Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
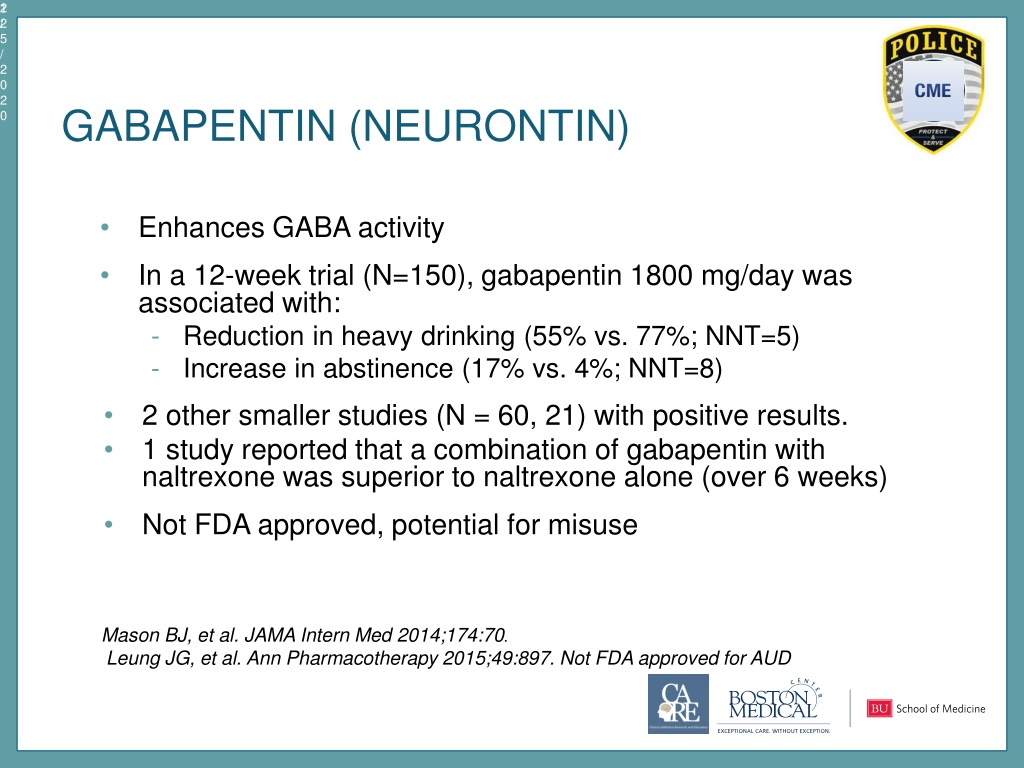
Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29,30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32,33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or -Opioid use disorder, prescribed opioids – For patients with alcohol use disorder and co-occurring opioid use disorder, our preference is to address both disorders with naltrexone (algorithm 1). However, naltrexone can only be started after a sufficient time has elapsed since last opioid exposure. GABAPENTIN AND ALCOHOL USE DISORDER No effect was found of gabapentin use for benzodiazepine treatment of alcohol withdrawal. It is notable that Bonnet et al and Nichols et al had similar fi ndings despite their studies being conducted in different countries using distinct comparators and methods. Bonnet et al,27 in another study, tried Gabapentin can be a second-line, off-label option to treat AUD. However, there is mixed evidence and concerns about abuse-misuse, and drug-related harms. Results are statistically significant unless indicated. Objective: Gabapentin (GBP) and pregabalin (PGB) have been used to treat alcohol use disorder (AUD) and alcohol withdrawal, but with inconsistent results. In this meta-analysis, we explored the effects of GBP/PGB treatment on AUD and their effects on withdrawal, craving, depression, and sleep disturbance in AUD patients. Is gabapentin an effective treatment for alcohol use disorder (AUD)? Gabapentin treatment avoided more heavy drinking days (> 5 standard drinks/day) than placebo (27% vs 9%). Gabapentin can be a second-line, off-label option to treat AUD. However, there is mixed evidence and concerns about abuse- Gabapentin, an anticonvulsant medication, has been proposed as a treatment for alcohol use disorder (AUD). A multisite study tested gabapentin enacarbil extended-release (GE-XR; 600 mg/twice a day), a prodrug formulation, combined with a computerized behavioral intervention, for AUD. Gabapentin can reduce your desire to drink and can help you stop drinking. Gabapentin may also help improve symptoms of anxiety and dificulty sleeping that may occur when stopping alcohol use. How does gabapentin work? • Gabapentin works on your brain to reduce your desire to drink alcohol. • Taking medicine for an alcohol use disorder is not substituting one drug for another. How should I take gabapentin? • The recommended dose of gabapentin for the treatment of alcohol use disorder is 300–600 milligrams (mg) three times daily. • Gabapentin can be taken with or without food. If you take an antacid containing aluminum Gabapentin is a medication used for epilepsy seizures, restless leg syndrome, and nerve pain caused by shingles. While it has been used to treat other addictions, it’s usually used specifically Gabapentin has been shown to be safe and effective for mild alcohol withdrawal but is not appropriate as mono-therapy for severe withdrawal owing to risk of seizures. During early abstinence, gabapentin may improve sleep, cravings, and mood—factors associated with relapse. NIH-funded study finds that gabapentin may treat alcohol dependence. Promising results from a randomized, controlled clinical trial of the medication. The generic anticonvulsant medication gabapentin shows promise as an effective treatment for alcohol dependence, based on the results of a 150-patient clinical trial of the medication. Evidence from single-site studies lend support to the safety and efficacy of gabapentin as a novel treatment for alcohol use disorder, with unique benefits for alcohol-related insomnia and negative affect, relative to available treatments. Running Head: GABAPENTIN FOR ALCOHOL USE DISORDER. Gabapentin as an Effective Treatment Option for Alcohol Use Disorder by Monica Hurst, PA-S, PT, DPT Bachelor of Science, University of Florida, 2013 Doctor of Physical Therapy, University of Miami, 2017 Contributing Author: Russell Kauffman, MPAS, PA-C A Scholarly Project Background and aims: Studies of the efficacy of gabapentin for treating alcohol use disorder (AUD) have yielded mixed findings. The aims of our study were to estimate gabapentin's effects on six alcohol-related outcomes, test potential moderators, examine publication bias and evaluate the quality of the studies. Alcohol misuse is the fifth leading risk factor for premature death and disability worldwide. Fewer than 10% of afflicted Americans receive pharmacological treatment for alcohol use disorder. Gabapentin is a calcium channel GABAergic modulator that is widely used for pain. Studies showing reduced dr This study showed that gabapentin is efficacious in promoting abstinence and reducing drinking in individuals with alcohol use disorder and especially so in those with more alcohol withdrawal symptoms. Gabapentin caused more dizziness, but this did not affect efficacy. Conclusions and relevance: These data, combined with others, suggest gabapentin might be most efficacious in people with AUD and a history of alcohol withdrawal symptoms. Gabapentin is effective at reducing drinking among people with alcohol use disorder (AUD) and strong withdrawal symptoms, according to a study published in JAMA Internal Medicine. Abstract Background and Aims: Studies of the efficacy of gabapentin for treating alcohol use disorder (AUD) have yielded mixed findings. The aims of our study were to estimate gabapentin’s effects on six alcohol-related outcomes, test potential moderators, examine publication bias, and evaluate the quality of the studies.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |