Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
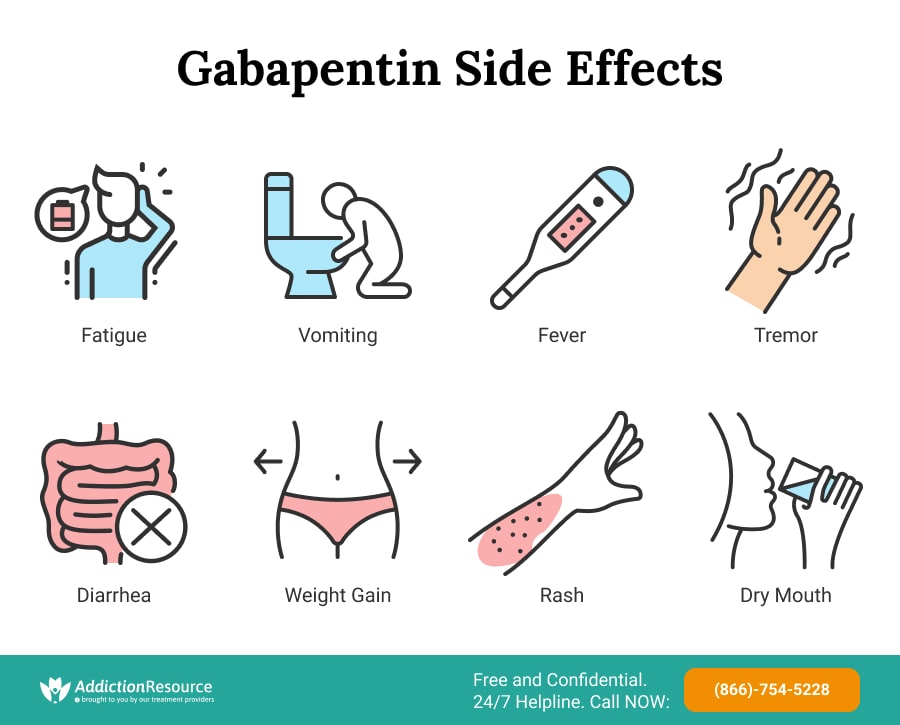
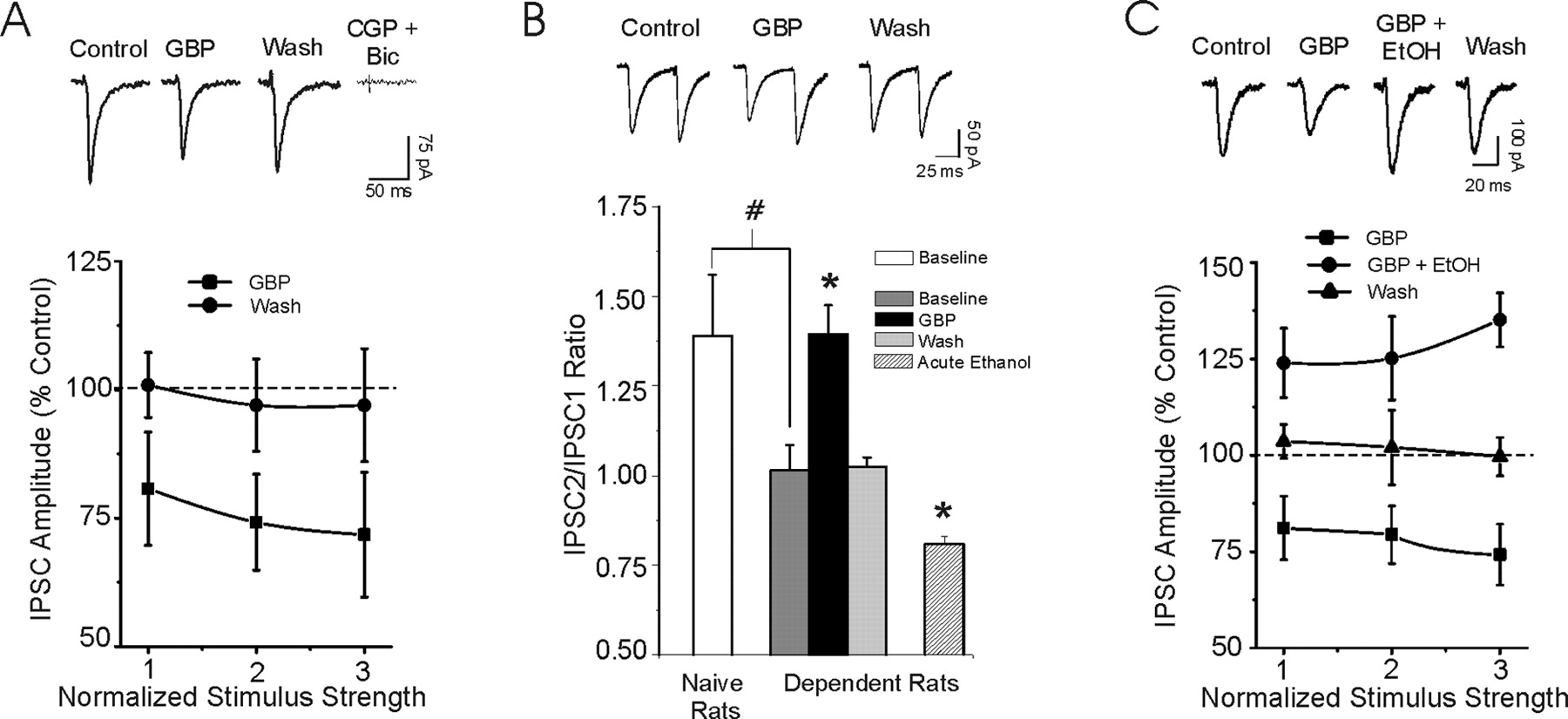
What Are the Dangers of Mixing Alcohol With Gabapentin? Gabapentin and alcohol can enhance each other’s depressant effects on the central nervous system, leading to intense intoxication and impaired function. Are there long-term effects of combining gabapentin with alcohol? Yes, long-term use of gabapentin and alcohol in combination can lead to increased tolerance, physical dependence, and in some cases, lasting impacts on cognitive function and mental health. Mixing alcohol and gabapentin can cause the effects of the two substances to become heightened. This means that the side effects of gabapentin can become worse while drinking alcohol, and the effects of alcohol can be more severe when drank while taking gabapentin. Like gabapentin, alcohol increases the effects of GABA in the CNS. Both drugs are depressants and slow down different body functions. When taken together, the risk of side effects and overdose from alcohol greatly increases. Gabapentin alone is usually not associated with overdose, but the risk increases when taken with alcohol. Gabapentin for Understanding the risks linked to combining Gabapentin and alcohol is crucial for ensuring safety and avoiding severe health complications. This article assesses the impacts of Gabapentin and alcohol on the body, the possible dangers of their interaction, and strategies for using them safely. Like gabapentin, alcohol depresses the central nervous system (CNS). As a result, these two substances can have a synergistic effect when taken together; in other words, they can amplify these depressive effects. These effects may include heightened drowsiness, dizziness, slowed breathing and impaired judgment, among others. Mixing alcohol and gabapentin can increase your risk of side effects like dizziness, drowsiness and concentration problems. Inform your doctor if you drink alcohol while taking gabapentin due to the interaction between these substances. Mixing Gabapentin and Alcohol Mixing Gabapentin and Alcohol Use Disorder. Aside from the serious health risks of mixing gabapentin and alcohol, struggling with alcohol dependency poses its own problems. An estimated 14 million adults met the diagnostic criteria for alcohol use disorder in 2018. Remember, gabapentin is the tenth most prescribed Mixing gabapentin and alcohol can worsen existing side effects and increase their severity. It also increases the risk of overdose or death. 6 Generally, you should avoid any medication that can cause dizziness while taking gabapentin. Taking gabapentin with alcohol can increase these side effects‚ which can be dangerous. Gabapentin can also increase the effects of alcohol‚ which can lead to impaired judgment‚ coordination‚ and balance. Drinking alcohol while taking gabapentin can also increase the risk of seizures in people with a history of seizures. Gabapentin carries a significant risk when mixed with alcohol. Both substances act as depressants, and their combined effects can lead to serious health complications. It's crucial to understand the dangers and potential consequences of combining these substances to make informed decisions about your health and well-being. Gabapentin Side Effects With Alcohol: Risks & Dangers. Combining gabapentin with alcohol can have serious consequences. Here are some of the major risks and dangers: Increased sedation: Both gabapentin and alcohol can cause drowsiness and sedation. When taken together, these effects can be much stronger, making it difficult to stay awake or alert. Understanding these interactions is essential for safe medication management and minimizing risks associated with gabapentin and alcohol use. Risks of Mixing Gabapentin with Alcohol. Combining gabapentin with alcohol poses significant risks due to their combined depressant effects on the central nervous system (CNS). Combining gabapentin with alcohol creates a dangerous synergistic effect that intensifies the central nervous system (CNS) depression. This interaction amplifies the sedative properties of both substances, leading to severe impairments in physical and mental function. As mentioned, gabapentin is a CNS depressant, meaning that it slows down the work of the neural network and calms down the nervous system. This relaxes the individual and can lead to a certain “high” that can be compared to the effects of cannabis, which places the user in a state of euphoria and an “elevated state of mind”. Combining gabapentin with alcohol poses significant risks. Understanding these dangers is crucial for anyone considering using gabapentin alongside alcohol. The interplay between gabapentin and alcohol can amplify each other's effects, leading to heightened side effects. Gabapentin might only cause a few mild side effects, especially when you first start taking it. Even if you experience short-term side effects that aren’t severe, you should be aware of how drinking alcohol may change this. For alcohol withdrawal. Before gabapentin is prescribed for alcohol withdrawal, potential benefits (reduction of withdrawal symptoms), side effects (sedation, fatigue), and risks (falls) should be discussed with the patient. 46 Patients should also be informed that benzodiazepines are the gold standard for alcohol withdrawal and that gabapentin What Happens When Gabapentin and Alcohol Are Mixed. Gabapentin and alcohol are both central nervous system (CNS) depressants, meaning they can slow down brain activity. When taken together, they can amplify each other’s effects, potentially leading to severe side effects. The most common effects reported include dizziness, loss of
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |