Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
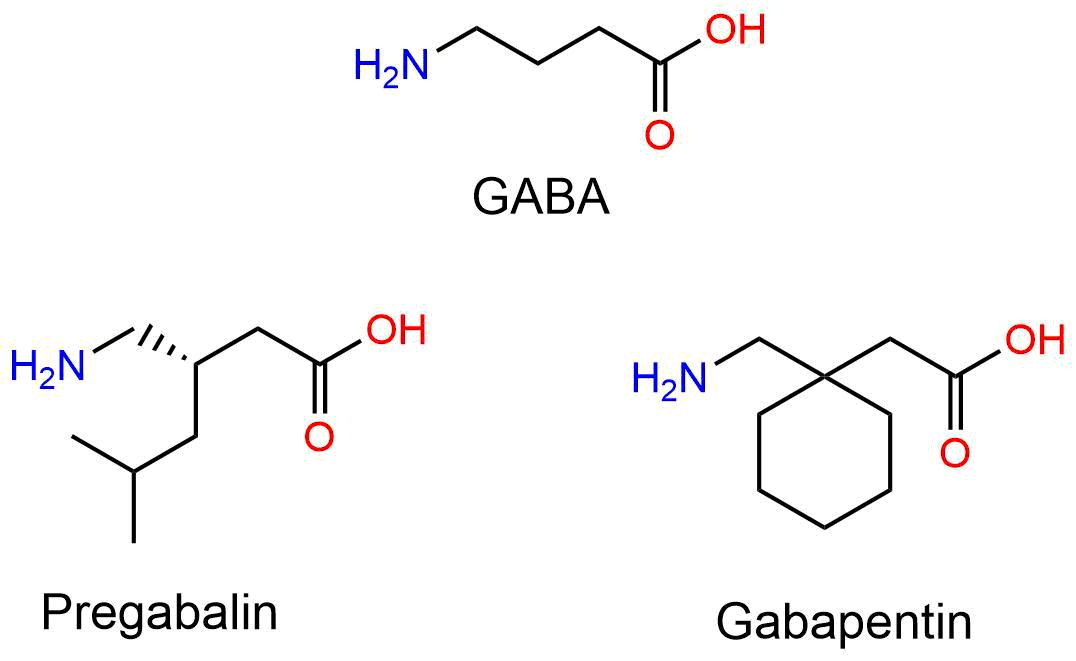 |  |
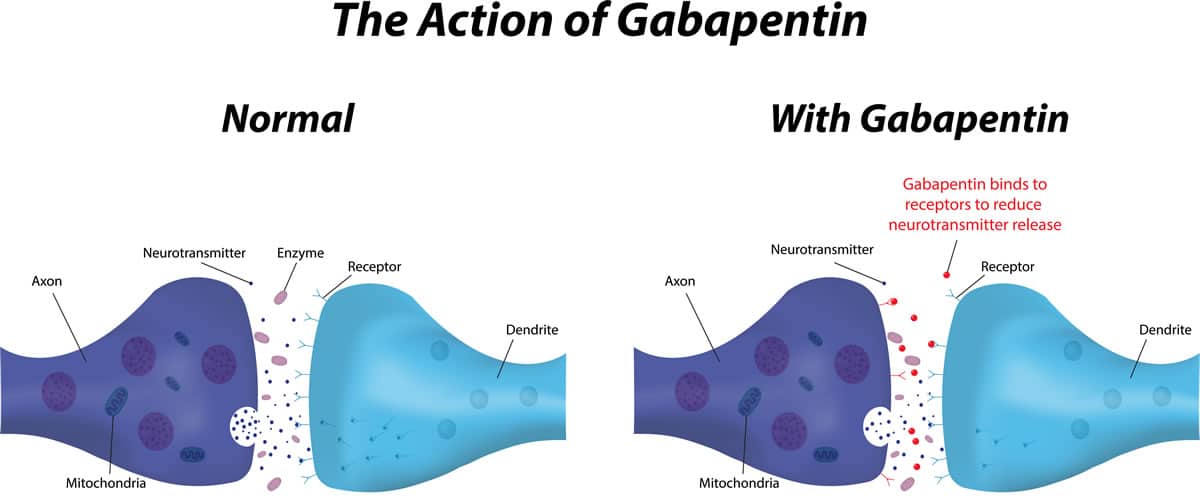
Decoding GABA: Understanding the Differences Between Over-the-Counter Supplements and Gabapentin. Understanding the Nuances: OTC GABA vs. Gabapentin. The Importance of Understanding the Differences; Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) What is GABA, and how does it work? Can you buy GABA over the counter? What are the benefits of taking GABA While gabapentin may help improve sleep for some people (especially if you have another health condition that worsens sleep), it’s unlikely to be the first medication your healthcare provider recommends. Gabapentin vs Trazodone for Sleep: A Comparative Analysis. When comparing the effectiveness of gabapentin and trazodone for sleep disorders, it’s important to consider that their efficacy can vary depending on the specific type of sleep issue and individual patient factors. Dosage and Administration of GABA for Sleep. Determining the optimal GABA dosage for sleep improvement can be a nuanced process, as individual needs can vary significantly. Generally, recommended GABA dosages for sleep range from 100 mg to 1000 mg, taken 30 to 60 minutes before bedtime. Conversely, gabapentin was first synthesized to be a GABA analog. However, gabapentin does not possess the same chemical composition or capacity as GABA. Gabapentin was designed to more readily cross the blood–brain barrier (BBB), in contrast to GABA, and its initial application was in the treatment of epilepsy [3]. Studies have shown that GABA supplements can increase GABA levels in the brain, leading to a range of benefits, including improved sleep quality, reduced anxiety, and enhanced mood. This promising potential of GABA supplements offers hope to those struggling with sleep and anxiety issues. Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) have been found to improve sleep, but the mechanism of action is not clear. 47, 48 A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of Neurontin: Gabapentin · Oral capsule: 100 mg, 300 mg, 400 mg · Oral tablet: 600 mg, 800 mg · Oral solution: 50 milligrams per milliliter (mg/mL) Gralise: Gabapentin · Oral tablet: 300 mg, 600 mg: Horizant: Gabapentin enacarbil · ER tablet: 300 mg, 600 mg: Lyrica: Pregabalin Both GABA and gabapentin are similar to each other but they have their differences. The first point of difference is their structural make-up. Gabapentin is a GABA analog, meaning that it looks very similar structurally but it is not completely the same. The primary function of GABA supplements is sleep. Studies show that GABA supplementation safely helps people to fall asleep more quickly, in one study by 5.3 minutes. GABA promotes sleep by activating the GABA A receptors in the nervous system. In another study, GABA combined with l-theanine, increased sleep latency by 15%, sleep duration by Preliminary evidence indicates that gabapentin can attenuate insomnia, bolster sleep quality, and increase total sleep duration. Moreover, gabapentin has been shown to increase slow-wave sleep (SWS), promote sleep maintenance, and decrease unwanted awakenings throughout the night. While endogenous (naturally produced) GABA is more effective at activating inhibitory brain receptors, there is promising evidence that supplemental GABA can also cross the blood-brain barrier and contribute to a relaxation response, making it easier to fall asleep and stay asleep.*
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |