Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/neck-surgery-recovery-5088728-FINAL-6cc0d7c853d142d892c31fa3795af00f.jpg) |  |
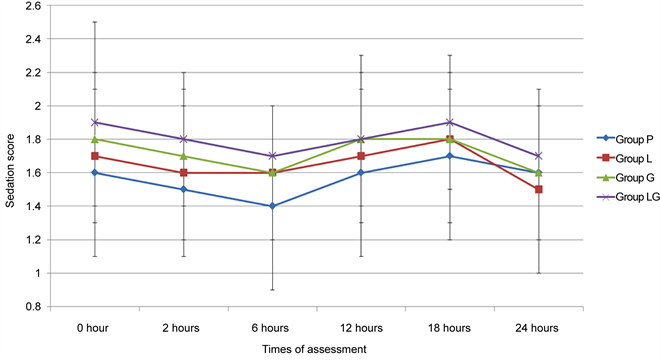
y and safety of gabapentin for pain management following spinal surgery. Methods: In January 2017, a systematic computer-based search was conducted in PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, and Google database. Data on patients prepared for spine surgery in studies that compared gabapentin versus placebo were retrieved. The primary endpoint was the visual The total fentanyl consumed after surgery in the first 24 h in the gabapentin group (233.5±141.9) was significantly less than in the placebo group (359.6±104.1; p<0.05). Turan et al., 2006 22 Turkey: Prospective: 40 patients Lower extremity surgery: Gabapentin (n= 20) 1.2 g 1 day before and for 2 days after surgery They found that gabapentin resulted in a 35% reduction in total analgesic consumption in the first 24 hours following surgery. Gabapentin also resulted in 27% to 39% reduction in visual analog scale (VAS) pain scores in the first 24 hours postoperatively. The goal of this study was to investigate gabapentin use in patients undergoing larger head and neck mucosal operations associated with significant risk of postoperative pain and dysphagia. 24 A 300-mg dose of gabapentin given twice daily was selected and continued for 3 days including the day of surgery. We selected narcotic use as an In addition, a high dose (≥900 mg/d) of gabapentin is more effective than a low dose (<900 mg/d). The number of included studies is limited, and more studies are needed to verify the effects of gabapentin in spinal surgery patients. Keywords: gabapentin, meta-analysis, spine surgery. 1. Introduction Increasing numbers of randomized trials indicate that gabapentin is effective as a postoperative analgesic. This procedure-specific systematic review aims to analyse the 24-hour postoperative effect of gabapentin on acute pain in adults. Patients who undergo head and neck mucosal surgery and receive perioperative gabapentin treatment perceive less postoperative pain. Effective postoperative pain management increases patient satisfaction, reduces cost, reduces morbidity, and shortens hospitalizations. A significant number of RCTs have demonstrated conflicting results in the use of preoperative gabapentin. 19 Bharti et al 20 studied gabapentin administration among patients (n=40) undergoing mastectomy (20 received gabapentin and 20 received placebo) and demonstrated a reduction in the amount of morphine required during the initial 24 hours Peri-operative gabapentin administration is effective in reducing pain scores, opioid requirements and opioid-related adverse effects in the first 24 hours after surgery. No serious side-effects were observed, though sedation was associated with gabapentin use. Objective: To investigate the effect of perioperative gabapentin treatment on postsurgical pain in patients undergoing head and neck mucosal surgery. Gabapentin is a novel drug used for the treatment of postoperative pain with antihyperalgesic properties and a unique mechanism of action, which differentiates it from other commonly used drugs. Various studies have shown that perioperative use of gabapentin reduces postoperative pain. Gabapentin for Postoperative Pain 1 Gabapentin for Postoperative Pain Management in Lumbar Fusion Surgery Eli A Perez BS1, Emanuel Ray BS1, Brian J Park MD1, Colin J Gold MD1, Ryan M Carnahan PharmD MS2, Matthew Banks PhD3, Robert D. Sanders MBBS 4,5, Catherine R Olinger MD6, Rashmi N Mueller MD1,7, Royce W Woodroffe MD1 Would you want to take Lyrica (pregabalin) or Neurontin (gabapentin) for pain relief after a major surgery? Both drugs belong to a class of nerve medication called gabapentinoids that are increasingly being prescribed to patients perioperatively (after surgery) as an alternative to opioid medication. Therefore, the authors investigated, in a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study, the effects of gabapentin on acute postoperative pain and morphine consumption in patients undergoing spinal surgery. Methods: After standard premedication, 25 patients in the control group received oral placebo, and 25 patients in the gabapentin group We defined new postoperative gabapentin as fills for 7 days before surgery until 7 days after discharge. We excluded patients whose discharge disposition was hospice or death. The primary outcome was prolonged use of gabapentin, defined as a fill>90 days after discharge. Opioid Management. Opioids remain a mainstay therapy for patients undergoing spine surgery. However, opioid therapy can also result in a number of adverse effects including nausea, vomiting, constipation, ileus, urinary retention, sedation, and respiratory depression. 5 Given increased attention to opioid-related adverse effects including persistent postoperative opioid use, opioid misuse, and Overall, gabapentin appears to have a significant beneficial effect on perioperative pain relief and analgesic consumption in otorhinolaryngology-head and neck surgery procedures within the first 24 hours. Background: Pain management after spinal surgery has been studied for years. Gabapentin is a third-generation antiepileptic drug that selectively affects the nociceptive process and has been used for pain relief after surgery. However, the relationship between gabapentin and postoperative pain in spinal surgery is still controversial. Perioperative gabapentin, 1200 mg, administered preoperatively plus 600 mg every 8 hours continued for 72 hours after surgery did not affect time to pain cessation, the rate of pain resolution, or the proportion of patients with chronic pain at 6 months or 1 year following surgery.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/neck-surgery-recovery-5088728-FINAL-6cc0d7c853d142d892c31fa3795af00f.jpg) |  |