Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
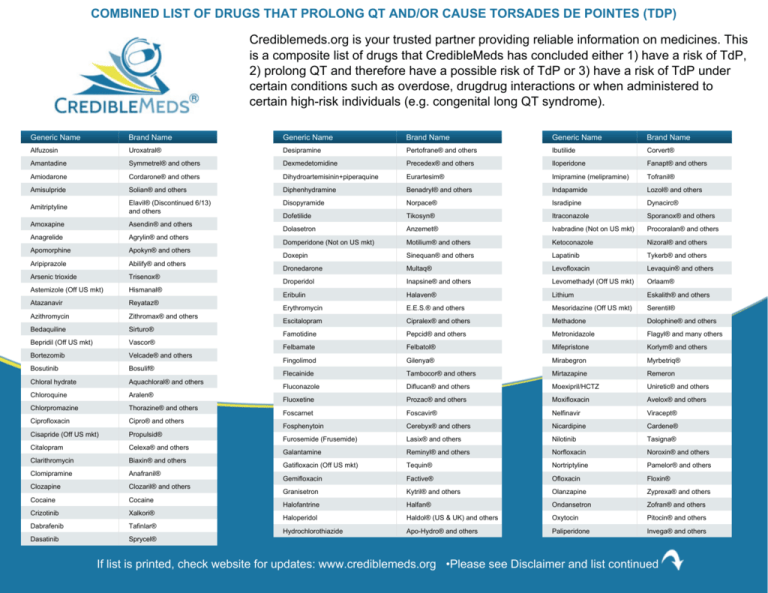
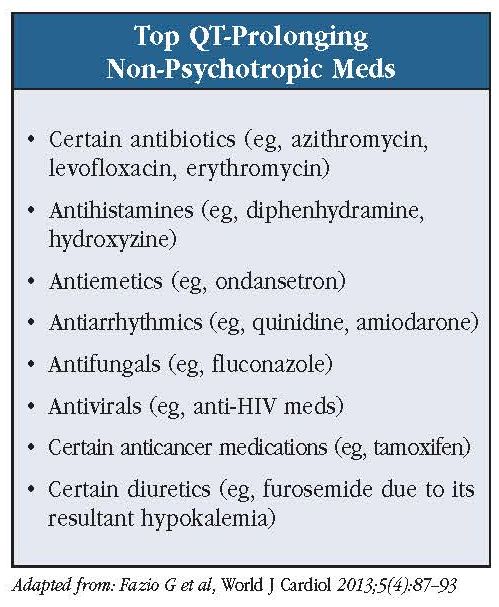
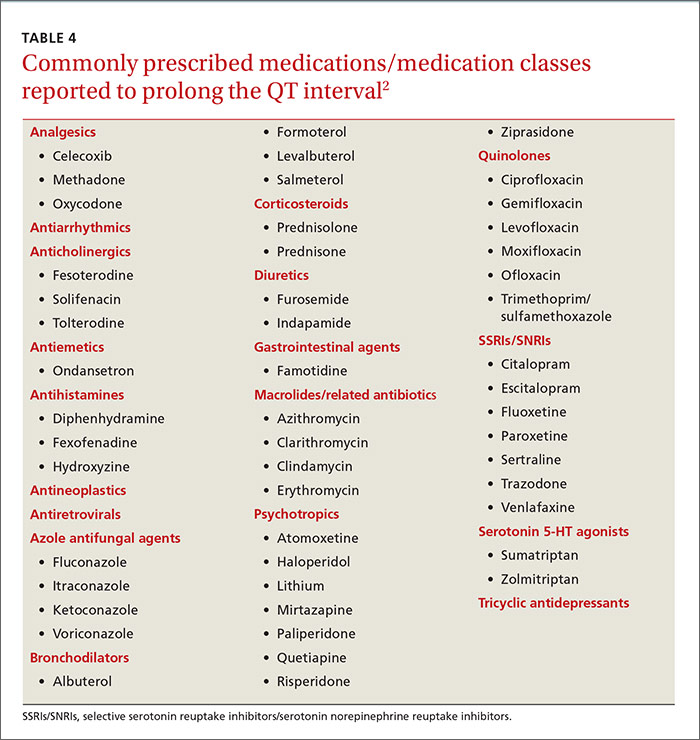
Considering that not all agents that prolong the QT interval increase TDR, drugs can be distinguished into the following groups depending on their simultaneous effects on the QT corrected using the Bazzet’s formula (QTc) interval and on TDR: (1) drugs inducing both QTc prolongation and increased TDR, characterized by a high torsadogenic Base-line QT prolongation 16 Subclinical long-QT syndrome 18,19 Ion-channel polymorphisms 20-22 Severe hypomagnesemia. n engl j med 350;10 www.nejm.org march 4, 2004 The new england journal of Long qt syndrome is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, also take Aspirin, and have High blood pressure. The phase IV clinical study analyzes which people have Long qt syndrome when taking Gabapentin, including time on the drug, (if applicable) gender, age, co drug-induced QT prolongation is often dose related and risk of torsades de pointes is increased with intravenous administration (particularly if given rapidly) mechanism for most potential QT-prolonging medications is inhibition of the KCNH2-encoded HERG (human ether-a-go-go related gene) potassium channel (4) Notes: The most commonly reported adverse events with gabapentin enacarbil 6000 mg were dizziness and somnolence (60.0% and 54.0%, respectively). Conclusion: In this population of healthy adults, gabapentin enacarbil at doses of 1200 and 6000 mg was not associated with QT prolongation and was generally well-tolerated. The risk of QT interval prolongation was evaluated in a thorough QTc trial in 247 healthy individuals following treatment with LCM at 400 or 800 mg/day. Exposure to LCM did not appear to cause QT prolongation, nor does it seem to have important effects on QRS duration {UCB, Inc., data on file}. The potential for QT prolongation by antiepileptic drugs in children. Pediatr Neurol. 2004;30:99–101. doi: 10.1016/S0887-8994(03)00405-3. [Google Scholar] 27. Dixon R, Job S, Oliver R, Tompson D, Wright JG, Maltby K, et al. Lamotrigine does not prolong QTc in a thorough QT/QTc study in healthy subjects. ¶ The "high risk" category includes drugs with evidence of likely or probable association with TdP or clinically significant QT prolongation typically defined as a mean QTc increase of >60 msec from baseline and/or a QTc increased to >500 msec in a significant proportion of patients. • Concomitant administration of another drug known to prolong the QT interval. It is therefore important to consider drug-related and individual patient factors prior to prescribing any new psychotropic drugs. QT prolongation might worsen weeks, months, or years after treatment is started because of In addition, the potential role of antiepileptic drugs has been suggested. While the preponderance of clinical data would suggest that use of most antiepileptic drugs does not pose excessive additional risk of QT prolongation, available data also do not provide sufficient evidence that these drugs are entirely free of risk in all patients. A comprehensive list of conditions and drugs that may prolong the QT interval, and cause torsade de pointes (TdP) and long QT syndrome (LQTS) is presented below. With regards to drugs, the risk of QT prolongation and TdP varies markedly across the list but tends to be rather similar within a drug class. Drugs associated with QT Prolongation, QTc prolongation including Antipsychotics, antiarrhythmics, antidepressants, and antihistamines Prolongation of the QT interval above 470 ms for men and 480 ms for women should be regarded as abnormal . Several risk factors for QT prolongation have been identified, including female sex, advanced age, drug-drug interactions, genetic predisposition, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, heart failure, and bradycardia [5, 6]. Prolongation of the QT interval can lead to a life threatening ventricular arrhythmia known as torsades de pointes which can result in sudden cardiac death. The risk of torsades de pointes depends on patient factors and current medication. Before puberty, a QTc <450 ms is considered normal, between 450 and 459 borderline, and ≥460 prolonged. After puberty in males, a QTc between 460 and 469 is borderline and ≥470 is considered prolonged. In post-pubertal females, 460 to 479 is borderline and ≥480 ms is considered prolonged. The QTc is considered prolonged if the values are greater than 450 milliseconds in males and greater than 470 milliseconds in females. 3 The risk of cardiac events correlates with the extent of QT prolongation. However, no QTc value has been established for cardiac arrhythmia. Electrocardiogram qt corrected interval prolonged is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 40-49 old, also take Mirtazapine, and have High blood pressure. Long QT syndrome is a cardiac repolarization disorder and is associated with an increased risk of torsades de pointes. The acquired form is most often attributable to administration of specific medications and/or electrolyte imbalance. Many drugs are notoriously known to prolong the QT interval, especially those used in cardiology and psychiatry practice. QT prolongation can remain asymptomatic or lead to torsades de pointes (TdP), a rare tachyarrhythmia which can be life-threatening or nearly fatal due to ventricular fibrillation and sudden cardiac death. For people with LQTS there are specific medications that can have a serious effect by further prolonging the QT interval. We give a list of these medicines below. This list includes drugs that can stimulate and irritate the heart by causing adrenaline-like effects.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |