Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
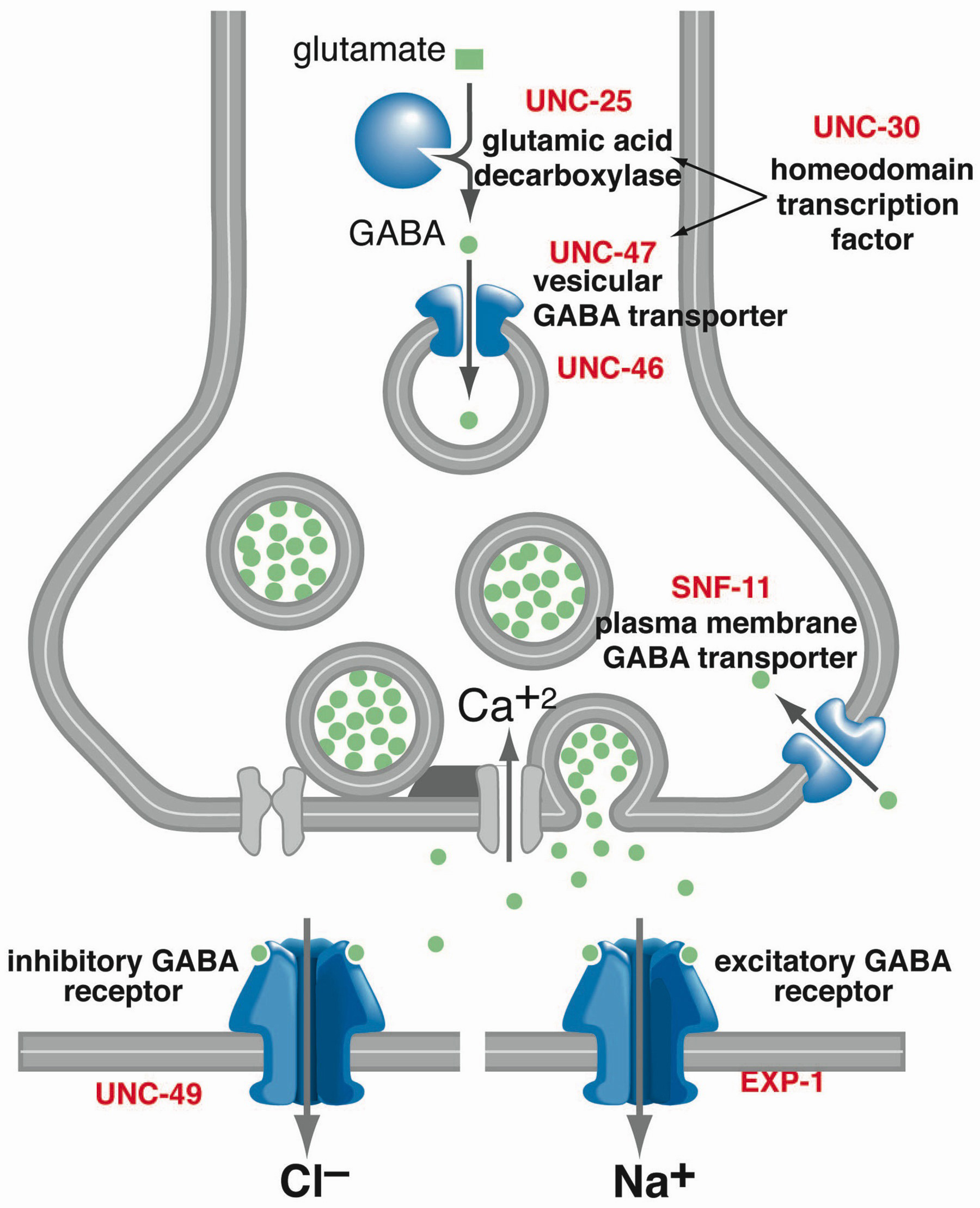
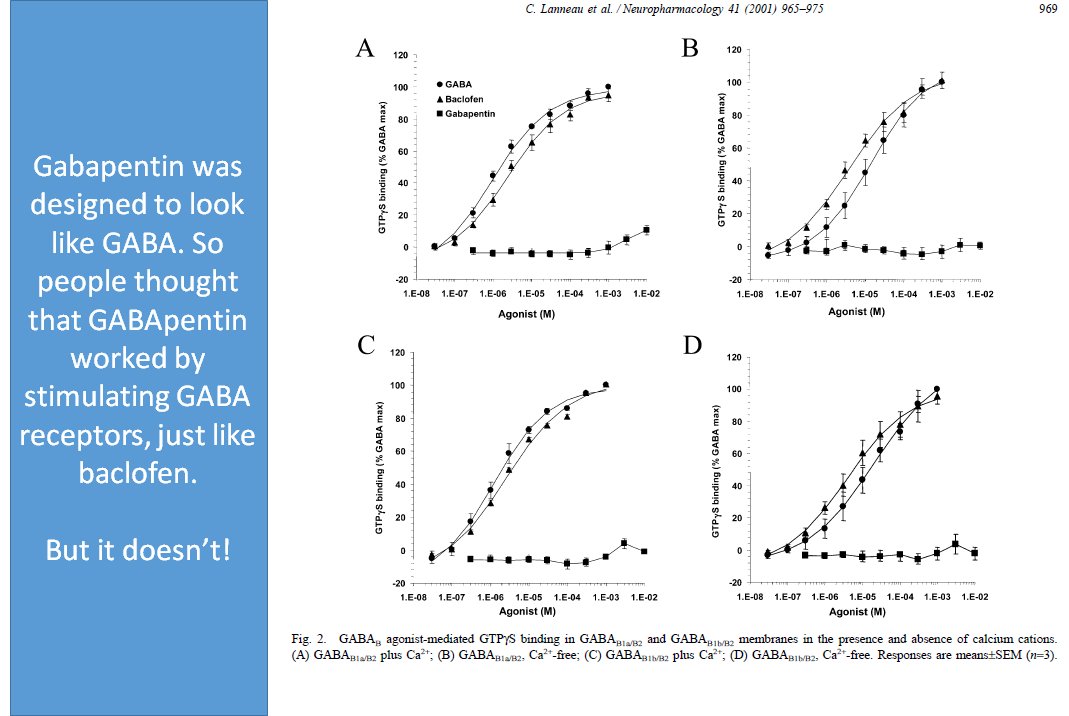
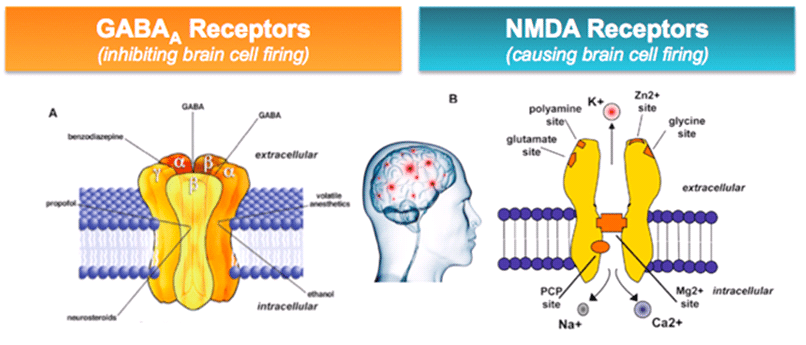
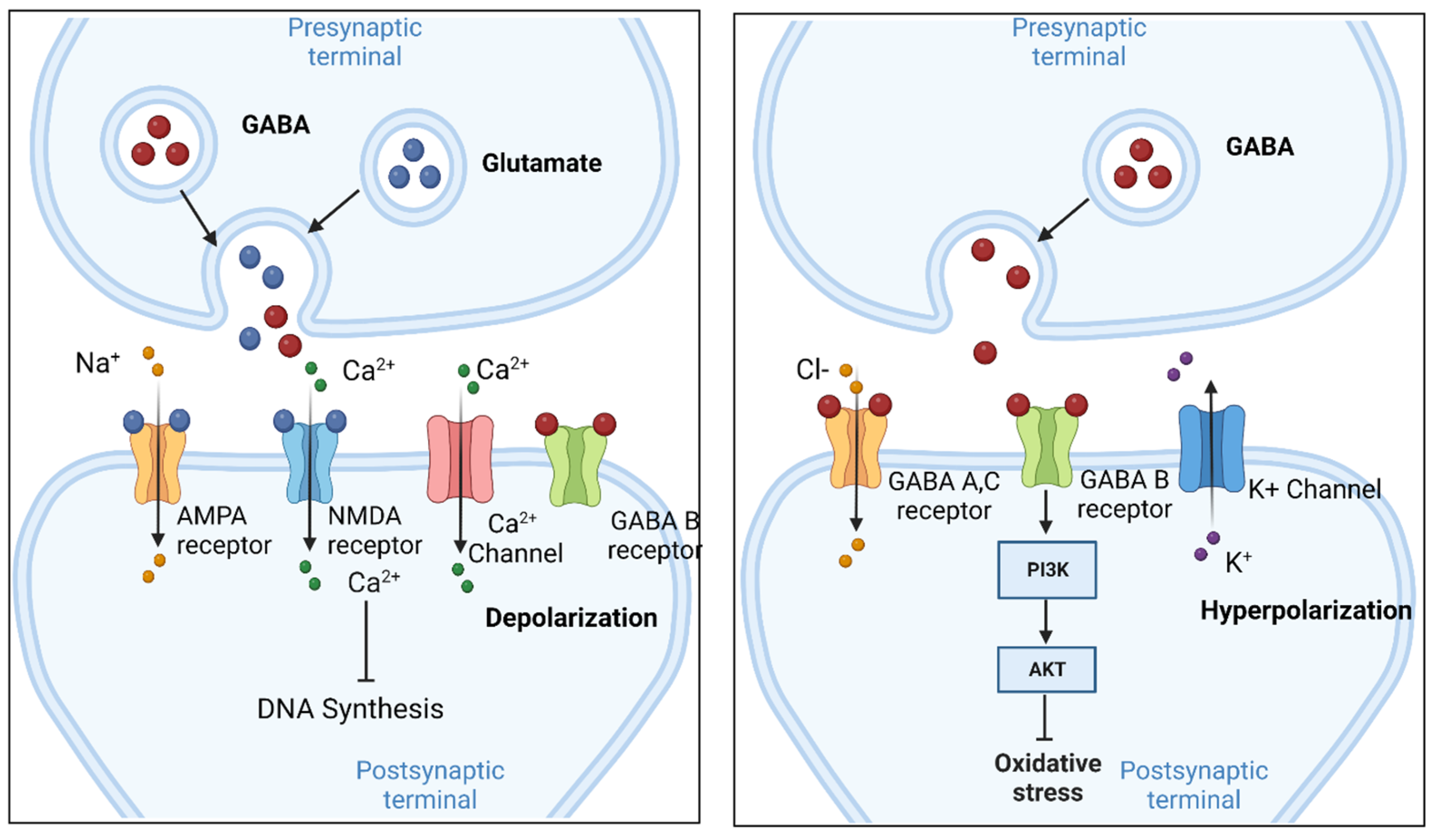
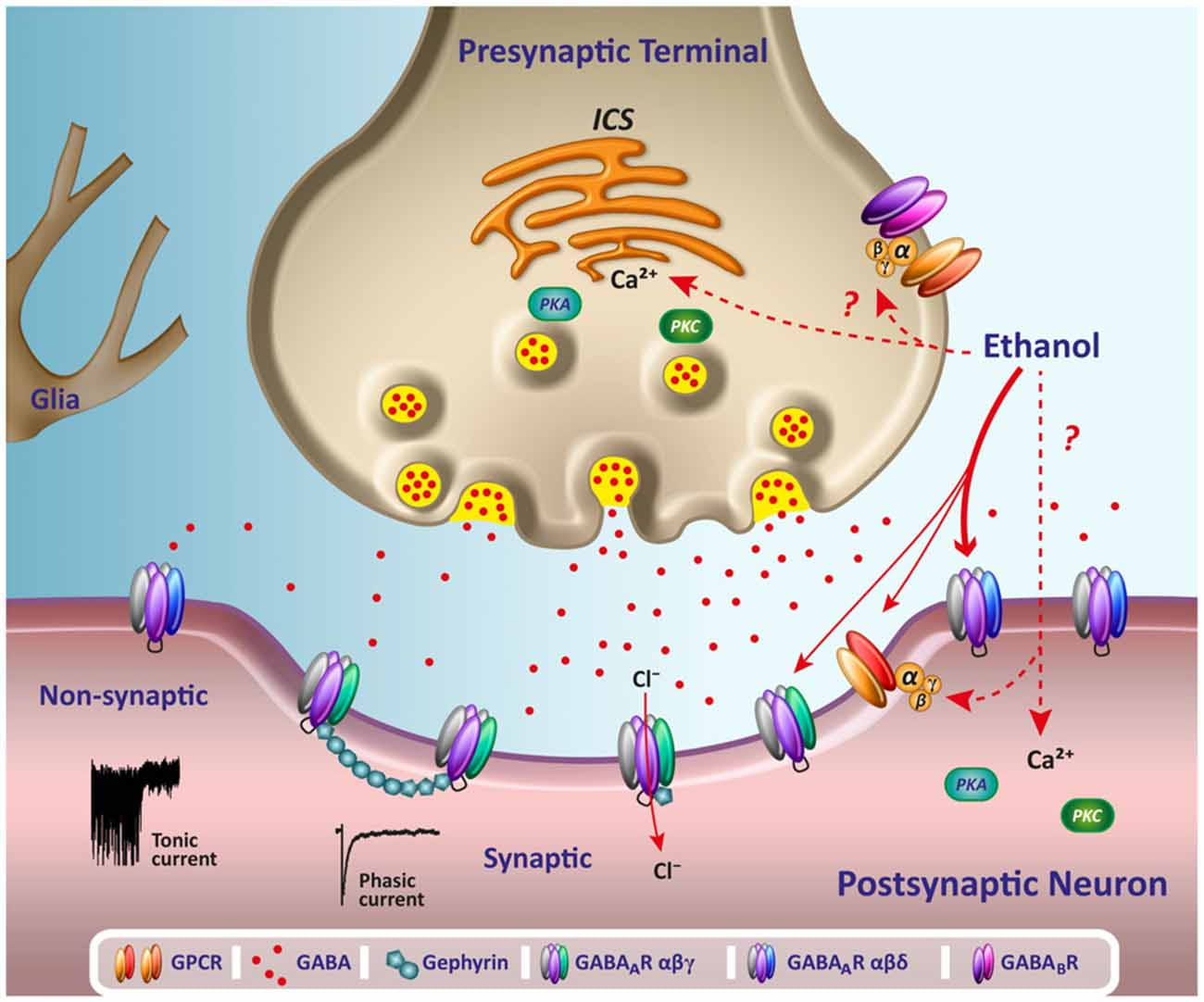
GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain that inhibits or slows down nerve activity, helping to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. On the other hand, Gabapentin is a medication that is structurally similar to GABA but does not directly bind to GABA receptors. Glutamine is the precursor of GABA. A dose of 2000 mg or more of glutamine a day when taken on an empty stomach with vitamin B6 (2mg or more), will increase your natural level of GABA and probably reduce your pain levels. Pure GABA is available as a tablet, capsule or in sublingual (under-the tongue) form in most health food stores or online. Gabapentin is a prescription medication known as a gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue. GABA reduces the excitability of nerve cells (neurons) in the brain, which play a role in seizures and the transmission of pain signals. Gabapentin mirrors the effects of GABA calming excited neurons. Research has shown gabapentin binds strongly to a specific site (called the alpha2-delta site) on voltage-gated calcium channels and this is thought to be the way gabapentin works to relieve nerve pain and lower the risk of seizures. Gabapentin enacarbil (brand name Horizant) is a prodrug of gabapentin that has been designed to overcome the GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter, while gabapentin is a synthetic medication designed to mimic GABA’s effects. GABA is available as a supplement, whereas gabapentin requires a prescription and is used for specific medical conditions like epilepsy and neuropathic pain. Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on glutamate are not known. 3. How long does it take for Gabapentin to start working? The onset of action of Gabapentin can vary depending on the individual and the condition being treated. It may take several days or weeks for the full effects to be noticeable. 4. Can Gabapentin be used for acute inflammation? Gabapentin is generally not recommended for acute inflammation. To understand how gabapentin might influence dopamine levels, we first need to explore its primary mechanisms of action. Contrary to its name, gabapentin does not directly interact with GABA receptors or influence GABA levels in the brain. Instead, its primary mode of action involves modulating voltage-gated calcium channels. Research has shown that gabapentin exerts a modulating effect at neuronal receptor sites, inhibiting the release of the neurotransmitters dopamine (5), serotonin and norepinephrine (6) and resulting in in- creased GABA concentrations in various locations throughout the brain (7). Gabapentin is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Its anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties suggest that it increases GABAergic inhibition; however, the molecular basis for these effects is unknown as gabapentin does not directly modify GABA type A (GABA A) receptor function, nor does it modify synaptic inhibition. Gabapentin is believed to decrease excitation of the central nervous system in multiple ways: It reduces the release of glutamate, a key component of the excitatory system 16. It increases the concentration of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain 7 GABA acts as a neurotransmitter and interacts with GABA receptors in the central nervous system, while gabapentin interacts with the α2δ subunit of the voltage-sensitive calcium channel. Both help reduce neuronal excitability, but the mechanisms are not fully understood. Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on glutamate are not known. Yes, GABA supplements are available and can be found in various forms, including capsules, tablets, and powder. These supplements are marketed for their potential to support relaxation, reduce stress, and promote better sleep. However, it's essential to approach GABA supplementation with caution and be aware of certain considerations. In people with partial seizures, gabapentin works by decreasing abnormal activity in the brain. Experts believe gabapentin may cause brain cells to produce more of a chemical called GABA, which reduces abnormal electrical activity of brain cells. Gabapentin has no direct GABAergic action and does not block GABA uptake or metabolism. Gabapentin blocks the tonic phase of nociception induced by formalin and carrageenan, and exerts a potent inhibitory effect in neuropathic pain models of mechanical hyperalgesia and mechanical/thermal allodynia. Gabapentin is a GABA analog, meaning that it looks very similar structurally but it is not completely the same. GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter found in the central nervous system (CNS) that regulates its excitability. Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin 5-HTP: Your body converts 5-HTP into serotonin, and serotonin can enhance GABA activity. 5-HTP is a synthetic form of tryptophan, which is found in turkey. However, tryptophan from food-based sources (like turkey, soybeans, and milk) is not thought to cross the BBB the way 5-HTP does. Please use one of the following formats to cite this article in your essay, paper or report: APA. Bennett, Chloe. (2019, July 18). GABA Activation and Dopamine Suppression.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |