Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
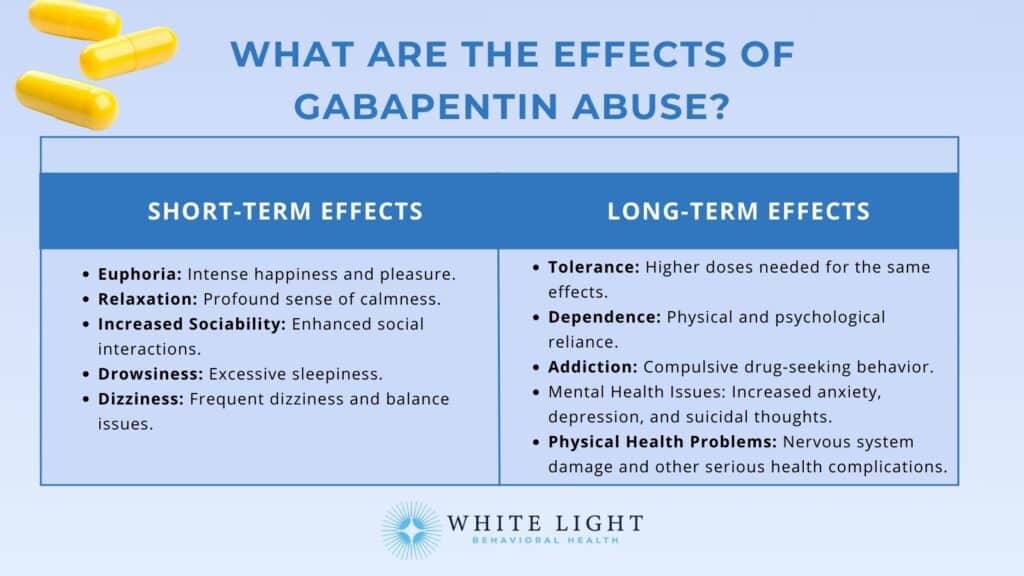 |  |
There have been numerous documented cases of gabapentin abuse, dependence, and withdrawal. Even though gabapentin is sometimes considered as a treatment option for alcohol and substance abuse, it is important to monitor for drug-seeking behaviors. A history of alcohol or substance abuse appears to b When gabapentin is taken alone and as prescribed, there is little potential for abuse or addiction. However, when a person takes gabapentin with other medications—such as muscle relaxants, opioids, or anxiety medications—it can produce a high. Withdrawal symptoms manifesting when gabapentin use is reduced or stopped. Gabapentin addiction can have serious health implications, but with appropriate support and treatment, recovery is possible. Gabapentin Withdrawal Symptoms. Gabapentin can lead to the presentation of withdrawal symptoms when its use is discontinued. The signs and symptoms of gabapentin addiction can vary among individuals, depending on frequency of use, dosage, genetics, and several other factors. These symptoms may affect your daily life and make it difficult to carry out regular tasks, thereby leading you deeper into dependence on the drug. Withdrawal symptoms from gabapentin, which may include anxiety, pain, nausea, and restlessness, can manifest within hours of cessation, underscoring the importance of proper medical supervision during discontinuation. Identifying Gabapentin Addiction: Signs and Symptoms This page will discuss what gabapentin is, side effects of the drug, its misuse liability, symptoms of gabapentin addiction, gabapentin withdrawal, and how a gabapentin rehab program can help with addiction recovery. Gabapentin, an anticonvulsant medication, is generally considered to have a low risk profile for addiction, but some people may still misuse and abuse it to get high. Chronic gabapentin abuse can increase the risk of developing a gabapentin addiction. People who develop physical dependence to gabapentin may experience withdrawal symptoms when they try to come off it. Withdrawal symptoms can begin within 12 hours to 7 days after quitting the medication and last up to 10 days. Symptoms of gabapentin withdrawal may include nausea, dizziness, headaches, insomnia, and anxiety. Gabapentin addiction is a type of anticonvulsant addiction that often begins with a prescription for managing pain or a condition like epilepsy. However, when you take Gabapentin long-term, your body can start to become more tolerant to its pain- or seizure-relieving effects. Gabapentin requires a prescription, but generally has no additional controls (66–69); however, pregabalin, its close structural relative, which was approved after gabapentin, was placed into Schedule V (abuse potential) in the US and included in the European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA)-Europol annual report on new The symptoms of gabapentin addiction include consuming the drug in larger amounts or for longer durations than prescribed, repeated unsuccessful efforts to reduce or control use, spending excessive time obtaining, using, or recovering from gabapentin, experiencing intense cravings, and continuing use despite negative effects on work, school, or Gabapentin is not likely to cause addiction, but it may lead to dependence or misuse under certain conditions. As such, doctors prescribe gabapentin carefully to avoid withdrawal symptoms and Many gabapentin users in early recovery abuse gabapentin because, at high doses (800mg or more), they may experience a euphoric-like high that does not show up on drug screens. Gabapentin abusers typically take the drug in addition to opioids to produce their desired high, a dangerous and potentially deadly combination. While the addiction potential for gabapentin is low compared to other stronger medications, like heroin and oxycodone, ceasing to use it all of a sudden can lead to withdrawal symptoms, a vital indicator of an underlying physical addiction. Though an off-label use, gabapentin has also been found useful in treating certain mental health disorders. 3 So, during addiction treatment, a person could be prescribed gabapentin to help with symptoms of cannabis, opioid, or alcohol use disorders or to help with co-occurring mental disorders such as anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder When taken as prescribed for an intended medical condition, gabapentin is well-tolerated and not considered addictive. However, addiction can occur or worsen when misused illicitly, at higher doses, or combined with opioids. Withdrawal can occur among people who use Neurontin for as little as 3 weeks and symptoms can begin within 12 hours to 2 days after the last use. 9 The effects of Neurontin withdrawal are similar to the symptoms of benzodiazepine withdrawal and may include sweating, anxiety, and irregular heartbeat. 9 Signs of gabapentin addiction include excessive drowsiness, confusion, and uncoordinated movements. Individuals may also exhibit behaviors such as doctor shopping, using higher doses than prescribed, and continuing use despite negative consequences. Psychological signs include anxiety, depression, and cravings for the drug. Signs and Symptoms of Gabapentin Addiction. Gabapentin addiction can cause behavioral changes similar to those of opioid addiction. These include: 12. Compulsive use of gabapentin despite adverse consequences; Experiencing cravings for gabapentin and increasing the dose without a doctor's recommendation Signs that you may be misusing or becoming addicted to gabapentin include: Taking larger doses or using this medicine more frequently than prescribed by your doctor. Experiencing withdrawal symptoms when you try to stop using gabapentin. You are having strong cravings to use gabapentin.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |