Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | &w=&do-not-index) |
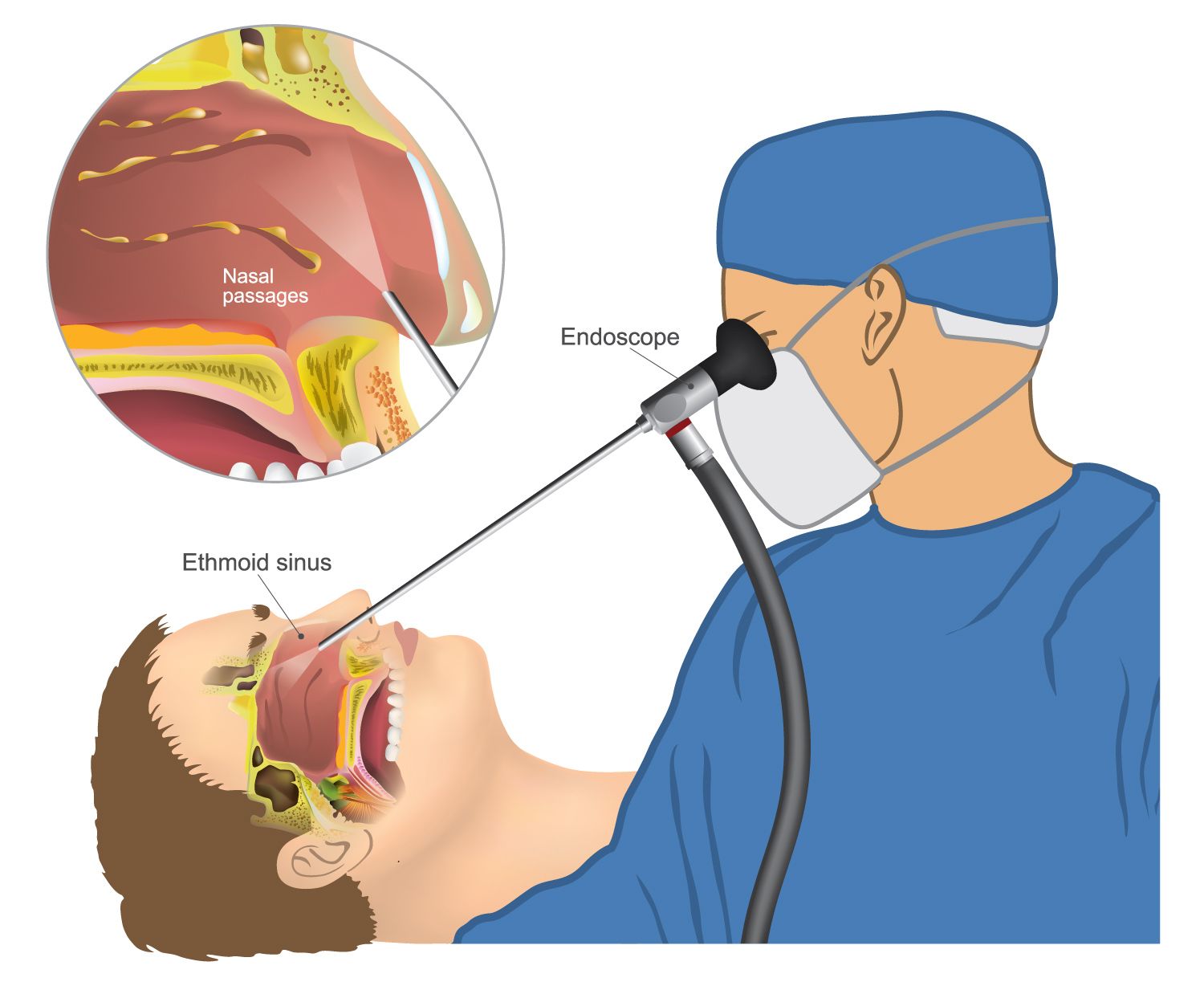
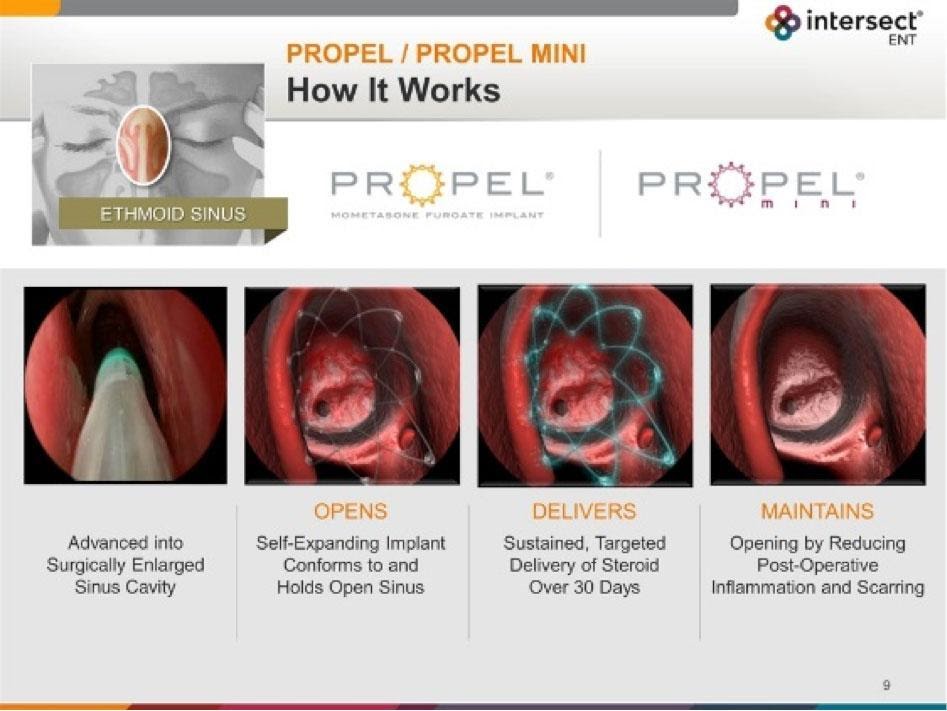
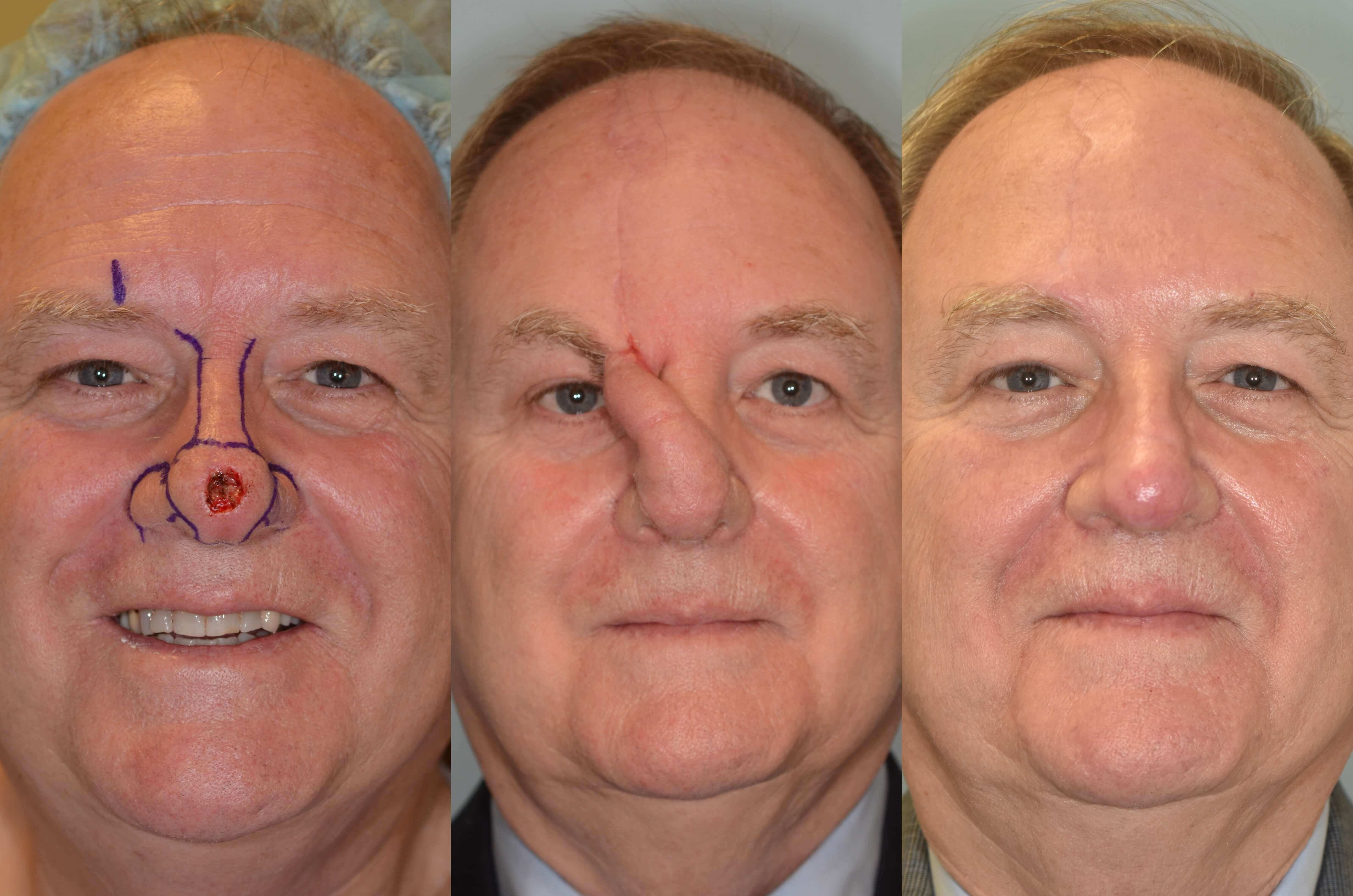
after the procedure. Patients should be counseled that: » Pain immediately after surgery is normal and an expected part of the healing process. » Pain is worst in the first 1-2 days after surgery, but improves over time. » Most pain can be effectively managed with medicines other than opioids, such as NSAIDS, acetaminophen, gabapentin Objective: This study investigates the impact of postoperative gabapentin on opioid consumption and pain control following endoscopic sinus surgery (ESS) and/or septoplasty. Methods: Patients who underwent ESS and/or septoplasty at a single institution from 2021 to 2022 were enrolled. There is so much information available about what to expect before and after sinus surgery; too much to go into here. So i am advising you to do a web search on 'sinus surgery'. If you know the specific kind of surgery you will have, such as septoplasty or balloon sinuplasty, you will narrow down the search. Gabapentin is a novel drug used for the treatment of postoperative pain with antihyperalgesic properties and a unique mechanism of action, which differentiates it from other commonly used drugs. Various studies have shown that perioperative use of gabapentin reduces postoperative pain. Most otolaryngology studies 17-22 that investigated gabapentin for acute postsurgical pain administered 600 to 1200 mg in a single preoperative dose and reported reduced pain medication use for up to 24 hours in patients undergoing tonsillectomy, thyroidectomy, and sinus surgery. Our cohort included more extensive operations, although Methods: Chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) patients undergoing functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS) with or without septoplasty were randomized to receive a 7-day pre- and post-operative course of placebo or gabapentin, starting at 300 mg daily and titrated to 300 mg three times daily, in a double-blind fashion. Primary endpoint was pain level Chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) patients undergoing functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS) with or without septoplasty were randomized to receive a 7-day pre- and post-operative course of placebo or gabapentin, starting at 300 mg daily and titrated to 300 mg three times daily, in a double-blind fashion. They found that gabapentin resulted in a 35% reduction in total analgesic consumption in the first 24 hours following surgery. Gabapentin also resulted in 27% to 39% reduction in visual analog scale (VAS) pain scores in the first 24 hours postoperatively. Gabapentin is commonly indicated in the treatment of seizures. 27 Gabapentin, which acts on the nociceptive processes involved in central sensitization, has been shown to reduce hypersensitivity associated with nerve injury (hyperalgesia) and postoperative pain and inflammation in animal models. 28 Interestingly, gabapentin’s antiemetic The etiology of pain after sinus surgery is incompletely understood, but it is thought to partially correlate with the degree of innervation of the anatomical structures affected by surgery. Manipulation of the septum and lateral nasal wall, which are largely innervated by the nasopalatine nerve, a branch of the maxillary nerve, likely results Chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) patients undergoing functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS) with or without septoplasty were randomized to receive a 7-day pre- and post-operative course of placebo or gabapentin, starting at 300 mg daily and titrated to 300 mg three times daily, in a double-blind fashion. The pain score (VAS scale), analgesic use, and complications were assessed at the second, sixth, and 16th hours after surgery. Results showed that the mean pain score in the control group was higher than pregabalin and gabapentin at all times after surgery (P < 0.001). We defined new postoperative gabapentin as fills for 7 days before surgery until 7 days after discharge. We excluded patients whose discharge disposition was hospice or death. The primary outcome was prolonged use of gabapentin, defined as a fill>90 days after discharge. 2) If patient is taking gabapentin, do not order pregabalin. Inform patient to take gabapentin dose on DOS. 3) If patient is extremely frail or you have concerns about multiple drug interactions causing over sedation, it is OK if you don’t order the medication. The anesthesia team should look at these orders the day prior to surgery. 4) As Functional Endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS) is a delicate and time consuming procedure, it is performed routinely under general anesthesia, so anesthesiologists have to plan the technique in such a way that will facilitate the operating team for achieving a bloodless field for better visualization of the intranasal structures and minimize intraoperative bleeding. The purpose of this study was to demonstrate prescribing patterns for pain management after functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS). Methods A 15-item web-based survey was electronically distributed to 1770 members of the American Rhinologic Society (ARS). There is evidence supporting the use of NSAIDs and gabapentin for the control of pain after endoscopic sinus surgery. Acetaminophen, α-agonists, and local anesthetics are also viable options for postoperative analgesia. But gabapentinoids also have risks and there is little evidence to support their use for postoperative pain relief, according to a large new study by a team of Canadian researchers. “No clinically significant analgesic effect for the perioperative use of gabapentinoids was observed. The purpose of this review is to critically appraise the evidence for the use of gabapentinoids for acute pain management and its impact on the development of chronic pain after surgery. Recent findings: Recent meta-analyses have revealed that prior data likely have overestimated the beneficial effects of gabapentinoids in acute perioperative Patients undergoing sinonasal surgery between July 2019 and January 2020 were followed. Groups were divided into those that received 600 mg of oral gabapentin 1 hour preoperatively (gabapentin) and those that did not (control).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | &w=&do-not-index) |