Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
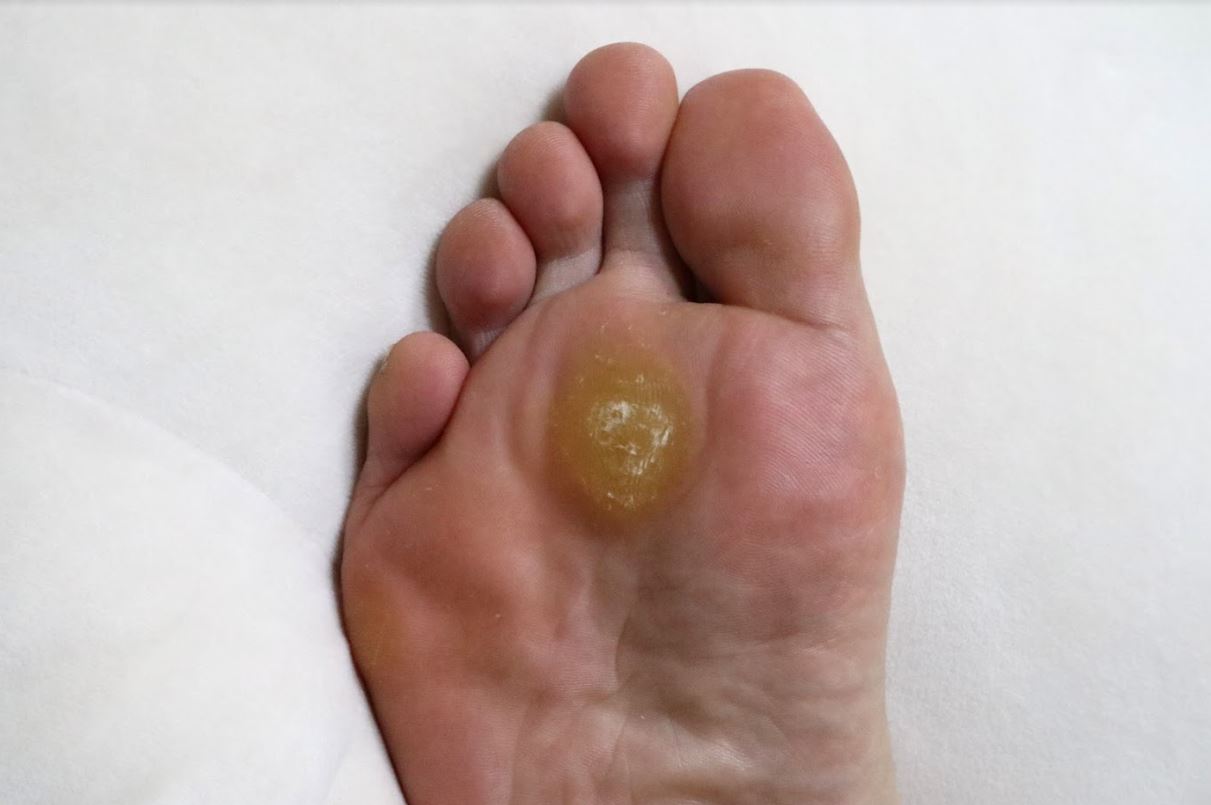
We defined new postoperative gabapentin as fills for 7 days before surgery until 7 days after discharge. We excluded patients whose discharge disposition was hospice or death. The primary outcome was prolonged use of gabapentin, defined as a fill>90 days after discharge. VAS-pain scores and opioid consumption was significantly reduced, and satisfaction with post-operative pain management was higher among patients who received gabapentin. 52 McKissac et al. performed a retrospective review highlighting that patients receiving gabapentin after foot and ankle procedures consumed significantly fewer opioids than But gabapentinoids also have risks and there is little evidence to support their use for postoperative pain relief, according to a large new study by a team of Canadian researchers. “No clinically significant analgesic effect for the perioperative use of gabapentinoids was observed. They found that gabapentin resulted in a 35% reduction in total analgesic consumption in the first 24 hours following surgery. Gabapentin also resulted in 27% to 39% reduction in visual analog scale (VAS) pain scores in the first 24 hours postoperatively. I just want to know if anyone has used or is still using gabapentin for neuropathy. I had foot surgery in 2015 and l had nerve pain so my surgeon put me on gabapentin and it wasn't once a day or twice a day. The purpose of this study is to assess whether gabapentin acts synergistically to improve postoperative pain among patients undergoing foot and ankle surgery. Methods: Patients from a single institution who underwent elective foot and ankle surgery were identified using CPT codes 27700, 27702, 27870, 28705, 28715, 28725, 28730, and 28740. Gabapentin is a novel drug used for the treatment of postoperative pain with antihyperalgesic properties and a unique mechanism of action, which differentiates it from other commonly used drugs. Various studies have shown that perioperative use of gabapentin reduces postoperative pain. after surgery is to start managing it before surgery. Before we take you to the operating room, we will give you a combination of non-opioid pain medicines, such as acetaminophen, celecoxib, gabapentin, ibuprofen and/or ketorolac to take with a sip of water. These medicines reduce inflammation, or swelling, that can lead to pain after surgery. What Helps With Nerve Pain After Surgery? Treatment options for nerve damage and pain after surgery include: Orthobiologics (e.g. platelet-rich plasma — PRP) Physical therapy may help. Medications that are commonly used to treat nerve damage after surgery include: Neurontin (Gabapentin) (12) Lyrica (Pregabalin) (13) Elavil (Amitriptyline) (14 Neurontin (gabapentin) 300mg every 8 hours for the first 3 days only. Hydroxyzine 25mg (or 10mg if >65 years of age) every 6 hours. Opiate Medications These medications should be used sparingly, just as needed, and for the first few days after surgery. Please see the below guidelines for details. 53 While more randomized clinical trials are needed to analyze further the effect of gabapentin on pain and opioid consumption after foot and ankle surgery, the current literature supports its Gabapentin is commonly indicated in the treatment of seizures. 27 Gabapentin, which acts on the nociceptive processes involved in central sensitization, has been shown to reduce hypersensitivity associated with nerve injury (hyperalgesia) and postoperative pain and inflammation in animal models. 28 Interestingly, gabapentin’s antiemetic Medications are often prescribed for short-term pain relief after surgery or an injury. Many types of medicines are available to help manage pain, including opioids and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Similarly, aside from 24 h after surgery, gabapentin significantly reduced pain with movement (25–27,31,34,35,37,38) by 18% to 28% (VAS 8.2 mm to 10.2 mm) after surgery . The pooled effects on VAS pain scores displayed significant heterogeneity, which was not explained by subgroup analyses based on surgical procedure, gabapentin dose or study The total fentanyl consumed after surgery in the first 24 h in the gabapentin group (233.5±141.9) was significantly less than in the placebo group (359.6±104.1; p<0.05). Turan et al., 2006 22 Turkey: Prospective: 40 patients Lower extremity surgery: Gabapentin (n= 20) 1.2 g 1 day before and for 2 days after surgery A free text search of “gabapentin orthopedic surgery,” “gabapentinoid orthopedic surgery,” “gabapentin pharmacology,” and “gabapentin surgery” were performed, and 8 articles specific to lower extremity orthopedic procedures and including 609 patients were analyzed. Our last electronic PubMed search was performed in December 2017. The purpose of this review is to critically appraise the evidence for the use of gabapentinoids for acute pain management and its impact on the development of chronic pain after surgery. Recent findings: Recent meta-analyses have revealed that prior data likely have overestimated the beneficial effects of gabapentinoids in acute perioperative Peri-operative gabapentin administration is effective in reducing pain scores, opioid requirements and opioid-related adverse effects in the first 24 hours after surgery. No serious side-effects were observed, though sedation was associated with gabapentin use. Several publications have shown that gabapentin, as a solo adjunct, decreases postoperative pain. Gabapentin is a synthetic analogue of g-amino butyric acid. It reduces neuron excitability and inhibits pain transmission through the spinal cord.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |