Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
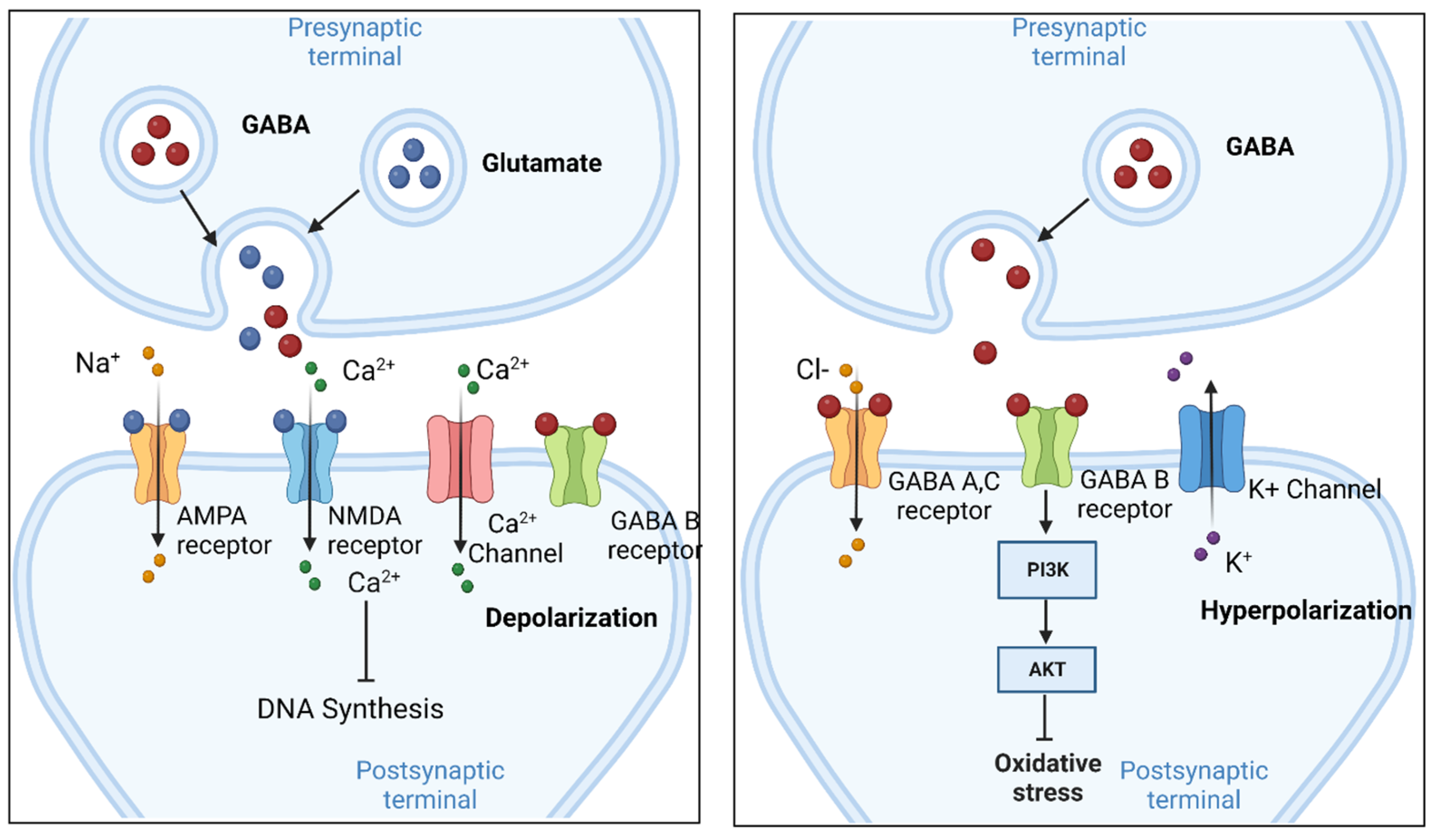 |  |
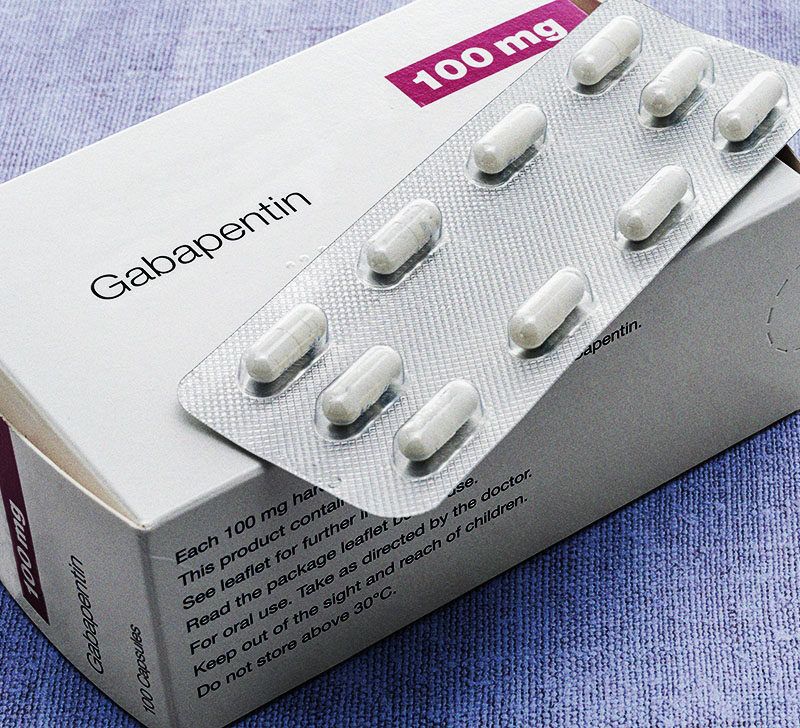
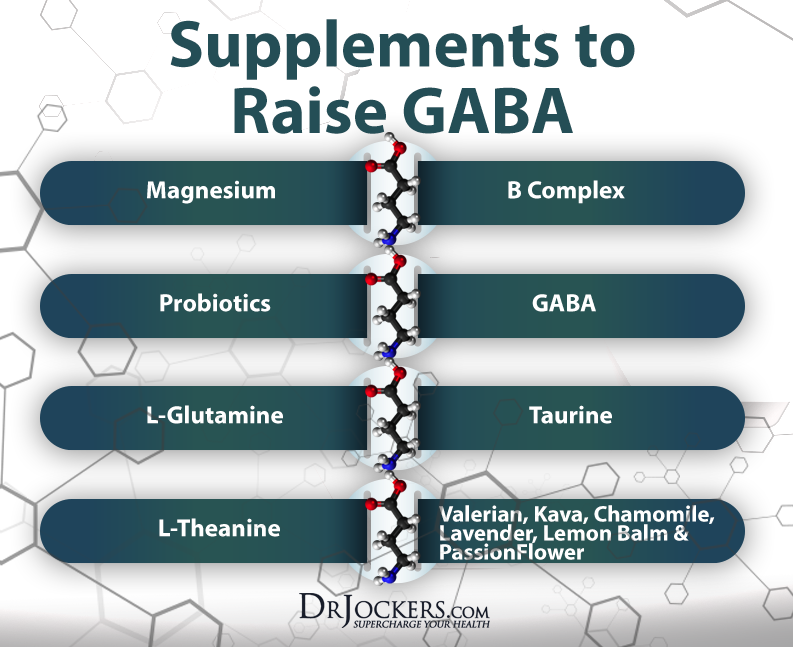
Although gabapentin is a GABA analogue, it does not bind to and modulate the GABA receptors nor does it affect GABA transport or metabolism. Gabapentin is a gabapentinoid, which acts as an inhibitor of the α2δ subunit-containing voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCCs) that are linked to neurotransmitter release. Antiseizure medications, including gabapentin, can increase your risk for suicidal thoughts or behavior. This can begin as early as one week after you begin taking gabapentin. If you’re taking gabapentin and you experience any new or worsening depression, or any changes in your behavior, let your prescriber know immediately. Gabapentin is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA, yet it has no direct effects on GABA A receptor function, nor does it increase inhibitory synaptic transmission [1, 8]. Thus, the molecular basis of gabapentin's GABAergic properties has remained enigmatic. 5-HTP: Your body converts 5-HTP into serotonin, and serotonin can enhance GABA activity. 5-HTP is a synthetic form of tryptophan, which is found in turkey. However, tryptophan from food-based sources (like turkey, soybeans, and milk) is not thought to cross the BBB the way 5-HTP does. Applies to gabapentin: oral capsule, oral solution, oral suspension, oral tablet, oral tablet extended release 24 hr. Serious side effects of gabapentin. Along with its needed effects, gabapentin may cause some unwanted effects. Although not all of these side effects may occur, if they do occur they may need medical attention. GBP promptly elevates brain GABA and presumably offers partial protection against further seizures within hours of the first oral dose. Patients may expect to experience the anticonvulsant effects of increased homocarnosine and pyrrolidinone with daily therapy. Although GABA concentration changes were small both within day (average 5.6%) and between day (average 4.8%), gabapentin administration was associated with an average increase in GABA GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain that inhibits or slows down nerve activity, helping to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. On the other hand, Gabapentin is a medication that is structurally similar to GABA but does not directly bind to GABA receptors. Gabapentin is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA, yet it has no direct effects on GABA A receptor function, nor does it increase inhibitory synaptic transmission [1,8]. Thus, the molecular basis of gabapentin's GABAergic properties has remained enigmatic. While gabapentin was designed as a GABA analogue, its GABA-like properties are not as straightforward as initially believed. The drug does not directly bind to GABA receptors or increase GABA levels in the brain. However, it may indirectly enhance GABAergic neurotransmission through its effects on calcium channels and other neuronal processes. Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on glutamate are not known. A dose of 2000 mg or more of glutamine a day when taken on an empty stomach with vitamin B6 (2mg or more), will increase your natural level of GABA and probably reduce your pain levels. Pure GABA is available as a tablet, capsule or in sublingual (under-the tongue) form in most health food stores or online. Gabapentin increases the concentration and probably the rate of synthesis of GABA in brain, which may enhance non-vesicular GABA release during seizures. 3. Gabapentin binds with high affinity to a novel binding site in brain tissues that is associated with an auxiliary subunit of voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels. Gabapentin is a GABA analog, meaning that it looks very similar structurally but it is not completely the same. GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter found in the central nervous system (CNS) that regulates its excitability. In people with partial seizures, gabapentin works by decreasing abnormal activity in the brain. Experts believe gabapentin may cause brain cells to produce more of a chemical called GABA, which reduces abnormal electrical activity of brain cells. Sprouting grains, seeds, and legumes may increase GABA content. Some studies suggest that the germination process can lead to an accumulation of GABA in sprouted products. It's important to note that the GABA content in food can be influenced by factors such as processing, cooking methods, and the specific cultivar or variety of the food.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |