Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
/man-with-ankle-in-cast-1aa0f355521d46a484d5ee81444b4c39.jpg) | /rheumatologist-examining-the-hand-of-a-patient-after-surgery-carpal-tunnel--530622518-5a9c48dbc5542e003644cfb2.jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 | /image-56a72afd5f9b58b7d0e78335.jpg) |
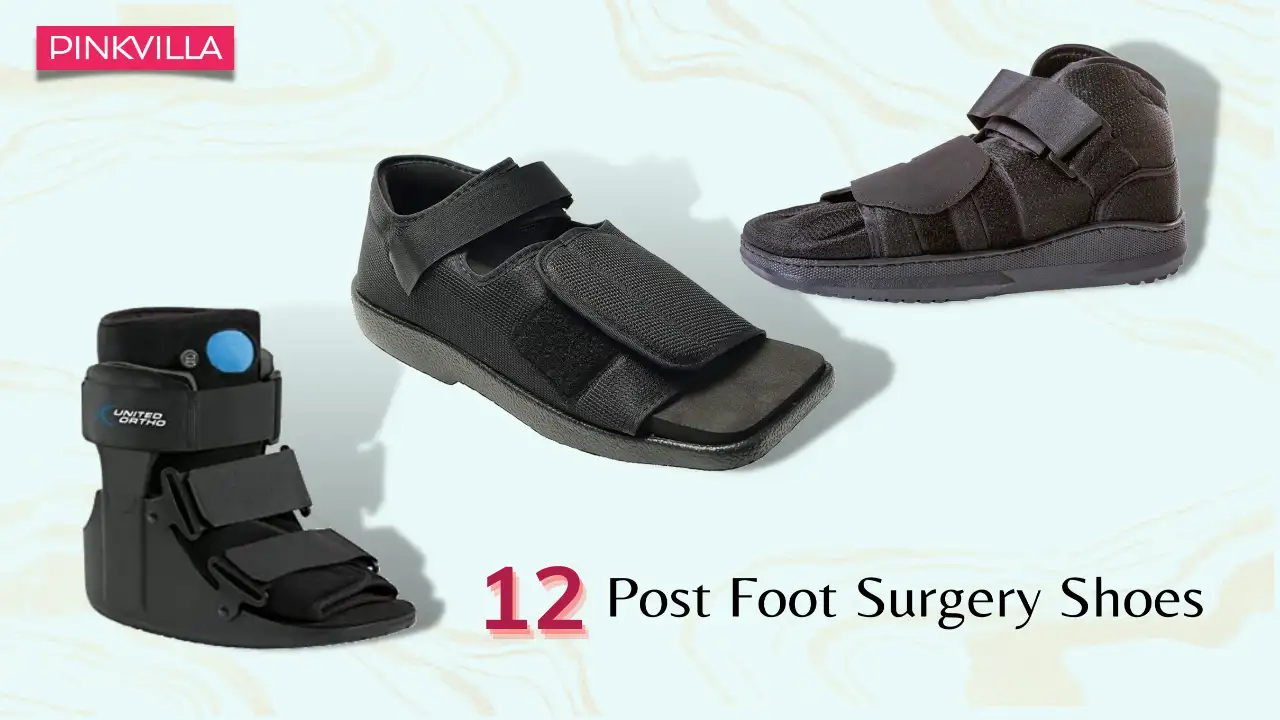 |  |
/sprained-ankle-1082763366-15114792660d4060b021d60c650e3611.jpg) |  |
A combination of therapies and medications will be used together for better pain control after your surgery. How do I know what to take to feel better? When you go home, your pain plan may have you start with a combination of non-medication therapies and non-opioid medications. •to surgery, one nutritional drink 2 hours prior to surgery Gabapentin 600mg #6, one PO taken every 12 hours x 3 days •surgery. Opioid of choice (Oxycodone or Hydrocodone) Table 1. ERAS guidelines adopted for our foot and ankle surgery patients Preoperative doses of the following: • Tylenol 1000 mg PO, given 1 hour prior to surgery Pretty sure I read somewhere 60% of acl surgery patients experience nerve pain, for me personally half of my lower shin muscle was completely numb for a long time but after 4 ish months I realised I had gained all sensation back. after surgery is to start managing it before surgery. Before we take you to the operating room, we will give you a combination of non-opioid pain medicines, such as acetaminophen, celecoxib, gabapentin, ibuprofen and/or ketorolac to take with a sip of water. These medicines reduce inflammation, or swelling, that can lead to pain after surgery. First time I fell out of bed first 2 weeks after surgery. I have wild dreams on the opiates. Smacked my foot on the floor hurt a little more the next two days and then felt like it did before. The total fentanyl consumed after surgery in the first 24 h in the gabapentin group (233.5±141.9) was significantly less than in the placebo group (359.6±104.1; p<0.05). Turan et al., 2006 22 Turkey: Prospective: 40 patients Lower extremity surgery: Gabapentin (n= 20) 1.2 g 1 day before and for 2 days after surgery In this trustworthy systematic review, use of gabapentin for post-operative pain management was scrutinized. In summary, the quality of evidence for a clinically relevant benefit of gabapentin is low, and, importantly, harm may be present. Much of the literature regarding surgical treatment of painful neuroma is published in the upper extremity and hand literature; reports in the lower extremity are comparatively limited with reports ranging from 3.4% after ankle arthroscopy and up to 50% after lower extremity amputation. 12,15,17,25,38 The current review will focus on treatment More than one-fifth of older adults prescribed gabapentin postoperatively filled a prescription >90 days after discharge, especially among patients with more comorbidities and concurrent prolonged opioid use, increasing the risk of adverse drug events and polypharmacy. Following foot and ankle surgery, certain core principles must be considered when formulating a perioperative analgesic regimen. These principles are briefly outlined below, and a review of detailed, evidence-based regimen recommendations is presented in subsequent sections. Their findings, recently published in the journal Anesthesiology, indicate that the analgesic benefits of pregabalin and gabapentin after surgery are negligible, regardless of the dose or type of operation. Gabapentinoids were also ineffective in preventing chronic pain from developing after surgery, one of the primary justifications for using We defined new postoperative gabapentin as fills for 7 days before surgery until 7 days after discharge. We excluded patients whose discharge disposition was hospice or death. The primary outcome was prolonged use of gabapentin, defined as a fill>90 days after discharge. A free text search of “gabapentin orthopedic surgery,” “gabapentinoid orthopedic surgery,” “gabapentin pharmacology,” and “gabapentin surgery” were performed, and 8 articles specific to lower extremity orthopedic procedures and including 609 patients were analyzed. Our last electronic PubMed search was performed in December 2017. 5 weeks after ankle surgery (not bone but ligament and tendon repair). My nerves are waking up right now and it’s not fun. I had some leftover gabapentin from an old injury and I’m going to see if that takes the edge off. Gabapentin is a novel drug used for the treatment of postoperative pain with antihyperalgesic properties and a unique mechanism of action, which differentiates it from other commonly used drugs. Various studies have shown that perioperative use of gabapentin reduces postoperative pain. Medications are often prescribed for short-term pain relief after surgery or an injury. Many types of medicines are available to help manage pain, including opioids and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). pain relief. In rare cases, I may recommend avoiding ibuprofen or aleve after surgery – this will be made clear at the time of surgery. Motrin or Advil (ibuprofen) 600mg every 6 hours OR Celebrex 100mg every 12 hours. Tylenol (acetaminophen) 650mg every 6 hours. Neurontin (gabapentin) 300mg every 8 hours for the first 3 days only. Gabapentin may be effective in reducing postoperative opioid consumption beyond the immediate postoperative period among elective foot and ankle surgery patients. Prospective clinical trials are warranted to further validate these results. They found that gabapentin resulted in a 35% reduction in total analgesic consumption in the first 24 hours following surgery. Gabapentin also resulted in 27% to 39% reduction in visual analog scale (VAS) pain scores in the first 24 hours postoperatively. My doctor told me today that I will most likely never regain full feeling in my foot again following ankle surgery. I have constant pins and needles, burning and itching surrounding my foot. I’m on 600mg Gabapentin 3x a day, I really want to try lyrica because my insurance actually covers it but doctor says gabapentin is fine.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
/man-with-ankle-in-cast-1aa0f355521d46a484d5ee81444b4c39.jpg) | /rheumatologist-examining-the-hand-of-a-patient-after-surgery-carpal-tunnel--530622518-5a9c48dbc5542e003644cfb2.jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 | /image-56a72afd5f9b58b7d0e78335.jpg) |
 |  |
/sprained-ankle-1082763366-15114792660d4060b021d60c650e3611.jpg) |  |