Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
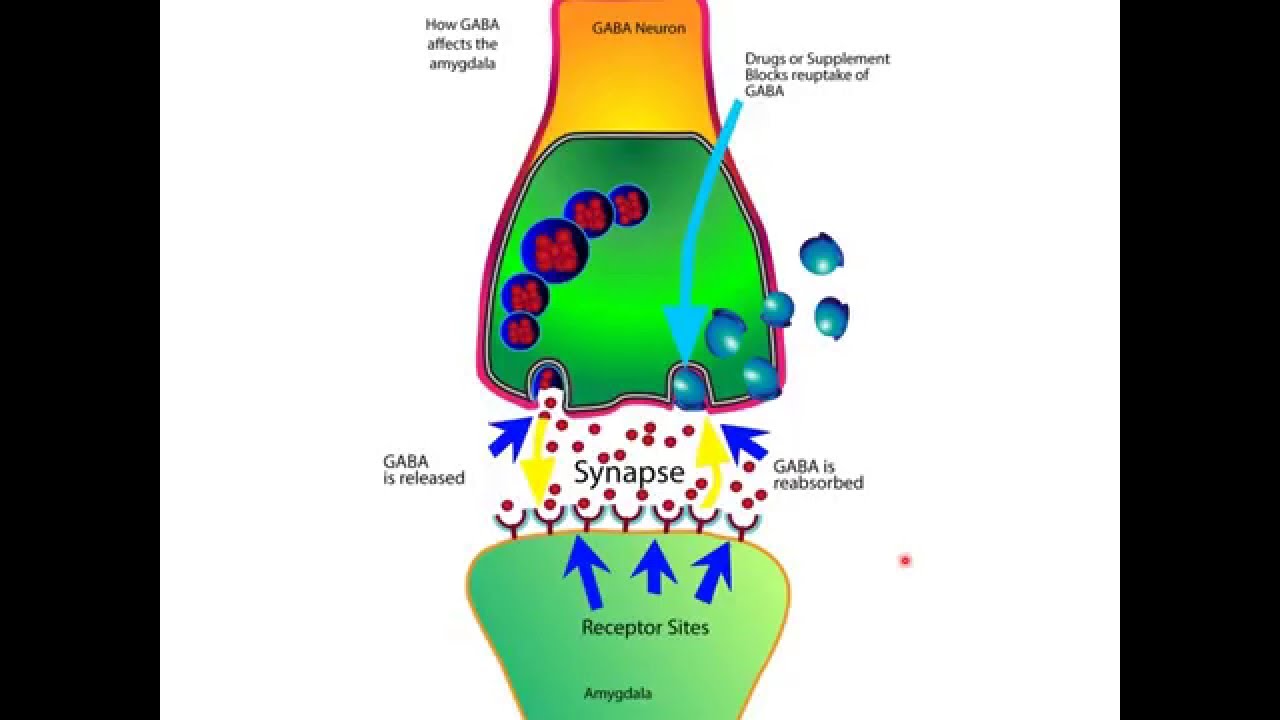
Controindicazioni Quando non dev'essere usato Gabapentin - Farmaco Generico. Non prenda Gabapentin Pfizer. se è allergico (ipersensibile) al gabapentin o ad uno qualsiasi degli altri componenti di questo medicinale (elencati al paragrafo 6). Gabapentin is a prescription medication known as a gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue. GABA reduces the excitability of nerve cells (neurons) in the brain, which play a role in seizures and the transmission of pain signals. Gabapentin mirrors the effects of GABA calming excited neurons. Il gabapentin è strutturalmente correlato al neurotrasmettitore GABA (acido gamma-aminobutirrico) ma il suo meccanismo di azione differisce da quello di numerose altre sostanze attive che interagiscono con le sinapsi GABAergiche quali valproato, barbiturici, benzodiazepine, inibitori della GABA transaminasi, inibitori della captazione GABA GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter, while gabapentin is a synthetic medication designed to mimic GABA’s effects. GABA is available as a supplement, whereas gabapentin requires a prescription and is used for specific medical conditions like epilepsy and neuropathic pain. Il gabapentin si lega ai canali del calcio voltaggio dipendente diminuendo l'attività di numerosi neurotrasmettitori come glutammato, noradrenalina, sostanza P ed amplificando l'attività del neurotrasmettitore GABA aumentandone la concentrazione intersinaptica. È attivo inoltre sull'attività GABAergica non sinaptica. While GABA and gabapentin share structural similarities, they are fundamentally different in their functions and applications. GABA is a neurotransmitter that directly inhibits neuronal activity, whereas gabapentin is a GABA analog that modulates calcium channels to achieve its therapeutic effects. Chemical structures of GABA and gabapentin, with commonalities highlighted. Gabapentin is a 3,3-disubstituted derivative of GABA. Therefore, it is a GABA analogue, as well as a γ-amino acid. [102] [103] It is similar to several other compounds that collectively are called gabapentinoids. Gabapentin (Neurontin) in monoterapia è un’alternativa alla Carbamazepina (Tegretol) in monoterapia nell’epilessia parziale, e ai farmaci antidepressivi triciclici nel dolore neuropatico associato a diabete o alla nevralgia post-erpetica. Pregabalin (Lyrica) è un analogo del GABA strettamente correlato al Gabapentin. The differences between GABA and gabapentin lie in their mechanisms of action in the brain – GABA targets GABA receptors whereas gabapentin interacts with voltage-gated calcium channels. Both GABA and gabapentin are similar to each other but they have their differences. The first point of difference is their structural make-up. Gabapentin is a GABA analog, meaning that it looks very similar structurally but it is not completely the same. GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is an inhibitory neurotransmitter. Although supplementation can increase growth hormone levels, the effects are short-lived. Some research has also reported beneficial effects on sleep quality, stress, and mood. What's the difference between gaba and gabapentin? NT vs Medication: Gaba is a normal neurotransmitter (nt) in the brain and other parts of the nervous system in the body. Gabapentin is a medication that affects GABA in the brain and nervous system. Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Gabapentin is from a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. Though commonly associated, GABA and Gabapentin are distinct entities, each possessing unique characteristics and similarities. This detailed guide delves into their individual attributes, thoroughly examining their differences and exploring their interrelation to dispel any confusion. GABA and gabapentin are often mistakenly used interchangeably, but they are not the same. GABA is an amino acid supplement and neurotransmitter, while gabapentin is a prescription medication. While practitioners may confuse the two, it’s important to understand their differences. Carenza di GABA e condizioni correlate . Bassi livelli di GABA sono stati associati a varie condizioni, tra cui: Disturbi d'ansia. Depressione. Insonnia. Epilessia. Dolore cronico. Disturbo da deficit di attenzione/iperattività . Gabapentin: un imitatore degli effetti del GABA . Il gabapentin è un farmaco da prescrizione classificato come Gabapentin è strutturalmente correlato al neurotrasmettitore GABA (acido gamma-aminobutirrico) ma il suo meccanismo di azione differisce da quello di numerose altre sostanze attive che interagiscono con le sinapsi GABAergiche quali valproato, barbiturici, benzodiazepine, inibitori della GABA transaminasi, inibitori della captazione GABA, GABA GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain that inhibits or slows down nerve activity, helping to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. On the other hand, Gabapentin is a medication that is structurally similar to GABA but does not directly bind to GABA receptors. GABA is not the same as gabapentin. GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is an amino acid supplement and neurotransmitter; gabapentin is a prescription medication. They are often used interchangeably (as you’ll read below) and should not be! Paradossalmente, il gabapentin non mostra alcun tipo di attività GABA-mimetica, ma si ritiene che il suo sito d'azione si trovi sui canali del calcio. Nonostante ciò, l'esatto meccanismo d'azione con cui questo principio attivo riesce a controllare le crisi epilettiche e con cui riesce a indurre analgesia in presenza di dolore neuropatico
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |