Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
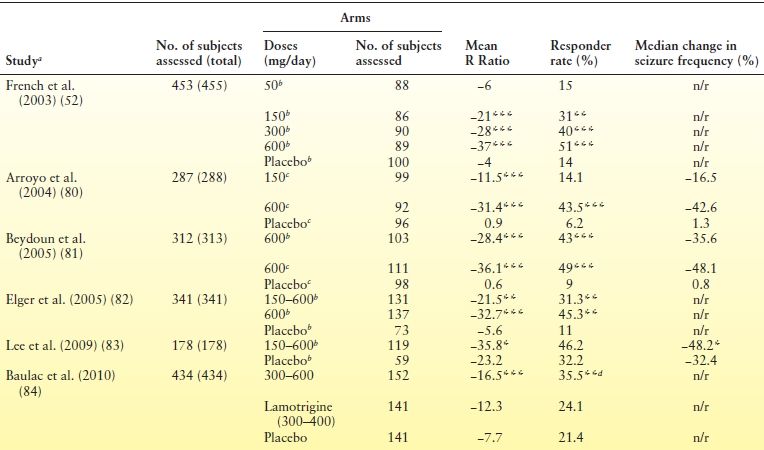
Several studies have evaluated the efficacy of gabapentin and pregabalin in the treatment of neuropathic pain, yielding contradictory results. On one hand, it has been observed that gabapentin is more effective, especially at higher doses, compared to pregabalin (8, 9). rolled trials (RCTs) with a focus on DPN patients receiving GBP, PGB, DLX, or OXC versus placebo. Noncompliant trials with incomplete information and observational studies were excluded. Results: Twelve (RCTs) of PGB, 2 of GBP, 3 of DLX, and 1 of OXC met the inclusion criteria. When drugs were compared for efficacy (direct comparison), GBP (Odd’s ratio [OR] = 3.208, P < 0.001) was most Gabapentin was superior to pregabalin and should be commenced before pregabalin to permit optimal crossover of medicines. Optimal pharmacologic treatment for chronic sciatica (CS) is currently unclear. While gabapentin (GBP) and pregabalin (PGB) are both used to treat CS, equipoise exists. This is the first trial aimed at comparing gabapentin with pregabalin in NLBP. Although the results are preliminary, in our pilot study pregabalin was found to be superior in pain reduction, gabapentin demonstrated better effect on anxiety, insomnia and fatigue symptoms. The results are preliminary Objective was to compare efficacy and safety of Pregabalin and Gabapentin in uremic pruritus among patients of chronic kidney injury undergoing haemodialysis. It was a comparative cross-sectional study, conducted at the Department of nephrology Abbottabad International Medical Institute. Gabapentin, pregabalin, and amitriptyline demonstrate similar effectiveness in alleviating neuropathic (NeP) pain. In terms of NPRS score, gabapentin is superior to both pregabalin and amitriptyline. Gabapentin has been reported to have fewer adverse effects, leading to improved patient adherence for long-term use. efficacy of Pregabalin and Gabapentin in the management of this condition. Methods : A double-blind, randomized, comparative study (clinical trial registry NCT05324761 on 11th April 2022) with two parallel arms with Pregabalin and Gabapentin were used in arms one and two, respectively. Visual analog scale was used for basal and Pregabalin vs Gabapentin: Pregabalin is generally considered to be safer. Gabapentin, on the other hand, has been associated with a higher risk of certain side effects, such as dizziness and ataxia. However, Gabapentin's safety profile is generally considered to be better than Pregabalin's in terms of cost and availability. Pregabalin demonstrates superior efficacy and safety compared with gabapentin in treating neuropathic pain, with improved pain control, quality of life, and fewer adverse events, Objective To systematically evaluate the clinical efficacy of pregabalin and gabapentin in the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia (PHN), including the difference in pain control and occurrence of adverse reactions. Methods PubMed, MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science databases were searched for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing the efficacy of pregabalin and There are limited studies directly comparing the efficacy of gabapentin to pregabalin. Based on the few studies examined, both drugs improve neuropathic pain but there is no clear difference between the two when it comes to pain reduction. However, pregabalin seems to result in quicker pain relief than gabapentin, which may be advantageous. A systematic review and meta-analysis by Finnerup NB showed pregabalin in patients with neuropathic pain had comparative efficacy to gabapentin but with better tolerability. Another comparative trial showed pregabalin had faster onset and pain intensity in adults was reduced more effectively. Tarride et al. conducted a comparative analysis of gabapentin and pregabalin in diabetic neuralgia and PHN in Canada, and found that pregabalin had better efficacy than gabapentin. However, there are other studies that indicate that gabapentin is preferable as a first-line drug over pregabalin and abundant previous clinical data [ 11 ]. Conclusion: In conclusion, pregabalin demonstrated superior and faster efficacy in alleviating neuropathic pain than gabapentin did. Additionally, it improved patient-reported outcomes, resulted in lower opioid consumption, and led to fewer adverse events. Efficacy: Pregabalin vs. Gabapentin . Numerous clinical trials have examined whether pregabalin or gabapentin is more effective for treating specific conditions. Some of the trial findings are explained below. Pregabalin (PGB) and gabapentin (GBP) are recommended as the first-line treatment for neuropathic pain due to SCI [18, 19]. Both drugs have been shown to be effective in the treatment of neuropathic pain due to postherpetic neuralgia [20 – 26] and diabetic peripheral neuropathy [24 – 29]. Conclusion: Our study revealed that Pregabalin is found to be more efficacious when compared to Gabapentin among Type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with painful peripheral neuropathy. Hence, we conclude that Pregabalin provided significant improvement in pain relief and other perspectives. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. In this context, the objective of this meta-analysis is to evaluate and compare pregabalin vs. gabapentin in terms of efficacy and safety in the treatment of neuropathic pain, aiming to provide a solid foundation for clinical decision-making and improve the management of this condition in medical practice. 2 Methods 2.1 Eligibility criteria The results of this analysis support the notion that there is no significant difference in meaningful pain reduction with gabapentin versus pregabalin. This study demonstrates that pregabalin may afford better tolerability and lower pill burden compared to gabapentin.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |