Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-tinnitus-causes-effects-and-treatment-1046499-FINAL-625c4e619521406f9539472b65f7a916.png) | 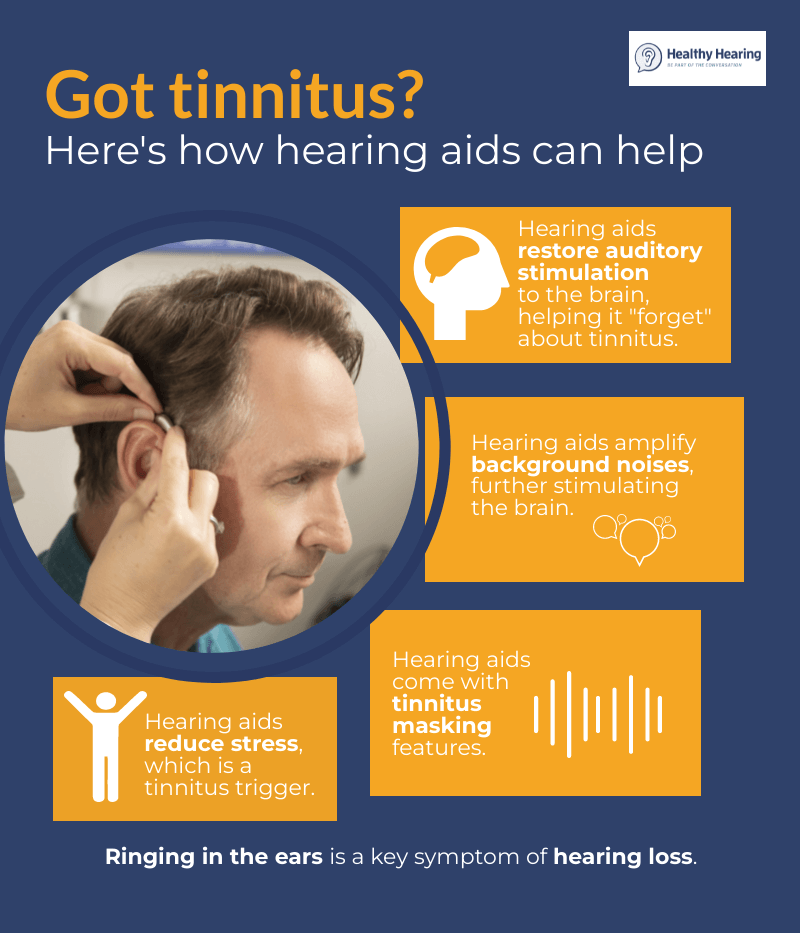 |
 |  |
 |  |
Arguably, one of the drugs that has been studied most extensively as a tinnitus treatment is gabapentin (marketed as Neurontin®). It is useful to look at the history of this drug to appreciate the promise and pitfalls encountered when searching for effective tinnitus treatments. Specifically, cases of: acoustic trauma tinnitus, typewriter tinnitus, post-viral (COVID) tinnitus, stroke-related tinnitus, and “central type” tinnitus – have benefited from gabapentin. However, gabapentin appears to be ineffective for patients with subjective idiopathic tinnitus . There are many meds that are ototoxic and can cause tinnitus, and I have never seen gabapentin on any list from a medical site like Mayo or Cleveland. Instead I saw that it was used to treat tinnitus. fected tinnitus patients; (4) the clinical identity of clini-cal types of tinnitus since 1822 [10]; and (5) the results of various modalities of therapy (i.e., medication and in-strumentation) attempting tinnitus relief [11–13]. Admittedly, the publication in question selected “se-verely disabled tinnitus patients,” but were they all the Exposure to sound therapy can reverse some of these neural changes and help silence tinnitus. Hearing aids can amplify external noises, making the tinnitus less noticeable. Wearable sound generators, tablets, radios, or other small electronic devices that fit in the ear produce soft, pleasant sounds that may relieve tinnitus. The pharmacologic management of tinnitus with brain-acting effects (for example, amitriptyline, acamprosate, and gabapentin) and those with anti-inflammation/anti-oxidant effect (for example, intra-tympanic dexamethasone injection plus oral melatonin) appear to serve as the preferable effective treatments for tinnitus without specific or The anticonvulsant agent, gabapentin, increases the synthesis of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the brain and improves inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA activity. Moreover similar to lidocaine, gabapentin can inhibit voltage-activated Na + channels . As an inhibitory neurotransmitter acting on voltage-gated calcium channels, the role of gabapentin in the treatment of tinnitus remains unclear. Gabapentin, however, has been reported to significantly improve annoyance and loudness of tinnitus related to acoustic trauma. Yes, Gabapentin can cause tinnitus that quickly. One lady got loud tinnitus the morning after taking just 1 100 mg pill. So your getting tinnitus after three days at a much higher dosage is consistent with what others have experienced. To be sure, some people don’t get tinnitus for several months after starting to take Gabapentin. The tinnitus was found to persist and intensify during 17 months of testing. Finally, the tinnitus was reversibly attenuated by treatment with gabapentin. In human use of gabapentin for tinnitus, Zapp 10 reported a case of the relief of tinnitus in a patient with chronic pain. Tinnitus can be a sign that a person has low levels of zinc. In these cases, supplements can help, but the researchers say it has little effect on people with typical zinc levels. Off-label In our patient, a unilateral tinnitus with an antecedent ipsilateral facial nerve injury, and a pre-existing hypertension and diabetes mellitus would likely support a secondary injury as cause for her tinnitus. The normal neuroimaging do not. Zapp JJ. Gabapentin for the treatment of tinnitus: A case report. Ear Nose Throat J. 2001;80(2):114. [Google Scholar] 184. Shulman A. Gabapentin and tinnitus relief. Int Tinnitus J. 2008;14(1):1–5. [Google Scholar] 185. Bauer CA, Brozoski TJ. Assessing tinnitus and prospective tinnitus therapeutics using a psychophysical animal model. Some studies suggested that gabapentin might be effective on tinnitus relief. The objective of the study is to perform a systematic review in order to evaluate the efficacy of oral gabapentin in patients with tinnitus. Just to be clear, Lyrica (the brand name of Pregabalin) can be thought of as an improved Neurontin (the brand name of Gabapentin). Lyrica can be taken in smaller doses than can Neurontin, and it is supposed to have fewer side effects. tumor, aneurysm, etc.), the best managementfor tinnitus has been reportedto be abehavioral approach." However, othermodalities,includingmedications, can help as well. As this case demonstrates, tinnitus might be causedby an underlying nerve injury. Ifso, gabapentin might be of benefit, as it was in this patient. References I. Peifer KJ, Rosen What does the research say? There is no evidence to show that gabapentin has a large positive effect in the treatment of tinnitus[2]. One study showed treatment with gabapentin led to an increase in tinnitus[3]. A different study showed no differences on the Tinnitus Handicap Inventory compared to placebo[4]. The authors of both studies reported that gabapentin was not superior to placebo in their primary outcomes. However, following the assessment of risk of bias and within-study clinical heterogeneities, this review concludes that there is insufficient evidence regarding the effect of gabapentin on tinnitus. Gabapentin is effective in reducing subjective and objective aspects of tinnitus in some individuals, with the best therapeutic response obtained in individuals with associated acoustic trauma. Gabapentin for Tinnitus: A Systematic Review. Link (Accessed 1/7/19) Ototoxicity: The Hidden Menace. PubMed (Accessed 1/7/19) A probable case of gabapentin-related reversible hearing loss in a patient with acute renal failure. PubMed (Accessed 1/7/19) Effect of gabapentin on the sensation and impact of tinnitus. PubMed (Accessed 1/7/19)
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-tinnitus-causes-effects-and-treatment-1046499-FINAL-625c4e619521406f9539472b65f7a916.png) |  |
 |  |
 |  |