Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 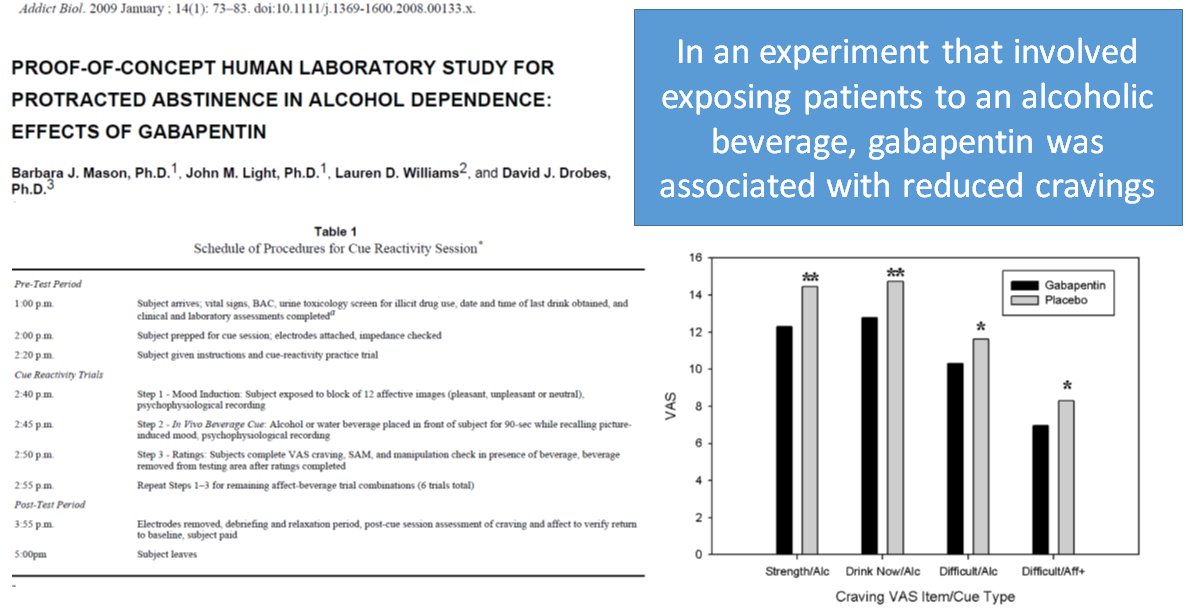 |
Gabapentin has been shown to be safe and effective for mild alcohol withdrawal but is not appropriate as mono-therapy for severe withdrawal owing to risk of seizures. During early abstinence, gabapentin may improve sleep, cravings, and mood—factors associated with relapse. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug that may help with alcohol withdrawal, cravings, and insomnia, but it also has risks of abuse and misuse. Learn how gabapentin works, what it can do for AUD, and how to prescribe it responsibly. Is gabapentin an effective treatment for alcohol use disorder (AUD)? Gabapentin treatment avoided more heavy drinking days (> 5 standard drinks/day) than placebo (27% vs 9%). Gabapentin can be a second-line, off-label option to treat AUD. However, there is mixed evidence and concerns about abuse- While gabapentin is not yet an FDA-approved treatment for alcoholism, a number of studies support the its use withdrawal and cravings: In a 12-day study detoxifying with either gabapentin or lorazepam (a benzodiazepine prescribed with the brand name Ativan), the former was less likely to drink – and had less craving, anxiety, and sedation. Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29,30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32,33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or Gabapentin reduces alcohol consumption and craving, which may help patients to maintain abstinence. These results, together with the virtual absence of side effects and a favorable safety profile, support gabapentin as a potential drug for the treatment of alcohol withdrawal and dependence. ment with gabapentin in reducing alcohol consumption and craving. METHOD Subjects Of 152 alcohol-dependent outpatients consecutively referred to an addiction psychiatrist for alcohol depen-dence treatment, 60 met the inclusion criteria. After all eligible patients had signed a written informed consent An alcohol interaction study showed that gabapentin alone impaired balance and, although it did not significantly alter the subjective or performance effects of alcohol or alcohol craving, it dose-dependently increased alcohol-induced tachycardia . Study objective: Gabapentin has been proved to be beneficial in promoting abstinence, decreasing alcohol cravings, and improving mood and sleep quality when given at higher doses; however, data are limited regarding the efficacy and safety of using high-dose gabapentin as part of the treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS). The aim of Find out what you need to know about gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal and discover the pros, cons, risks, and benefits, and how it may affect health. While benzodiazepines are considered the standard of care for alcohol withdrawal, gabapentin is a valuable alternative that can also help with cravings and abstinence long term. Read on to find out more. Conclusions and relevance: Gabapentin (particularly the 1800-mg dosage) was effective in treating alcohol dependence and relapse-related symptoms of insomnia, dysphoria, and craving, with a favorable safety profile. Increased implementation of pharmacological treatment of alcohol dependence in primary care may be a major benefit of gabapentin Gabapentin can reduce your desire to drink and can help you stop drinking. Gabapentin may also help improve symptoms of anxiety and difficulty sleeping that may occur when stopping alcohol use. How does gabapentin work? • Gabapentin works on your brain to reduce your desire to drink alcohol. In a 28‐day, placebo‐controlled, randomized, double‐blind clinical trial, investigators found that gabapentin (300 mg, twice daily) can reduce AUD patients’ number of drinks per day, the mean percentage of heavy drinking days, craving for alcohol, and increased percentage of days of abstinence in the gabapentin group than those in the Conducted by scientists supported by the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA), part of the National Institutes of Health, the study found that alcohol dependent patients using gabapentin were more likely to stop drinking or refrain from heavy drinking than those taking placebo. Both gabapentin and alcohol have sedative effects, so taking them together can make you even more sleepy, lightheaded, and clumsy. How Does Gabapentin Affect Alcohol? It is important to note that gabapentin does not tackle the underlying reasons for alcohol addiction. Our analysis of pooled data provides evidence that the use of gabapentin to manage alcohol withdrawal symptomatology and related cravings is at least moderately effective. However, given the limited number of available well-designed studies, these findings require further support through more rigoro Gabapentin is a calcium channel GABAergic modulator that is widely used for pain. Studies showing reduced drinking and decreased craving and alcohol-related disturbances in sleep and affect in the months following alcohol cessation suggest therapeutic potential for alcohol use disorder. Gabapentin can help with alcohol withdrawal by counteracting the physiological effects of the syndrome. Evidence indicates that symptoms of alcohol withdrawal syndrome stem from reduced Brünen S, Bekier NK, Hiemke C, et al. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Naltrexone and 6β-Naltrexol During Anti-craving Treatment in Alcohol Dependence: Reference Ranges. Alcohol Alcohol 2019; 54:51. Mason BJ, Quello S, Goodell V, et al. Gabapentin treatment for alcohol dependence: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med 2014; 174:70.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |