Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
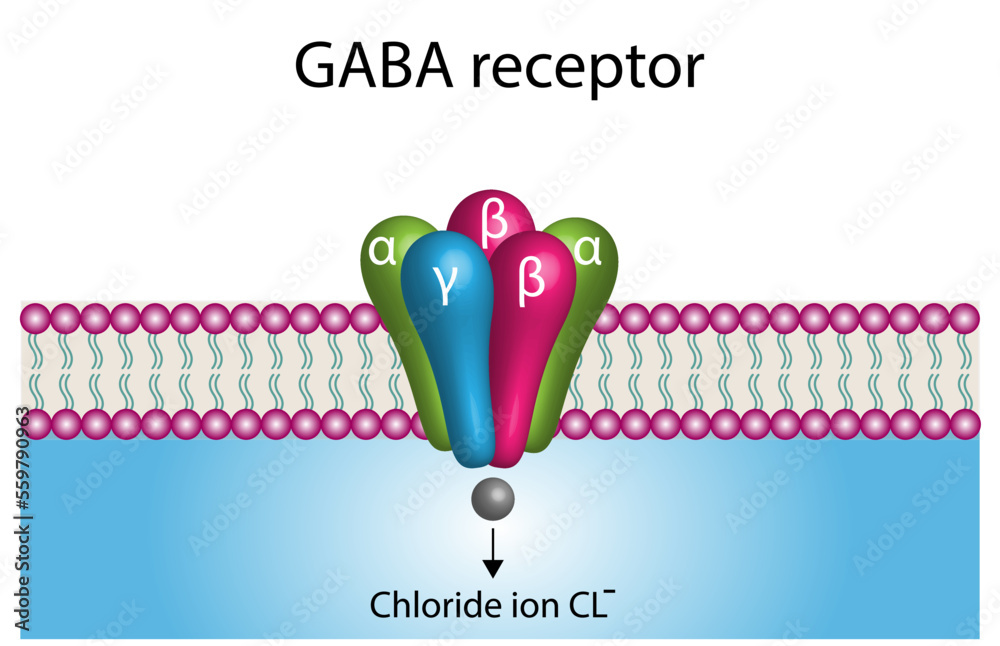
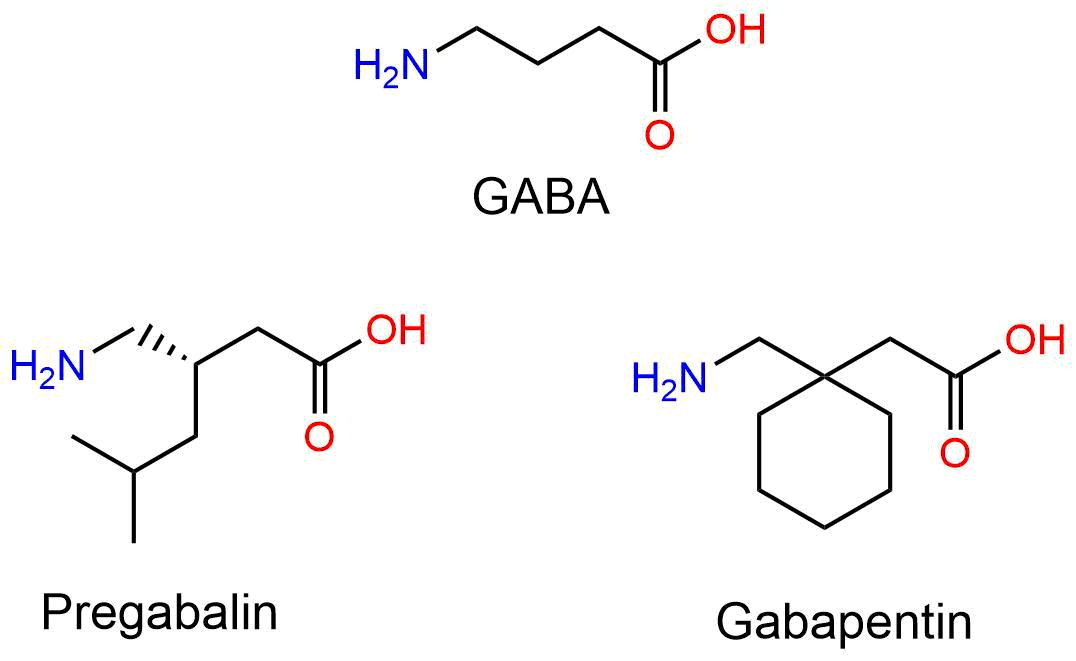
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is an amino acid supplement and neurotransmitter; gabapentin is a prescription medication. They are often used interchangeably (as you’ll read below) and should not be! Here are some of the many responses showing how GABA and gabapentin is used interchangeably by a variety of practitioners: GABA and gabapentin is used interchangeably by a variety of practitioners. Here are some of the many responses showing how GABA and gabapentin is used interchangeably by a variety of practitioners: Jennifer shared this: Yes in the vet world, gabapentin is often called gaba. Not surprising since western medicine likes to pretend that supplements Eines der am häufigsten verschriebenen GABA-Derivate ist Gabapentin. Studien haben gezeigt, dass die Einnahme von Gabapentin die GABA-Konzentration im Gehirn erhöhen kann. Wie genau dieser Mechanismus erfolgt, ist nicht bekannt. Das Medikament wird normalerweise zur Behandlung von Epilepsie verschrieben. [35] Baclofen: A muscle relaxant that promotes GABA-B binding; Valproic acid: Inhibits GABA uptake; acts as a mood stabilizer and anti-epileptic treatment; Zolpidem: Works on the GABA-A receptor for a sedative-hypnotic effect; Gabapentin: Increases GABA function; is commonly prescribed to treat neuropathic pain GABA supplements are classified as dietary supplements and can be purchased over-the-counter, while gabapentin requires a doctor's prescription and medical oversight due to its potential side effects and interactions with other medications. While both relate to the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), they are fundamentally different in their origin, mechanism of action, and legal status. In short, over-the-counter (OTC) GABA is a dietary supplement, while gabapentin is a prescription medication. Both GABA and gabapentin are similar to each other but they have their differences. The first point of difference is their structural make-up. Gabapentin is a GABA analog, meaning that it looks very similar structurally but it is not completely the same. GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is a neurotransmitter in the brain. Learn about the benefits of GABA supplements and its medical significance. gabapentin helps manage nerve pain; baclofen can We compare the side effects and drug effectiveness of Gaba and Gabapentin. The phase IV clinical study is created by eHealthMe based on reports (from sources including the FDA) of 428,042 people who take Gaba and Gabapentin, and is updated regularly. GABA is an amino acid supplement and neurotransmitter, while gabapentin is a prescription medication. While practitioners may confuse the two, it’s important to understand their differences. Key Takeaways: GABA is a natural supplement that helps alleviate anxiety and physical tension. GABA is a natural neurotransmitter that plays a key role in regulating brain activity, while Gabapentin is a synthetic drug designed to mimic some of GABA’s effects to treat specific medical conditions. You must be a member to get the full test results along with ConsumerLab.com recommendations and quality ratings. You will get results for 10 GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) supplements selected for testing by ConsumerLab.com, as well as two other products that are included for having passed the same testing through ConsumerLab's voluntary Quality Certification Program. Gabapentin is a prescription medication known as a gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue. GABA reduces the excitability of nerve cells (neurons) in the brain, which play a role in seizures and the transmission of pain signals. Gabapentin mirrors the effects of GABA calming excited neurons. The differences between GABA and gabapentin lie in their mechanisms of action in the brain – GABA targets GABA receptors whereas gabapentin interacts with voltage-gated calcium channels. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter, while gabapentin is a synthetic medication designed to mimic GABA’s effects. GABA is available as a supplement, whereas gabapentin requires a prescription and is used for specific medical conditions like epilepsy and neuropathic pain. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain that inhibits or slows down nerve activity, helping to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. On the other hand, Gabapentin is a medication that is structurally similar to GABA but does not directly bind to GABA receptors. Child 6–11 years 10 mg/kg once daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 1, then 10 mg/kg twice daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 2, then 10 mg/kg 3 times a day (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 3; usual dose 25–35 mg/kg daily in 3 divided doses, some children may not tolerate daily increments; longer intervals (up to weekly) may be more appropriate, daily dose maximum to be given in 3 divided GABA and Gabapentin, though distinct entities share a common goal: to promote calmness and regulate neuronal activity. While GABA is a natural neurotransmitter with diverse functions, Gabapentin is a synthetic medication mimicking some of its effects for specific therapeutic purposes. Receptor Interaction: GABA works by binding to GABA receptors in the brain, whereas Gabapentin does not directly interact with these receptors. Therapeutic Use: GABA’s role is primarily within the normal functioning of the brain, while Gabapentin is used to treat various neurological disorders. Take-home message: - gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) is a major neurotransmitter that regulates much of our brain function. It was previously thought that ingested GABA could not cross the blood-brain barrier, but new research suggests that it may be able to. - Drugs that mimic the action of GABA are numerous, work in a variety of ways, and can have effects ranging from treating epilepsy to
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |