Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
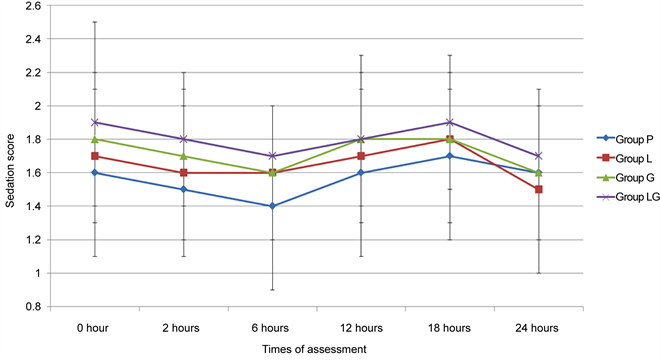
A prior case report by Kavalieratos and Dimou demonstrated successful pain management of a blind glaucomatous eye with gabapentin after 6 months of treatment. 21 Similarly, we present a case of chronic ocular pain treated successfully with low-dose gabapentin. The case described herein involves a lower treatment dose than described in the In the absence of either criteria, discontinue prior to surgery. Irreversible MAO antagonists may require 2 weeks after discontinuation of drug for normal MAO function to return. Therefore these medications should be tapered and discontinued two weeks before elective surgery. De-Paris and colleagues reported that gabapentin reduced anxiety induced by simulated public speaking in human volunteers [16] in agreement to the present study results, Me´nigaux and colleagues studied the effects of preoperative 1200 mg oral gabapentin on pain and anxiety after knee surgery and they reported, decreased pain scores, anxiety I had cataract surgery 9 months ago on both eyes. After the right eye surgery, I had stabbing pain if I moved my right eye too extremely, looked far to the right or looked down sharply. I was told that it would go away. It has been 9 months, and if I move my right eye too far down or right, I hit an instant 20 on a pain scale of 0-10. 2) If patient is taking gabapentin, do not order pregabalin. Inform patient to take gabapentin dose on DOS. 3) If patient is extremely frail or you have concerns about multiple drug interactions causing over sedation, it is OK if you don’t order the medication. The anesthesia team should look at these orders the day prior to surgery. 4) Pregabalin and gabapentin are effective in reducing postoperative pain following refractive surgeries, with pregabalin showing a greater effect. Both medications are safe, with no significant increase in adverse events. Purpose: To evaluate oral gabapentin for postoperative pain after photorefractive keratectomy (PRK). Design: Prospective, nonrandomized clinical trial. These studies have found that post-PRK pain peaks the day of or the day after surgery and then decreases until re-epithelialization is complete, which for most patients occurs by 96 hours after surgery. 1-3 Almost all patients report post-PRK pain, and a majority report the pain levels as severe (≥ 7/10) for at least a portion of the recovery Gabapentin is a novel drug used for the treatment of postoperative pain with antihyperalgesic properties and a unique mechanism of action, which differentiates it from other commonly used drugs. Various studies have shown that perioperative use of gabapentin reduces postoperative pain. Pregabalin and gabapentin are effective in reducing postoperative pain following refractive surgeries, with pregabalin showing a greater effect. Both medications are safe, with no significant increase in adverse events. Odin was prescribed gabapentin as an adjunct to a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) to treat pain from a chronic eye condition. After the problematic eye was removed, gabapentin was given post-surgically and then tapered off. As you can probably tell, I am a huge fan of gabapentin for dogs. Postoperative opioid consumption was reduced when using gabapentin within the initial 24 hours following surgery (standard mean difference −1.35, 95% confidence interval [CI]: −1.96 to −0.73; P <0.001). There was a significant reduction in morphine, fentanyl, and tramadol consumption (P <0.05). Researchers evaluated a random sample of 1,307 patients who developed AAG after gabapentin and pregabalin exposure in the year before diagnosis. The sample, drawn from a medical and pharmaceutical claims database over a 10-year period ending Dec. 31, 2016, also included 13,070 controls. Dry eye is the leading cause of pain and discomfort after refractive surgery. Artificial tears, nutritional supplements such as omega 3 fatty acids and flax seed oil, lacrimal punctal occlusion, lifitegrast and topical cyclosporine may alleviate the symptoms of dry eye. LASIK induces neurotrophic epitheliopathy and thus causes ocular dryness. The details of a study by Seoul National University Hospital recently published to clinicaltrials.gov will evaluate the effectiveness of pretreatment with gabapentin after the first operation on reduction of pain at second operation. First, we repeated the analysis by defining gabapentin exposure on the day of surgery without requiring a 2-day minimum length of stay after surgery. Then, we explored a dose-response relationship using a 4-dose category of gabapentin (no use, 1 mg to <600 mg, 600 mg to <1200 mg, or ≥1200 mg). But gabapentinoids also have risks and there is little evidence to support their use for postoperative pain relief, according to a large new study by a team of Canadian researchers. “No clinically significant analgesic effect for the perioperative use of gabapentinoids was observed. We defined new postoperative gabapentin as fills for 7 days before surgery until 7 days after discharge. We excluded patients whose discharge disposition was hospice or death. The primary outcome was prolonged use of gabapentin, defined as a fill>90 days after discharge. They found that gabapentin resulted in a 35% reduction in total analgesic consumption in the first 24 hours following surgery. Gabapentin also resulted in 27% to 39% reduction in visual analog scale (VAS) pain scores in the first 24 hours postoperatively.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |