Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
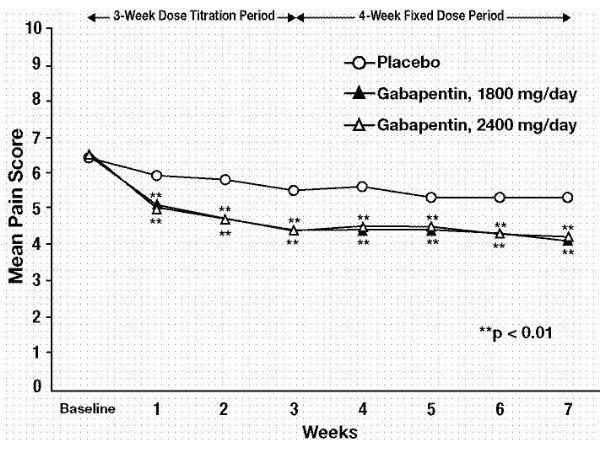 |  |
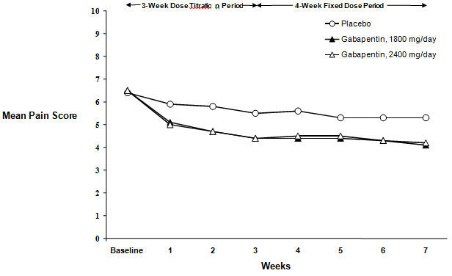
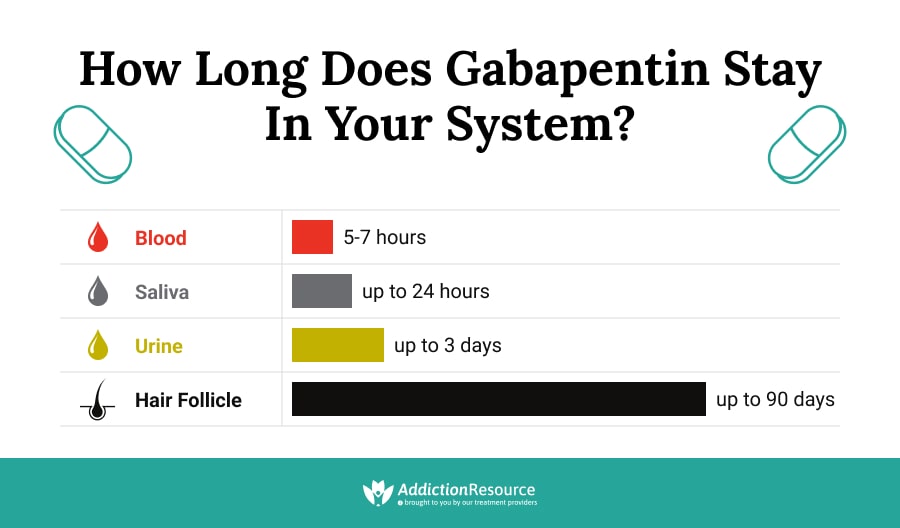
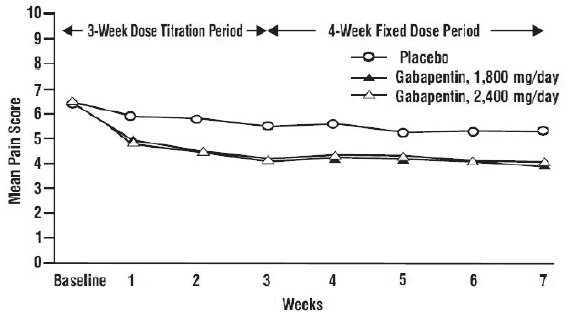
Gabapentin is generally safe in people with liver cirrhosis. [99] Gabapentin is eliminated renally in the urine. [94] It has a relatively short elimination half-life, with the reported average value of 5 to 7 hours. [94] Because of its short elimination half-life, gabapentin must be administered 3 to 4 times per day to maintain therapeutic Adults, normal: 5 to 7 hours; increased half-life with decreased renal function; anuric adult patients: 132 hours; adults during hemodialysis: 3.8 hours. <3% In CrCl <30 mL/minute, half-life is approximately 52 hours (immediate release). Gabapentin has a half-life of 5 to 7 hours, but it can vary by dosage, formulation, and individual factors. Gabapentin’s half-life and how long it stays in the body influence how long the effects last and possible risks. Table 2. Dosage Adjustments for Renal Impairment in Adults Receiving Gabapentin Gastroretentive Tablets60; Cl cr (mL/minute). Adjusted Dosage Regimen. 30–60. 600 mg to 1.8 g once daily; initiate at 300 mg once daily and may titrate according to same schedule recommended for those with normal renal function based on individual patient response and tolerability Gabapentin enacarbil (brand name Horizant) is a prodrug of gabapentin that has been designed to overcome the limitations of gabapentin, such as poor absorption and a short duration of action. It requires hydrolyzation in the gastrointestinal tract to become active. Gabapentin belongs to the group of medicines known as anticonvulsants. 2. Upsides The mean gabapentin half-life ranged from about 6.5 hours (patients with creatinine clearance >60 mL/min) to 52 hours (creatinine clearance <30 mL/min) and gabapentin renal clearance from about 90 mL/min (>60 mL/min group) to about 10 mL/min (<30 mL/min). Gabapentin has a short half life of 5-7 hours and as mentioned, the immediate release formulations are typically dosed three times a day in people with healthy kidney function. The extended release Gralise or Horizant may provide patients with longer steady pain coverage, however they often come with a hefty price tag In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, gabapentin capsules may be initiated on Day 1 as a single 300 mg dose, on Day 2 as 600 mg/day (300 mg two times a day), and on Day 3 as 900 mg/day (300 mg three times a day). The dose can subsequently be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a dose of 1,800 mg/day (600 mg three times a day). The reported half-life (the time it takes for 50% of the drug to be metabolized) is 5 to 7 hours, which necessitates a dosing frequency of 3 to 4 times daily for it to be effective. Most studies report that gabapentin has a duration of action of 6 to 8 hours. To determine the average amount of time it takes to excrete gabapentin, it is necessary to consider its half-life within the range of 5 to 7 hours. This indicates that after you’ve taken a gabapentin dose, approximately 50% will have been cleared from your system within 5 to 7 hours (on average). The recommended dosing interval for 300 mg of gabapentin is 8-12 hours. Gabapentin should be taken in divided doses throughout the day, with the maximum single dose being 600 mg. Spreading out doses helps maintain consistent levels of the medication in the bloodstream. Taking 300 mg every 8-12 hours is a commonly recommended dosing regimen. The half-life of gabapentin is estimated to be anywhere from 5 to 7 hours. It has a constant clearance rate, and its eliminated by renal excretion. Older adults or people with problems in renal function may have a reduced clearance rate if they take the drug. In a study in anuric adult subjects (N=11), the apparent elimination half-life of gabapentin on nondialysis days was about 132 hours; during dialysis the apparent half-life of gabapentin was reduced to 3.8 hours. In adult patients, the half-life of gabapentin is about 5 to 7 hours. In other words, it takes the body about 5 to 7 hours to eliminate its gabapentin concentration by half. This estimate can be altered by many factors including but not limited to kidney function. Half-life for pediatric patients is roughly 4.7 hours. In a study in anuric adult subjects (N=11), the apparent elimination half-life of gabapentin on nondialysis days was about 132 hours; during dialysis the apparent half-life of gabapentin was reduced to 3.8 hours. Hemodialysis thus has a significant effect on gabapentin elimination in anuric subjects. Side effects typically go away within days of stopping gabapentin because of its relatively short half-life. Gabapentin Half-Life. Immediate-release gabapentin has a half-life of about 5–7 hours. In addition to patient-specific factors such as age, kidney function and presence of other medications or substances, this number may increase as This gabapentin half life calculator shows how gabapentin accumulates and how long it stays in your body. Get dose and frequency with ease! In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, gabapentin may be initiated on Day 1 as a single 300 mg dose, on Day 2 as 600 mg/day (300 mg two times a day), and on Day 3 as 900 mg/day (300 mg three times a day). The dose can subsequently be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a dose of 1800 mg/day (600 mg three times a day). The elimination half-life of gabapentin is 5 to 7 hours, and it takes 2 days for the body to eliminate gabapentin from its system. The elimination rate constant, as well as plasma and renal clearance, correlate directly with creatinine clearance. Half-life The elimination t 1/2 of gabapentin in patients with normal renal function is 5-7 hours. 16 , 17 , 5 In patients with reduced renal function, the elimination t 1/2 may be prolonged - in patients with a creatinine clearance of 30 mL/min, the reported half-life of gabapentin was approximately 52 hours. 16 , 17
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |