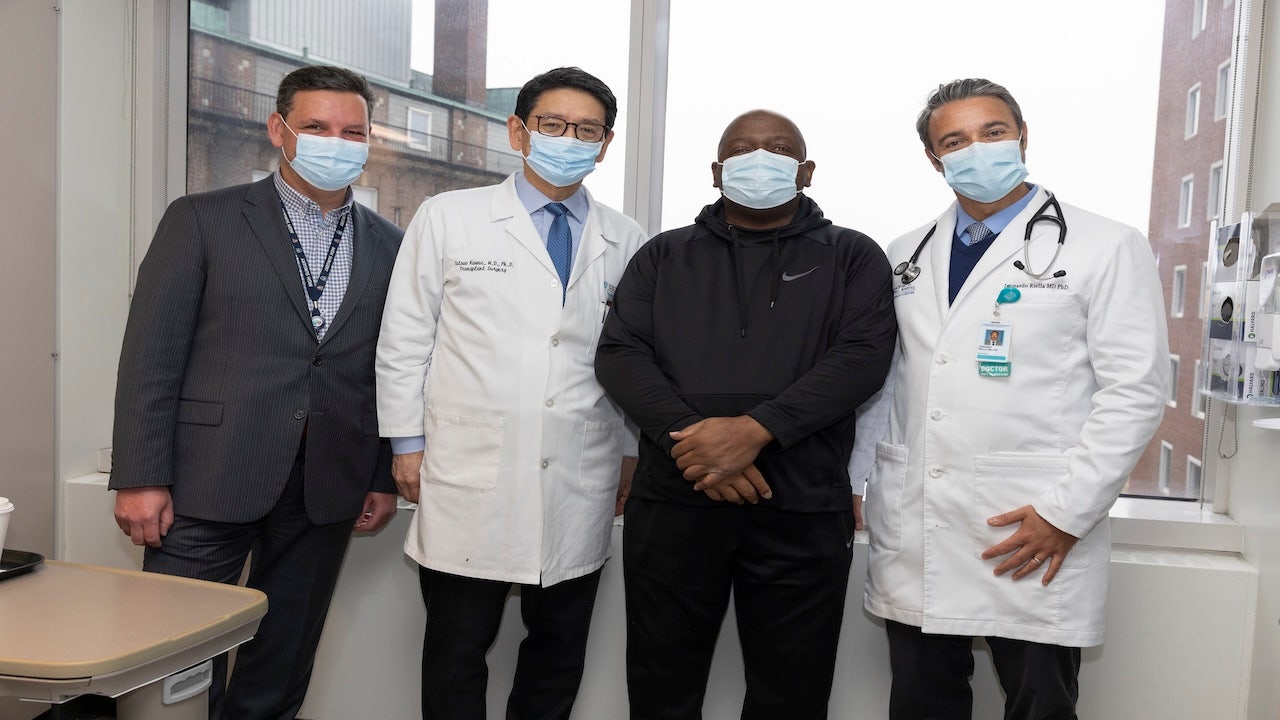
Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
In this issue of CJASN, Chen et al. 5 present results of an observational study using national registry data from the United States Renal Data System (USRDS), demonstrating new evidence that gabapentinoids are associated with a higher risk of death among kidney transplant recipients. Opioid use after kidney transplant has been associated with an increased risk of death and graft loss. Several transplant centers have reported reductions in opioid use using multimodal analgesia and education. This study evaluated the impact of an opioid minimization protocol on inpatient opioid us Strategies to Manage Neuropathy after Transplant. Friday May 3, 2024. Presenter: Kelsey Barrell MD, Assistant Professor in the Division of Neuromuscular Medicine, University of Utah. Presentation is 37 minutes long with 21 minutes of Q & A. Summary: Many bone marrow/stem cell transplant patients experience neuropathy (nerve pain) after Gabapentin has shown great effectiveness in managing post-transplant pain and improving the overall quality of life for kidney transplant recipients. Gabapentin works by reducing the abnormal electrical activity in the brain, which can help to alleviate pain sensations. Materials and methods: The medical data of 553 kidney transplant recipients and 258 liver transplant recipients who received transplant procedures at the Baskent University Transplantation Center between 2008 and May 2016 were retrospectively reviewed. Fifty-one patients who were examined by an expert neurologist and diagnosed with neuropathic Your care team is a group of experts who will instruct you on staying healthy after a kidney transplant. If you have questions about making healthy choices, ask your transplant care team. For more resources and information on post-transplant care, visit the National Kidney Foundation and United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS). kidney failure and worsen high blood pressure. High doses of salicylates may also cause kidney problems and should be avoided. Low dose asprin (81mg or 325mg once daily) for prevention of heart disease appears to be safe but you still must have your creatinine followed closely. Acetaminophen is the OTC pain medication of choice for transplant Neurologic diseases after kidney transplantation are frequently underdiagnosed and have been reported in up to 30%–60% of patients . Notably, in a systematic review and meta-analysis by Mohammadi et al. , the total prevalence of neurologic disorders in 4674 patients after kidney transplantation was 8%. We found that patients with chronic kidney disease had elevated serum gabapentin concentrations, in some cases leading to gabapentin toxicity; those with advanced age and multiple comorbidities were more prone to the toxicity, and the toxicity tended to be underrecognized. The medicines you will be taking after your transplant to keep your body from rejecting your new kidney are called immunosuppressants. You will have to take these medicines every day for as long as you have your transplant. Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. Kidney transplant is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for 1 - 2 years also take Aspirin, and have Hyperparathyroidism secondary. Opioid use after kidney transplant has been associated with an increased risk of death and graft loss. Several transplant centers have reported reductions in opioid use using multimodal analgesia and education. This study evaluated the impact of an Gabapentinoids, commonly used for treating neuropathic pain, may be misused and coprescribed with opioid and benzodiazepine, increasing the risk of mortality and dependency among kidney transplant recipients. We suggest that gabapentin may cause acute renal dysfunction by a mechanism involving renal afferent vasoconstriction. Caution should be employed when considering the use of gabapentin in transplant recipients, especially when combined with other agents that may potentiate renal vasoconstriction. In the context of pruritus, studied doses have actually been lower, ranging from 100 to 300 mg three times per week to 400 mg of gabapentin two times per week after dialysis 7–11,49 and 25–75 mg of pregabalin daily 11,50 and 75 mg three times per week postdialysis. 12,51 Similarly, gabapentin doses ranging from 200 to 300 mg three times per Kidney transplant recipients prescribed gabapentinoids had a higher risk of post-transplant mortality, and the risk was higher with opioids or benzodiazepine coprescription. Gabapentinoid coprescription with both benzodiazepines and opioids among kidney transplant recipients increased over time. Gabapentinoid coprescription with both benzodiazepines and opioids among kidney transplant recipients increased over time. Kidney transplant recipients prescribed gabapentinoids had a higher risk of post-transplant mortality, and the risk was higher with opioids or benzodiazepine coprescription. Herbal supplements are typically not allowed after transplant due to potential harm to the transplanted organ and drug interactions with the transplant medicines. Multivitamins are safe to take post-transplant but you must be sure they do not contain any ingredients that may be harmful including herbal supplements or ingredients that "boost In the context of pruritus, studied doses have actually been lower, ranging from 100 to 300 mg three times per week to 400 mg of gabapentin two times per week after dialysis 7–11, 49 and 25–75 mg of pregabalin daily 11, 50 and 75 mg three times per week postdialysis. 12, 51 Similarly, gabapentin doses ranging from 200 to 300 mg three times
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |