Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
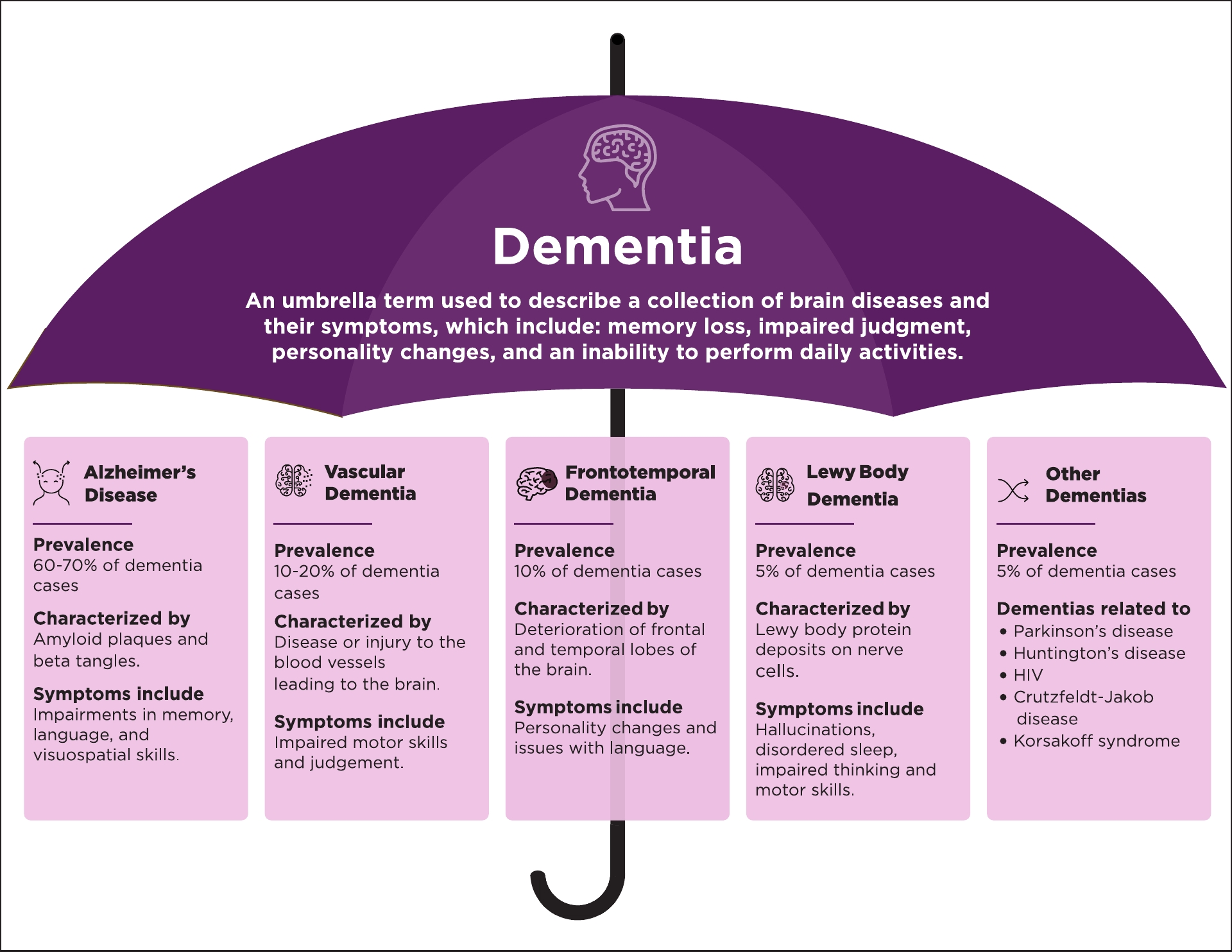
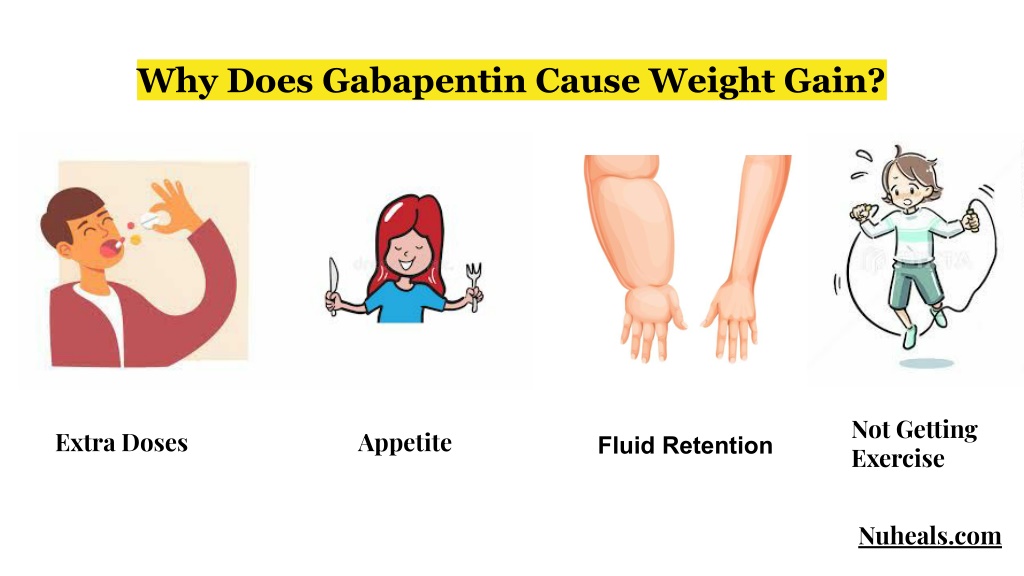
Moreover, the stratification analysis revealed that the risk of dementia associated with gabapentin or pregabalin exposure was significant in all age subgroups; however, it was higher in younger patients (age <50) than in the older patients (hazard ratio, 3.16; 95% CI, 2.23-4.47). Applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria yielded 201,492 patients for the study: 25,373 in the dementia cohort and 174,930 in the non-dementia cohort. Post 1:1 matching, and after excluding recent gabapentin use (within three months of the index date), the study comprised 22,769 individuals in the dementia cohort and 22,644 in the non-dementia While studies haven’t definitively confirmed gabapentin causes long-term memory loss or impairment as severe as dementia, patients can experience brain fog and slight confusion. However, it is important to acknowledge the existing evidence that links long-term gabapentin use to cognitive decline including memory. Though generally well-tolerated, gabapentin can cause side effects such as dizziness, fatigue, and coordination issues. In some cases, individuals may experience cognitive changes, such as memory loss or difficulty concentrating. Because of these potential effects, gabapentin should only be used under medical supervision. The multivariate-adjusted hazard ratio of risk of dementia for gabapentin or pregabalin exposure versus the matched non-exposed group was 1.45 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.36–1.55). The risk of dementia increased with higher cumulative defined daily doses during the follow-up period. Our analysis suggests that in patients with chronic pain, long-term gabapentin use does not markedly alter dementia risk across varying cumulative dosages, regardless of age or gender. These findings may have significant implications for chronic pain management and underscore the potential cognitive safety of prolonged gabapentin administration. The prevalence of gabapentin use increased from 2006 to 2019, both in overall population and within every subgroup (i.e., cognitive status, age group, and sex). About 10–30% of gabapentin users reported to concurrently use gabapentin with opioids. Over one-half of gabapentin users with dementia concurrently used gabapentin with antidepressants. Gabapentin use has been associated with memory loss and cognitive decline. Studies suggest that the risk of dementia may be higher in patients treated with gabapentin. It is important for patients and healthcare providers to be aware of the potential cognitive side effects of gabapentin. Background Today, gabapentinoids such as Gabapentin (GBP) and pregabalin (PGB) are widely used as painkillers. This may alter the function of the nervous system; hence their results may include a difference in memory and processes that end in memory formation. This study aims to conclude whether gabapentinoids can alter memory or not by reviewing and analyzing clinical and preclinical studies The evidence of gabapentin and dementia is mixed, with two studies looking at hundreds of thousands of people and coming to completely different conclusions. In the study suggesting that there The results revealed that the risk of dementia associated with gabapentin or pregabalin exposure was significant in all subgroups except for the strata having depression or head injury. The risk of dementia development was higher in the younger group (age <50 years) than that in the older group. Two common classes of drugs have been linked to dementia. Fortunately, there are alternatives to both. If you're worried about developing dementia, you've probably memorized the list of things you should do to minimize your risk—eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, getting adequate sleep, and keeping your mind and soul engaged. Here are four common drug classes linked to dementia, and what the research says about your risk. 1. Anticholinergic medications block a chemical called acetylcholine in the body. Acetylcholine works like a chemical messenger in the nervous system. It affects learning, memory, movement, and even emotions. Gabapentin is an effective treatment for chronic neuropathic pain but may cause dizziness, drowsiness, and confusion in some older adults. The goal of this study was to assess the association between gabapentin dosing and adverse outcomes by Gabapentin use was significantly associated with decline in cognitive and functional status among older adults with initially normal cognition. Further studies are needed to examine the association. 3.2 Functional status decline. The same sample was used for assessing functional status change as measuring cognitive decline ().At the first visit after index, the association of gabapentin initiation with functional decline was not significant for either change in FAQ sum (OR [95% CI]: 1.50 [0.76, 2.96]) or FAQ mean (1.56 [0.93, 2.63]). Some studies report that gabapentin can cause erectile dysfunction in men. However, older studies also report cases of sexual dysfunction and loss of libido in women. Additionally, the side There is evidence that certain medications — both prescription and over-the-counter — are associated with an increased risk of dementia. The latest study to confirm this connection came out in June 2019 in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA). There has been an ongoing debate on whether gabapentin and memory loss are linked. However, it seems that Gabapentin alone cannot cause memory loss, but when combined with similar drugs like baclofen, it can. One study found that long-term administrations of Gabapentin alone did not cause memory loss or memory impairment. Especially in older adults, gabapentin is prescribed to treat behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia (BPSD) (Kim et al., 2008). Several studies have reported that gabapentin has a deleterious effect on cognition (Leach et al., 1997; Meador et al., 1999; Shem et al., 2018).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |