glutamate synthetic and metabolizing enzymes reveals a complex pattern of activity and provides an incomplete explanation for its anticonvulsant effects. Gabapentin functions by modulating enzymes involved in GABA synthesis. It differs in chemical structure from GABA and its half-life is much longer (McLean, 1994). One MRS study in humans has found that the administration of gabapentin increased brain GABA levels by 55.7% (Cai et al., 2012). Gabapentin is a prescription medication used to treat seizures and nerve pain. It modulates the enzymes responsible for making GABA, increasing the amounts of the neurotransmitter in your brain. According to MedlinePlus, there are no foods to avoid with gabapentin, and it can be taken with or without food. It is, however, recommended that you Gabapentin is a GABA analog, meaning that it looks very similar structurally but it is not completely the same. GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter found in the central nervous system (CNS) that regulates its excitability. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain that inhibits or slows down nerve activity, helping to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. On the other hand, Gabapentin is a medication that is structurally similar to GABA but does not directly bind to GABA receptors. Gabapentin is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Its anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties suggest that it increases GABAergic inhibition; however, the molecular basis for these effects is unknown as gabapentin does not directly modify GABA type A (GABA A) receptor function, nor does it modify synaptic inhibition. gabapentin’s effects on GABA and glutamate synthetic and metabolizing enzymes reveals a complex pattern of activity and provides an incomplete explanation for its anticonvulsant In vitro, gabapentin modulates the action of the GABA synthetic enzyme, glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) and the glutamate synthesizing enzyme, branched-chain amino acid transaminase. Results with human and rat brain NMR spectroscopy indicate that gabapentin increases GABA synthesis. Gabapentin (Neurontin®) is a second-generation antiepileptic drug widely used for treatment of neuropathic pain. It is also used to treat anxiety, insomnia, bipolar disorder, and restless leg syndrome. Although first introduced as an adjunct therapy for epilepsy, gabapentin became a blockbuster drug for the management of chronic pain from many nerve conditions [8]. Side effects are usually If you’re taking other medications, especially those that affect mood or brain function, they might interact with gabapentin to produce unique emotional effects. This interplay between different medications is something we also see with other mood-altering medications , highlighting the importance of considering the full picture of a patient Common brand names for gabapentin include Gralise, Horizant, Neuraptine, and Neurontin. This drug works by stimulating the release of neurotransmitters in the brain, specifically GABA and serotonin. Usually, drugs that affect serotonin levels come with the risk of producing serotonin syndrome. But can gabapentin cause serotonin syndrome? I wish to find a medication that counteracts that. There seems to be conflicting medical papers on Gabapentin's mechanism of action. One paper stated that gabapentin reduces serotonin, dopamine and norepinephrine, also blocking calcium channels. It stated that gabapentin eventually would remove dopamine so that the brain would no longer produce it. Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on glutamate are not known. Gabapentin is a GABA analogue used to treat epilepsy and neurotic pain. Gabapentin causes an increase in GABA levels in the brain. Another GABA analog is gamma-hydroxybutyrate, or GHB. Excessive intake of GABA supplements may lead to side effects or interactions with medications. Dietary sources of Gamma-aminobutyric acid. Here are you can find some food sources that contain GABA: Fermented Foods. Fermented foods are known to contain higher levels of GABA due to the action of certain bacteria that produce GABA during Gabapentin has no direct GABAergic action and does not block GABA uptake or metabolism. Gabapentin blocks the tonic phase of nociception induced by formalin and carrageenan, and exerts a potent inhibitory effect in neuropathic pain models of mechanical hyperalgesia and mechanical/thermal allodynia. 5-HTP: Your body converts 5-HTP into serotonin, and serotonin can enhance GABA activity. 5-HTP is a synthetic form of tryptophan, which is found in turkey. However, tryptophan from food-based sources (like turkey, soybeans, and milk) is not thought to cross the BBB the way 5-HTP does. Research has shown that gabapentin exerts a modulating effect at neuronal receptor sites, inhib- iting the release of the neurotransmitters dopamine (5), serotonin and norepinephrine (6) and resulting in in- creased GABA concentrations in various locations throughout the brain (7). However, I can't find out exactly how GABAergic gabapentin really is, and whether or not it would even produce a noticable cross tolerance with other GABAergic drugs. So does Gabapentin produce GABA tolerance, and also can you increase GABA tolerance using only artificial indirect GABA increasing drugs? Here, we postulated that gabapentin increases expression of δ subunit-containing GABA A (δGABA A) receptors that generate a tonic inhibitory conductance in multiple brain regions including the cerebellum and hippocampus.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_What-to-Know-About-Gaba_Illustrator_Jessica-Olah_Final-ea5963205783442fa62455edbc5851ef.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |