Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
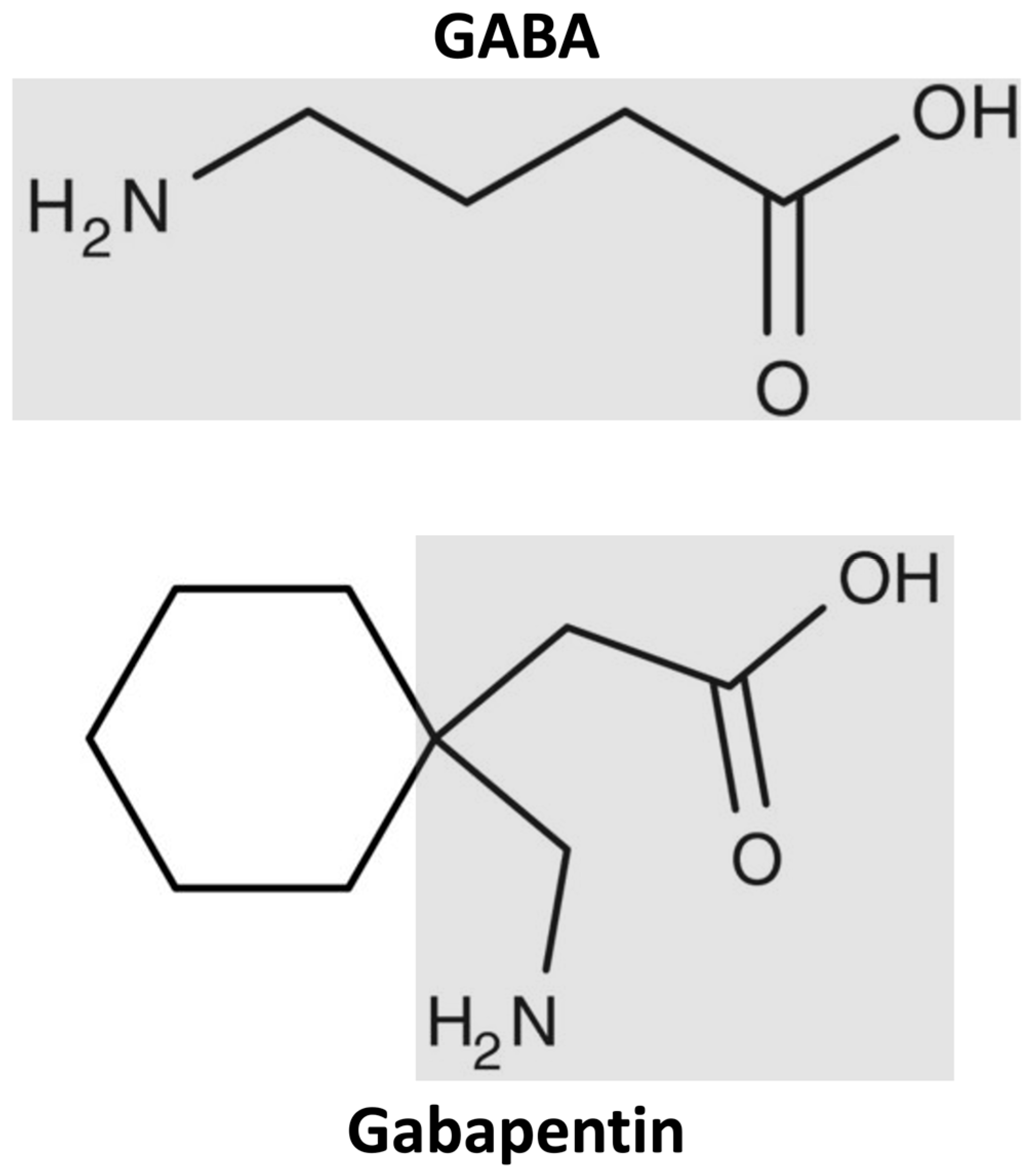
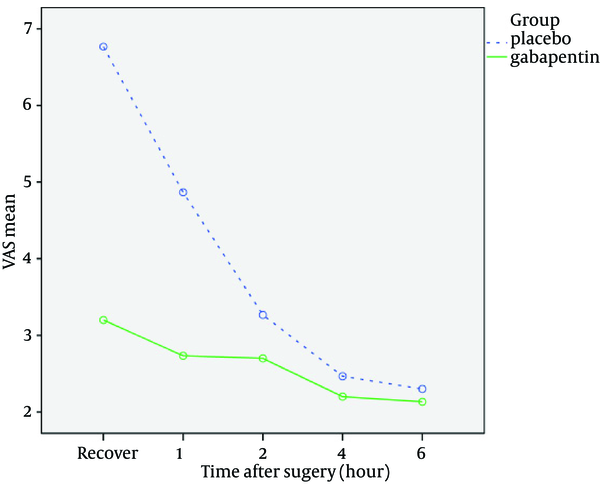
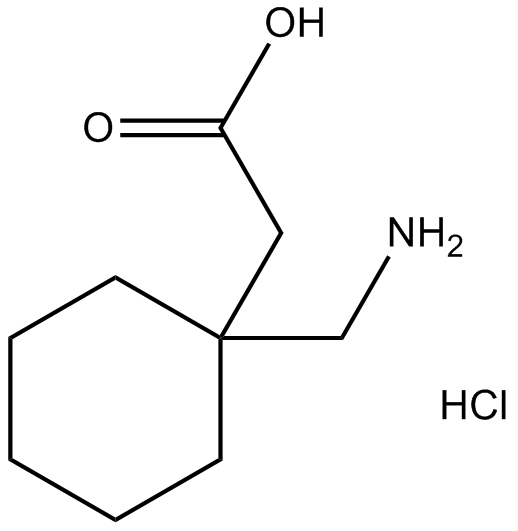
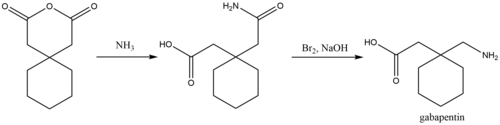
A GABA analogue is a compound which is an analogue or derivative of the neurotransmitter gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) (the IUPAC of which is 4-aminobutanoic acid). Many GABA analogues are used as drugs, especially as anticonvulsants, sedatives, and anxiolytics. Gabapentin is a GABA neurotransmitter analog; however, it does not inhibit GABA uptake or degradation. It appears to interact with GABA cotical neurons, but its relationship to functional activity as an anti convulsant is unknown. Used in conjunction with other anticonvulsants to control certain types of seizures in patients with epilepsy. GABA analogs are medicines that have a very similar structure to GABA but act in a different way, although experts aren’t exactly sure how they work. Most agree they bind to calcium-channels within the nerve cells, improving how well brain cells respond to GABA or making the release of GABA easier. Gabapentinoids, also known as α2δ ligands, are a class of drugs that are chemically derivatives of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) (i.e., GABA analogues) which bind selectively to the α 2 δ protein that was first described as an auxiliary subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs). [1][2][3][4][5] GABA analogues are a class of drugs that mimic GABA, a neurotransmitter that calms the brain. They are used to treat epilepsy, muscle spasms, anxiety, and pain. Common brands include Gabapentin, Pregabalin, and Topiramate. These medications are generally safe but can cause side effects. It's important to follow medical advice when taking them. Gabapentin is one of the new antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) launched recently. The advantage of new AEDs includes newer mechanism of action, broad spectrum of antiseizure effects, lesser drug interactions and fewer side effects. Gabapentin (GBP) a GABA analogue, is efficacious in several neurological an We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Gabapentin is a GABA analog, meaning that it looks very similar structurally but it is not completely the same. GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter found in the central nervous system (CNS) that regulates its excitability. it has been observed to increase brain levels of GABA 1); gabapentin is an amino acid & a structural analog of GABA, but does not bind to GABA receptors. may inhibit the formation of new synapses in the CNS Type: Anticonvulsants; GABA analog; Dosage Forms: capsule, tablet, oral solution 250mg/5mL; Common Trade Names: Neurontin, Gralise; Adult Dosing Partial Seizures. Adjunctive therapy for partial seizures with or without secondary generalization; Initial: 300mg PO q8hr; May increase up to 600mg PO q8hr; Post herpetic neuralgia. Day 1: 300mg PO qDay Gabapentin (kemiskt namn 1-(aminometyl)cyklohexanättiksyra [1]) är ett antiepileptikum som används vid epilepsi och smärtsam diabetesneuropati. Det är en GABA -analog; däremot agerar den inte på GABA-receptor utan inhiberar specifika kalciumkanaler. In this article, we have addressed the fundamental differences and similarities between GABA and its analog, gabapentin, from the standpoint of chemical structure, mechanism of action, metabolism, and side effect profile. Gabapentin is designed as GABA analog (similar to pregabalin), which means it binds to the α2δ (alpha-2-delta) subunit of presynaptic voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels (VSCCs), and block the release of excitatory neurotransmitters such as glutamate. GABA analogues are compounds that are structurally similar to gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and are used in the field of neuroscience. These analogues, such as gabapentin and pregabalin, bind to specific subunits of calcium channels to regulate certain types of neurotransmission, despite the exact mechanism of action remaining unclear. Gabapentin and Pregabalin are both 3-alkylated gamma-amino butyric acid (GABA) analogs. Gabapentin was designed as a lipophilic GABA analog and was first synthesized as a potential anticonvulsant and was launched in 1994 as add-on therapy for the treatment of epilepsy. In this review the discovery a gabapentin (may however be due to pharmacokinetic interactions). Increase serum & brain levels of gabapentin with CBD. No effect of gabapentin with CBD. Cannabidiol (CBD)increase the activity of gabapentin. Unclear - may be attributed to penetration in brain or elimination through kidney (gabapentin is not attached with plasma proteins Gabapentin is an alkylated GABA analog. The exact mechanism of action is unknown. Gabapentin acts as an antagonist on presynaptic voltage-gated channels. It binds to the alpha-2 delta subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels, which inhibit inward calcium currents and decrease neurotransmitter release. Gabapentin is a prescription medication known as a gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue. GABA reduces the excitability of nerve cells (neurons) in the brain, which play a role in seizures and the transmission of pain signals. Gabapentin mirrors the effects of GABA calming excited neurons. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Gabapentin is a structural analog of GABA, which readily crosses the blood-brain barrier when given systemically . Gabapentin, however, does not bind to GABA receptors . Although gabapentin may influence the synthesis and release of GABA , it does not affect the uptake and metabolism of endogenous GABA . Gabapentin and pregabalin: Are both structural analogues of GABA; Have no direct action on the GABA A receptor; Act on the α 2 δ subunit of voltage gated Ca 2+ channels in the CNS, inhibiting neurotransmitter release; May have some NMDA receptor activity; Comparison of GABA Analogues
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |