Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 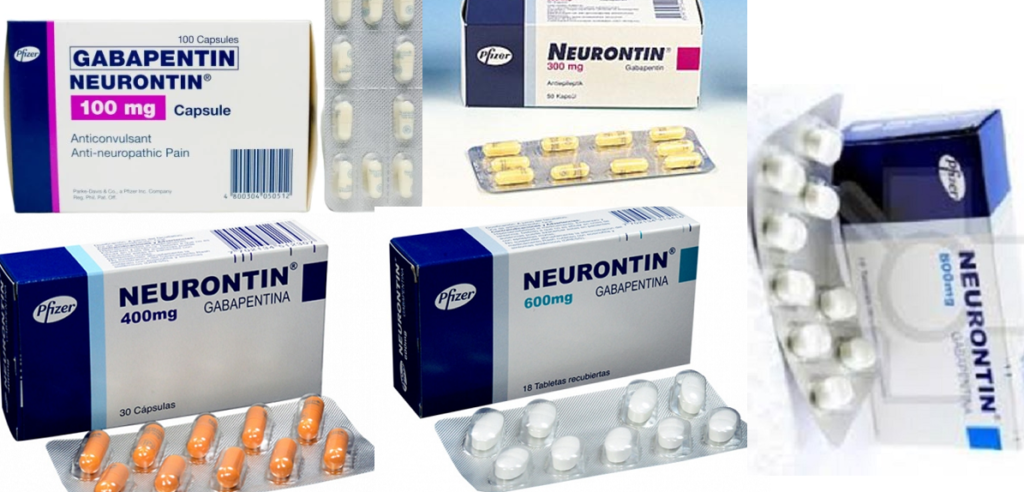 |
Learn about the common, severe, and rare side effects of gabapentin, a drug used to treat nerve pain and seizures. Find out how gabapentin can affect your nervous system, respiratory system, and other body functions. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used to treat seizures, postherpetic neuralgia, and restless legs syndrome. Learn how to take gabapentin, what precautions to follow, and what side effects to expect. Gabapentin is a prescription medication used to treat seizures, nerve pain and restless legs syndrome. Learn about the different forms, strengths and dosages of gabapentin, as well as the possible side effects and interactions with other drugs. Antacids containing aluminum or magnesium may interfere with the absorption of this medication. If you are also taking an antacid, it is best to take gabapentin at least 2 hours after taking the antacid. Different forms of gabapentin (such as immediate-release, sustained-release, enacarbil sustained-release) are absorbed in the body differently. Gabapentin may cause side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, and dizziness. It is important to follow the prescribed dosage and seek medical attention if experiencing serious side effects or changes in mood or behavior. Gabapentin is prescribed by healthcare professionals and should only be taken under medical supervision. Learn how to take gabapentin for epilepsy, postherpetic neuralgia, and restless legs syndrome. Find out the usual, maintenance, and maximum doses for adults and children, and the renal dose adjustments for different strengths and forms of gabapentin. Gabapentin is a medication that treats nerve pain by calming overactive nerves in your body. It may also prevent and control seizures in people with epilepsy. You can take this medication by mouth with a glass of water. Neurontin/Gabapentin comes as a capsule to take by mouth. Neurontin is taken three times a day. To minimize Neurontin side effects, take the very first Neurontin dose at bedtime. Then take this Neurontin medication at evenly spaced times throughout the day and night to ensure a constant level of Neurontin/gabapentin in your body. Gabapentin is commonly used to treat and prevent seizures in people with epilepsy or to treat nerve pain (postherpetic neuralgia) that can occur after a viral infection called shingles. Gabapentin is a prescription drug most commonly prescribed to relieve nerve pain following shingles in adults and the pain of postherpetic neuralgia. Learn about side effects, drug interactions, dosages, warnings, and more. Never take double doses of Neurontin (gabapentin) that’s an adamant rule whereas on Neurontin (gabapentin) medication. However, if you missed a dose on that point and promptly remembered it hours before consequent dose, you will take one to catch up. however if it’s close to the time for consequent dose, higher forego that missed dose and proceed to consequent one. Adulte et enfant de plus de 12 ans: la posologie est individuelle et déterminée par le médecin en fonction de l'efficacité et de la tolérance du traitement ; elle varie habituellement entre 900 mg et 3 600 mg par jour. Enfant de 6 à 12 ans: 25 à 35 mg par kg et par jour, en association avec un autre antiépileptique. Each white, elliptical, film-coated tablet with "Neurontin 800" printed on one side contains 800 mg of gabapentin. Nonmedicinal ingredients: candelilla wax, copolyvidone, cornstarch, hydroypropylcellulose, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, poloxamer 407 NF, red iron oxide, yellow iron oxide, and talc. Adults— At first, 300 milligrams (mg) as a single dose in the evening. Your doctor may adjust your dose as needed and tolerated. However, the dose is usually not more than 1800 mg per day. Children—Use and dose must be determined by your doctor. 800 mg Chaque comprimé ovale, blanc et pelliculé, portant l'inscription « GAB 800 » sur la face sécable et « APO » sur l'autre, renferme 800 mg de gabapentine. Ingrédients non médicinaux : copovidone, hydroxypropylcellulose, hydroxypropylméthylcellulose, stéarate de magnésium, polyéthylèneglycol, eau purifiée et dioxyde de titane. A third study compared gabapentin 900 mg/day, in three divided doses (N=111), and placebo (N=109). An additional gabapentin 1200 mg/day dosage group (N=52) provided dose-response data. A statistically significant difference in responder rate was seen in the gabapentin 900 mg/day group (22%) compared to that in the placebo group (10%). “Neurontin/400 mg” on the cap Tablets • 600 mg: white elliptical film-coated scored tablets debossed with “NT” and “16” on one side • 800 mg: white elliptical film-coated scored tablets debossed with “NT” and “26” on one side Oral solution • 250 mg per 5 mL (50 mg per mL), clear colorless to slightly yellow solution Gabapentin is a medication that modulates calcium channels and is used for various conditions such as epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and restless legs syndrome. The dosage depends on the indication, renal function, and response, and can range from 100 mg to 3.6 g/day in divided doses. Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. The typical starting dosage of gabapentin for seizures is 300 mg by mouth three times a day, with or without food. Your prescriber may adjust your gabapentin dosage to up to 600 mg 3 times a day (1,800 mg per day). The maximum gabapentin dosage is 3,600 mg per day, but higher doses are more likely to cause side effects.Restless legs syndrome
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |